nsw independent trial exams – 2004 - legalstudies-preliminary-aiss
advertisement

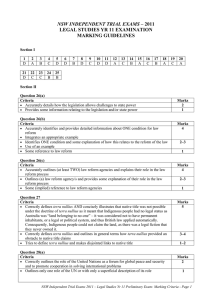
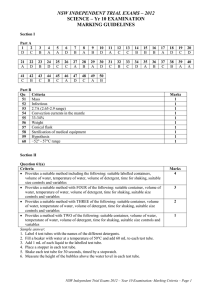
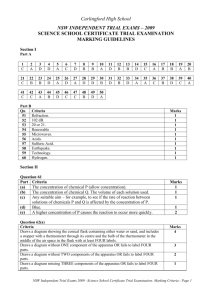
NSW INDEPENDENT TRIAL EXAMS – 2010 LEGAL STUDIES YR 11 EXAMINATION MARKING GUIDELINES Section I 1 D 2 A 3 B 4 D 5 B 6 C 7 B 8 C 9 C 10 D 11 A 12 D 13 B 14 A 15 A 16 A 17 D 18 B 19 D 20 D Section II Question 21 Criteria Marks 8–10 Explicitly defines law reform and indicates that it is a process by which law is modified/repealed/introduced to take into account changes in society Sketches in general terms the conditions that contribute to law reform Clearly integrates relevant example/s 4–7 Defines law reform and generally outlines the relevant conditions with an appropriate example 1–3 Only defines law reform with general or superficial coverage of conditions and example(s) Answers may include: Law reform occurs mainly by parliament and to a lesser extent the courts. Law reform is a response to perceived needs and its aim is to improve and advance society. Conditions that give rise to law reform include: changing social values, new concepts of justice and new technology. Response should link these to specific law reform examples such as domestic violence, IVF, same sex relationships, environmental initiatives, sexual assault laws, cyber crime and driving restrictions on young people. Question 22(a) Criteria Marks 2 Clearly explains the rule of law May use an example/the stimulus 1 Attempts to explain the rule of law Answers may include: The rule of law means that no individual, institution or government is above the law. Question 22(b) Criteria Marks 3–4 Clearly explains how the rule of law can protect human rights Integrates the article into the response 1–2 Attempts to explain how the rule of law can protect human rights Answers may include: The rule of law protects citizens by ensuring the government cannot arbitrarily abuse power. The Constitution protects the system and there is recourse through the judiciary. Without either the citizens may not have the protection of the rule of law in Fiji. Question 22(c) Criteria Marks 4–6 Demonstrates thorough knowledge of the limitations of international law Makes clear reference to both the article and at least ONE example 1–3 Demonstrates some knowledge of the limitations of international law May make reference to the article and/or an example Answers may include: Explanation of sovereignty; lack of international mechanisms/political will; international law not binding or enforceable e.g. Fiji, Sudan (Darfur), Israel, East Timor, Australia re: asylum seekers, etc. NSW Independent Trial Exams 2010 – Legal Studies Yr 11 Preliminary Exam: Marking Criteria - Page 1 Question 23 Criteria Marks 7–8 Clearly identifies the issues and provides points for and/or against the statement Integrates ONE relevant example 5–6 Identifies the issues and provides points for and/or against the statement Attempts to integrate ONE relevant example 3–4 Attempts to provide points for and/or against parts of the statement Mentions ONE example 1–2 Makes general statements about technology Answers may include: Technological inventions happen so fast that it is difficult for the law to keep up to date. Often common law may raise issues for lawmakers. Often technological issues may be contentious therefore lawmakers may not want to address them as the electorate may not approve. Examples could include medical research and ethical issues such as stem cell research, intellectual property issues and private versus public good. Section III Question 24(a) Criteria Correctly identifies TWO contemporary legal issues Identifies ONE contemporary legal issue Answers will vary depending on student choice. eg. The detention of David Hicks, Detention of the ‘Bali nine’, DNA evidence etc. Marks 2 1 Question 24(b) Criteria Marks 6–8 Accurately outlines the role of the mechanisms in responding to the needs of individuals in relation to each of these TWO issues Uses relevant legal terminology 3–5 Outlines the role of the mechanism(s) in responding to the needs of individuals in relation to ONE – TWO issues Uses some accurate legal terminology 1–2 Makes some statements about mechanisms and/or issues Answers may include: Legal (parliament, courts, tribunals, etc) and non-legal mechanisms (non-government organisations, the media, etc). Question 24(c) Criteria Marks 12–15 Accurately makes an evaluation of the responsiveness of the legal system in attempting to achieve justice Integrates reference to the TWO issues Presents a sustained, logical and cohesive response containing relevant sources, such as cases, legislation, media, international instruments and documents 7–11 Some evaluation of the responsiveness of the legal system in attempting to achieve justice Reference to TWO issues Presents a logical and cohesive response containing relevant sources, such as cases, legislation, media, international instruments and documents 3–6 Some comment on the responsiveness of the legal system in attempting to achieve justice Some reference to ONE – TWO issues 1–2 General statements about the legal system Answers may include: The fact that sometimes the legal system is unable or unwilling to respond to issues and it may be left to non-legal responses to highlight issues/problems. NSW Independent Trial Exams 2010 – Legal Studies Yr 11 Preliminary Exam: Marking Criteria - Page 2 NSW INDEPENDENT TRIAL EXAMS – 2010 LEGAL STUDIES YR 11 EXAMINATION MARKING GUIDELINES QUESTION Section I 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Section II 21 22(a) 22(b) 22(c) 23 Section III 24(a) 24(b) 24(c) MARKS 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 OUTCOME ASSESSED P1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 2.1, 2.2, 3.1, 3.2, 4.3, 5.1 10 2 4 6 8 P1.1, 2.3, 3.3, 4.1, 4.2, 5.4 P1.1, 2.3, 5.4 P1.1, 2.3, 3.1, 3.2, 5.4 P1.1, 2.3, 3.1, 3.2, 5.4 P1.1, 2.3, 3.1, 3.2, 5.4 2 8 15 P1.1, 2.3, 3.3, 4.1, 4.2, 5.4 P1.1, 2.3, 3.3, 4.1, 4.2, 5.4 P1.1, 2.3, 3.3, 4.1, 4.2, 5.4 NSW Independent Trial Exams 2010 – Legal Studies Yr 11 Preliminary Exam: Marking Criteria - Page 3