SS 11 Key Terms & Info
advertisement

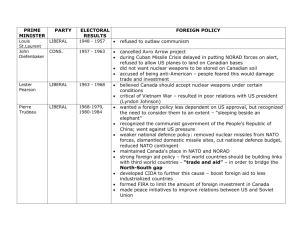
Social Studies 11 – Key Terms, Concepts, and Information Canadian Government System and Government Titles Federal Provincial / Territorial 1. 2. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. monarch / sovereign head of state (monarch - Queen Elizabeth II) governor general Chief Electoral Officer head of government prime minister Prime Minister’s Office (PMO) Privy Council’s Office House of Commons (Lower House) Members of Parliament (MPs) Senate (Upper House) (“somber second thought”) Senators executive branch legislative branch judicial branch judiciary Supreme Court of Canada Chief Justice hansard opening of parliament dissolution of parliament Speech from the Throne Speaker of the House political parties cabinet cabinet solidarity cabinet ministers portfolios / departments vestigial (used to describe senate) senate reform Triple-E Senate party whip party solidarity cross the floor cooperative federalism official opposition balance of power question period backbencher shadow cabinet federal-provincial conference federal grants vote of no confidence Types of Government that form 1. 2. 3. majority minority coalition lieutenant-governor executive branch legislative branch judicial branch territorial commissioner provincial legislature Members of the Legislative Assembly (MLAs) Provincial Courts Appeal Court of BC territorial government (i.e. Nunavut) hansard Ombudsman / Office of Ombudsman opening of parliament dissolution of parliament Speech from the Throne Speaker of the House political parties cabinet cabinet solidarity cabinet ministers portfolios / departments party whip party solidarity cross the floor official opposition question period backbencher shadow cabinet federal-provincial conference Municipal / Local 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. 82. 83. municipal government mayor / reeve trustee alderperson town / city council councilor by-law constituents regional district school board Hospital Regional Authority Aboriginal 84. 85. 86. 87. 88. 89. Aboriginal self-government Chief Band Council Assembly of First Nations Nisga’a Nunavut SS 11 – Key Terms, Concepts, & Info - Carrie Schlappner Page 1 of 10 Elections & Election Process 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. Elections Canada Elections BC National Register of Electors representation-by-population constituencies ridings electoral districts dissolution (of Parliament) (by GG) enumeration nomination campaigning balloting tabulation federal rules / provincial rules voter eligibility candidacy Chief Electoral Officer writ of election “dropping the writ” returning officer Deputy Returning Officer ballot preferential ballot recall Elections Act secret ballot gerrymandering poll clerk judicial recount federal franchise provincial franchise scrutineer limits on election spending no fixed election date – but federal elections must be held every 5 years Senate Reform 3-R Senate referendum / plebiscite by-election appointed vs. elected Political Ideologies / Spectrum / Concepts / Parties 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. right-wing left-wing authoritarian/ism democratic communism liberalism socialism conservatism libertarian fascism dictatorship / military dictatorship Totalitarian/ism Autocracy theocracy Liberal party Conservative Party (Conservatives) New Democratic Party (NDP) Co-operative Commonwealth Federation (CCF) Green Party Reform Party Canadian Alliance Party Bloc Québécois absolute monarchy divine right means of production anarchy decree Social Credit (Alberta) (money policy) Union Nationale Parti Québécois Progressive Party Progressive Conservative Party how political party leaders are chosen party convention formation / dissolution of political parties examples of modern dictatorships – Lybia, Iraq public vs. private ownership capitalism social policies Electoral Systems 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Single Member Plurality System First-Past-the-Post System proportional representation majority plurality Simple Plurality System elections officer Chief Electoral Officer popular vote Single-Transferable-Vote (STV) SS 11 – Key Terms, Concepts, & Info - Carrie Schlappner Page 2 of 10 Canadian Constitution / Issues 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. constitutional monarchy bicameral legislature (2 chambers) British North America Act (BNA Act) (1867 – Confederation) sovereignty-association Federal, provincial , and shared powers/responsibilities residual powers parliamentary democracy written constitution unwritten constitution repatriating the constitution amending formula notwithstanding clause reasonable limits English Bill of Rights -1689 Royal Proclamation of 1763 Quebec Act – 1774 Act of Union – 1840 Manitoba Act – 1870 Supreme Court decisions since 1875 Statute of Westminster – 1931 Alberta & Saskatchewan Act – 1905 1980 Québec Referendum Canada Act – 1982 Constitution Act – 1982 (“kitchen compromise”) Charter of Rights and Freedoms 1982 Meech Lake Accord (1987) Charlottetown Accord (1992) 1995 Québec Referendum aboriginal title Terms Related to Passage of a Bill 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. bill law act statute government bill passage of a bill Private Member’s Bill cabinet solidarity party solidarity first reading second reading third Reading committee stage royal assent (GG) free vote Order in Council Governor in Council (GG) regulation money bill (cannot be introduced by Senate) Economic Theory 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. private vs. public ownership capitalism government subsidy Keynesian economics trickle-down theory invisible hand flat tax progressive vs. regressive taxation Charter of Rights and Freedoms 1. 2. 3. 4. 4a. 4b. 4c. 4d. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. notwithstanding clause mobility rights does not include property rights fundamental freedoms freedom of religion freedom of expression freedom of peaceful assembly freedom of association due process legal rights (“life, liberty, and security”) section 1: “reasonable limits” democratic rights Constitutional supremacy habeas corpus application of the Charter equality rights Charter Challenge aboriginal title amending formula Influencing Government / Policies 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. civil disobedience lobbying boycotting passive resistance petition letters-to-the-editor protest demonstration public inquiry direct action community service advocacy voting running for political office joining a political party litigation / court action election campaigning pressure groups advertising campaigns mass mailings letters /e-mails/phone calls to gov. officials special interest groups SS 11 – Schlappy’s Key Terms, Concepts, & Info Page 3 of 10 Canadian Identity re: Independence from Britain 1. 2. Upper and Lower Canada Rebellions of 1837-38 Responsible government (1848) 3. British North America Act (BNA ACT) / Confederation (1867) Department of External Affairs established (1909) 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. WWI – proved selves (1914-1919) Vimy Ridge (1917) Paris Peace Conference & Treaty of Versailles (independent signatory) (1919) League of Nations (own seat) (1919) Chanak Crisis (1922) Halibut Treaty (1923) Imperial Conference (London – Commonwealth created)) / Balfour Declaration / Report (1926) King-Byng Crisis (1926) Statute of Westminster (1931) CBC (1936) National Film Board (1939) WWII (declared war independent of Britain) (1939-1945) important WWII battles – Dieppe, Italy (Ortona), D-Day, Normandy 18. Bretton Woods Conference ( 1944) - Canadian delegation took part independent of Britain established the International Monetary Fund and the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development 19. United Nations (1945) – independent seat Human Rights 1. 1a. 1b. 1c. 1d. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. United Nations (UN) Security Council General Assembly Economic and Social Council International Court of Justice (Louise Arbor) UN Declaration of Human Rights (1948) John Humphreys Eleanor Roosevelt UN Convention /Declaration of the Rights of the Child (1989) discrimination stereotyping prohibited grounds bona fide occupational requirement differential treatment individual assessment BC Human Rights Commission / Code liberté, egalité, et fraternité Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen American Declaration of Independence American Bill of Rights Canada’s Charter of Rights and Freedoms (1982) Human Rights Legislation “crimes against humanity” Genocide human rights abuses – i.e. Holocaust, Cambodia, Rwanda, Bosnia, Kosovo, South Africa, Afghanistan, USA, Canada (history) 20. Supreme Court of Canada becomes highest court in Canada (1949) 21. Canada – member of NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) (1949) 22. Suez Crisis (peacekeeping mission – Pearson) (1956) 23. Canadian Flag (1965) 24. Canada Act / Charter of Rights & Freedoms – repatriation of Constitution (1982) SS 11 – Schlappy’s Key Terms, Concepts, & Info Page 4 of 10 Non-Governmental Organization (NGOs) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Amnesty International Red Cross Corporate Watch Oxfam Greenpeace Doctors Without Borders World Vision Save the Children Fund Free the Children UNICEF MADD World Wildlife Fund Council of Canadians David Suzuki Foundation United Nations 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. United Nations (UN) United Nations Charter General Assembly Security Council Economic and Social Council International Labour Organization (ILO) United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) World Health Organization (WHO) World Bank (WB) United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948) Convention on the Rights of the Child International Court of Justice International Criminal Tribunal (1993) International Criminal Court (1998) Human Development Index (HDI) Economic Organizations/Agreements/Issues 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. World Bank (WB) International Money Fund (IMF ) World Trade Organization (WTO) North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) (1994) Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) (1997 protest) Free Trade Agreement (FTA) (1989) Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Group of 8 (G8) General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) Organization of American States (OAS) unions collective bargaining working conditions fair wages benefits pensions job security child labour good faith bargaining dispute resolution arbitration collective agreement strike essential service lock out human rights environmental harm European Union International Environmental Agreements / Issues 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Montreal Protocol – 1989 (Ozone) Earth Summit – 1992 – Rio De Janeiro Kyoto Accord/ Protocol -1997 (Global Warming) biodiversity biotechnology hazardous waste global warming / greenhouse effect sustainable development / renewable resources softwood lumber dispute ozone layer depletion SS 11 – Schlappy’s Key Terms, Concepts, & Info Page 5 of 10 International Organizations / Agreements 1. 1a. 1b. 1c. 1d. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. United Nations Security Council General Assembly Economic and Social Council International Court of Justice (the Hague) World Bank (WB) International Money Fund (IMF) World Trade Organization (WTO) North Atlantic Trade Organization (NATO) Group of 8 (G8) North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD) Kyoto Protocol / Accord Montreal Protocol / Accord Softwood Lumber Agreement / dispute le Francophonie Commonwealth Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Organization of American States (OAS) International Land Mines Treaty Foreign Aid 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. foreign aid bilateral aid multilateral aid tied aid Canadian International Development Agency (CIDA) – est. 1968 Human Security Program – est. 1996 Colombo Plan (1950) NGOs WB & IMF UN & its agencies – i.e. UNICEF, WHO, etc. Department of Foreign Affairs History of Canadian Identity / Rights 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. Manitoba Act (1870) Indian Act (1876) residential schools (1874-1996) anti-potlatch legislation (1884) Chinese Immigration Act – 1885 (Head Tax) and Exclusion Act (1923) Komagata Maru incident (1914) Separate but equal (Nova Scotia) (1918-1954) women’s suffrage (right to vote in federal elections) (1918) The Persons Case (1929) War Measures Act (WWI, WWII, October Crisis) SS St Louis (1939) Japanese internment (WWII – 1942-1946) Canadian Bill of Rights (1960) Aboriginal suffrage (right to vote in federal elections) (1960) Quiet Revolution (Québéc) 1960s The Immigration Act (1967) Bilingualism and Bicultural Commission - Official Languages Act (1969) October Crisis (1970) front de liberation du Québéc (FLQ) Multiculturalism policy (1971) – cultural mosaic Bill 101 (Québéc) (1977) Québec separatist referendum – “sovereigntyassociation” (1980) Multiculturalism Act (1988) Bilingualism - Quebec – canadiens – separatist movement Meech Lake Accord (1987) distinct society clause Charlottetown Accord (1992) Québec’s 2nd Separatist Referendum (1995) Nisga’a Treaty (1999) aboriginal title regionalism – / regional alienation - issue of cultural and political division in Canada statement of reconciliation restitution political representation by women SS 11 – Schlappy’s Key Terms, Concepts, & Info Page 6 of 10 Involvement in International Conflicts / Peacekeeping Missions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. Boer War (1899-1902) World War One (WWI) (1914-1919) Spanish Civil War (1936-1939) World War Two (WWII) (1939-1945) Israel (1948) Korean War (1950-1953) Suez Crisis (1956) Vietnam War (1965-1972) Congo (1960-64) Cyprus (1964) Cambodia (1970s) Bosnia (1992-present) Haiti (1990-1991) Gulf War – 1991 Somalia (1993) Rwanda (1994) Kosovo (1999-present) East Timor (1999-2001) Afghanistan (1988-90; 2001-present) Iraq Occupation – (2003 – present) Lester B. Pearson (Nobel Peace Prize – 1957) Department of Foreign Affairs / Foreign Affairs Canada Social Safety Net 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. welfare universal health care two-tiered health care national child care program low income cut-off Liberal Party & Social Safety Net Great Depression Income Tax (1917) Co-operative Commonwealth Federation (CCF) (1932) & Regina Manifesto (1933) Bennett’s “New Deal” (1934-35) Alberta Social Credit Party – prosperity certificates / money system (1936) Employment Insurance (EI) (first called Unemployment Insurance (UI) -1940) Family Allowance Benefit (1944) Saskatchewan Medicare Act (1944) Old Age Pension (OAP) (1951) Canadian Pension Plan (CPP) (1965) Medical Care Act (1966) Medical Services Plan of BC (MSP) (1960s) 19. Canada Health Act (1984) 20. Child Tax Benefit (1993) SS 11 – Schlappy’s Key Terms, Concepts, & Info Page 7 of 10 World History Events & Concepts 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. Boer War (1899-1902) World War One (WWI) (1914-1919) Vimy Ridge (1917) – Canadian Identity War Measures Act reparation payments Treaty of Versailles (1919) suffrage (the right to vote) women’s right to vote in federal elections (1918) Russian Revolution (1917) Winnipeg General Strike (1919) Old Age Pension Act (1927) Chanak Affair (1922) King-Byng Crisis (1926) Balfour Report (1926) prohibition (1920s) urbanization economic boom Persons Case (1929) Agnes MacPhail Emily Murphy “roaring ‘20s” Stock market /crash Great Depression (1929-39) anti-Semitism On-to-Ottawa Trek (1935) unemployment New Deal (American - Roosevelt) welfare state Regina Manifesto (1932) J.S. Woodsworth (CCF) William Aberhart (Social Credit Party) Maurice Duplessis “Little New Deal” Canadian Broadcast Corporation (CBC) Benito Mussolini Adolf Hitler German National Socialist Party – Nazi Party “master race” / Aryans Kristallnacht / Crystal Night Nuremburg Laws concentration camps Holocaust “Final Solution” Dr. Norman Bethune appeasement Spanish Civil War (1936-1939) World War Two (WWII) (1939-1945) Prime Minister of Britain – Winston 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. 82. 83. 84. 85. 86. 87. 88. 89. 90. 91. 92. 93. 94. Churchill Pearl Harbour (1941) reasons for Canadian participation in wars T.C. “Tommy” Douglas Japanese internment camps Nuremburg Trials UN Convention on Genocide (1948) “crimes against humanity” Cold War (1947-1991) Korean War (1950-1953) Suez Crisis (1957) Vietnam War (1965-1972) Agent Orange South Africa – apartheid (1948-1990) African National Congress (ANC) Nelson Mandela sanctions F.W. de Clerk Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) weapons of mass destruction United Nations Lester B. Pearson Lloyd Axworthy October Crisis (1970) War Measures Act (WWI, WWII, October Crisis) Front de libération du Québéc (FLQ) Lester Pearson UN Peacekeeping Israel (1948) Suez Crisis (1956) Congo (1960-64) Cyprus (1964) Civil Rights Act (USA) (1964) Cambodia (1970s) Bosnia (1992-present) Tiananmen Square Massacre (1989) Haiti (1990-1991) Gulf War – 1991 Somalia (1993) Rwanda (1994) Kosovo (1999-present) Kosovo War – Slobodan Milosevic – indicted 1999 East Timor (1999-2001) Afghanistan (1988-90; 2001-present) September 11, 2001 / Taliban Iraq Occupation – (2003 – present) Darur – Sudan (2003 - present) SS 11 – Schlappy’s Key Terms, Concepts, & Info Page 8 of 10 Political Figures 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Prime Minister (PM) John A. Macdonald (Conservative) 1st PM of Canada from Confederation – 1867 –1873, and 1878-1891. PM Sir Robert Laird Borden (Conservative) – PM from 1911-1920 - during WWI; invoked War Measures Act; conscription crisis 1917; introduced 1st income tax; Winnipeg General Strike 1919 PM William Lyon Mackenzie King (Liberal) – PM from 1921-30; 1935-1948 - beginning of Great Depression 1929-1930; again in 1935 – WWII; King-Byng Crisis 1925; created CBC & National Film Board; Chanak Crisis 1922; Statue of Westminster 1931; Conscription crisis 1944; helped found UN; retired from politics PM Richard Bedford Bennett (Conservative) - PM from 1930-35 - relief camps, On-to-Otawa Trek, “New Deal” during Depression PM Louis St. Laurent (Liberal) - PM from 1948-1957 - (post-WWII – beginning of Cold War – joined NATO, supported UN; created Canada Council for Arts; Newfoundland joined Confederation 1949; equalization payments - 1956) PM John Diefenbaker (Progressive Conservative) - PM from 1957- 1963. instrumental in bringing in the Canadian Bill of Rights in 1960; granted federal franchise (vote) to aboriginal people in 1960; his refusal to allow nuclear weapons into Canada led to several resignations from his Cabinet and the collapse of his government in 1963. PM L. B. Pearson (Liberal) – PM from 1963-68 - Nobel Peace Prize for role in Suez Crisis – 1957; created UN peacekeeping force; introduced important social programs (including universal health care, the Canada Pension Plan, and Canada Student Loans); refused to enter Vietnam War; introduce dpoint-system immigration; retired from politics) PM Pierre Trudeau (Liberal) - PM from 1968 to 1979, and from 1980 to 1984. when he retired. PM during the October Crisis – invoked War Measures Act; responsible for repatriating the constitution and entrenchment of the Charter of Rights and freedoms in 1982; espoused participatory democracy as a means of making Canada a “Just Society”; PM Brian Mulroney (Progressive Conservative) PM from 1984-1993 - negotiated Meech Lake Accord (1987) and Charlottetown Accord (1992) with provincial premiers (both failed to pass); signed FTA (1989) and negotiated NAFTA (1994) with USA and Mexico; implemented GST. PM Kim Campbell (Progressive Conservative) PM in 1993 - ** ONLY WOMAN PM!! PM Jean Chrétien (Liberal) – PM from 1993 to 2003, when he retired; introduced a new and far-reaching Youth Criminal Justice Act, which replaced the old Young Offenders Act, and changed the way youths were prosecuted for crimes in Canada; did not support the US-led 2003 invasion of Iraq but was the first non-member of the US-led coalition to provide significant financial aid to the post-war reconstruction effort, relative to Canada’s size; very soon after his retirement, Chrétien’s legacy was marred by the sponsorship scandal - although implicated, no direct evidence has yet been found directly linking him to it. PM Paul Martin (Liberal) – PM until Jan 23/06 – PM from 2003-2006 (Jan 23); was Finance Minister under Chrétien; stopped the sponsorship program as soon as he became PM and set up the Gomery Commission which has uncovered the details of the scandal; though not implicated, he has been criticised for not being aware of what was going on while Finance Minister, which led to a fall in popularity for him and the Liberal Party. Stephen Harper (Conservative) – NOW PRIME MINISTER as of Jan 23/06 Maurice Duplessis - founder and leader of the conservative Union Nationale party of Québec; led the “Quiet Revolution” in Québec in the 1960’s Rene Lesvesque - 1960s - Québec separatist – left the federal Liberal party to form the Parti Québécois in 1968; passed the Quebec Charter of the French Language (also known as “Bill 101”), whose goal was (and still is) to make French the common language of all Quebecers at a time when the language of the English minority dominated the economic scene; his government held the 1980 Quebec referendum on its sovereignty-association plan. Lucien Bouchard – first leader of the Bloc Quebecois, the federal separatist party, in 1991, after the failure of the Meech Lake Accord. Jacques Parizeau – leader of the Parti Quebecois during the 1995 Separatist Referendum in Quebec J.S. Woodsworth – leader of Co-operative Commonwealth Federation (CCF) - est 1932 - 1st socialist party in Canada – which eventually became the NDP; Regina Manifesto - 1933 SS 11 – Schlappy’s Key Terms, Concepts, & Info Page 9 of 10 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. T.C. (Tommy) Douglas - Co-operative Commonwealth Federation (CCF) – which eventually became the NDP. William Aberhart- Social Credit Party of Alberta – est. 1935 Preston Manning – 1st leader of Reform Party (est. 1987) – in reaction to feelings of regionalism / that West was Left out of federal politics - party of Western interests – eventually became Canadian Alliance Party – conservative ideology Stockwell Day - 1st leader of Canadian Alliance (est. 2000 – eventually merged with Progressive Conservative Party to become the Conservative Party of Canada – 2003) Ujjal Dosanjh – In 2000, became Premier of BC (NDP) making him Canada’s first non-white and first Indo-Canadian provincial premier. Key Figures 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Famous Five – Beginning in 1927, Five Alberta women, Emily Murphy, Henrietta Muir Edwards, Nellie McClung, Louise McKinney and Irene Parlby, contested, in the Supreme Court of Canada, the interpretation of the word "persons," which at that time meant that women were not allowed to be appointed to the Senate because they were not considered “persons” under the law. That time, they did not succeed. But two years later (1929), the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council of Great Britain, which was still the highest Court of Appeal for Canada, declared that the word "persons" included men and women. Nellie McClung - was a Canadian feminist politician, and social activist. She was a part of the social and moral reform movements prevalent in Western Canada in the early 1900s. Her great causes were women’s suffrage and temperance. Part of Famous Five in Persons Case. Agnes MacPhail - was the first woman to be elected to the Canadian House of Commons, and one of the first two women elected to the Legislative Assembly of Ontario. Cairine Wilson had the honour of being appointed Canada’s first woman Senator. She was named to the position by her friend Prime Minister Mackenzie King four months after a ruling in the Person’s Case determined that Canadian women were persons and therefore eligible to sit in the Senate (Feb 15, 1930). None of the Famous Five women who initiated the case were appointed to the Senate. She served in the Senate until her death in 1962, gaining recognition for her dedication to causes such as supporting refugees and the League of Nations. Cairine Wilson became the first female president of the League of Nations Society in Canada. In 1949 Senator Wilson became the first Canadian woman to be a delegate to the UN General Assembly. Elijah Harper - became the first Treaty Indian to be elected as a provincial politician when he contested and won the sprawling northern Manitoba riding of Rupertsland for the NDP. Roy Miki - Canadian poet and scholar. very active in the Japanese-Canadian community and has fought hard for redress from the federal government for the internment of Japanese-Canadians during WWII Emily Murphy - was a Canadian women’s rights activist. In 1916, she became the first woman police magistrate in Alberta, and in the British Empire.She is best known for her contributions to Canadian feminism, specifically to the question of whether women were “persons” under Canadian law (part of Famous Five). During her term as a judge, several defence lawyers questioned her qualification to sit in judgment over their clients, questioning if she was even a “person” under the law. Louise Arbour - Ontario Supreme Court and Court of Appeal Justice who was appointed chief prosecutor of the Internaltion Criminal Tribunals for Rwanda and the former Yugoslavia by the UN Security Council; now serves on Supreme Court of Canada Beverly McLaughlin - first woman to head the Supreme Court of Canada (2000) Lloyd Axworthy - Minister of Foreign Affairs under Jean Chrétien; His greatest success was the Ottawa Treaty, an international treaty to ban anti-personnel land mines. Stephen Lewis - currently serving as United Nations special envoy for HIV/AIDS in Africa. SS 11 – Schlappy’s Key Terms, Concepts, & Info Page 10 of 10