table of content
advertisement

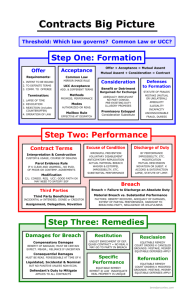
SECTION: 4 Breach of Contract and Associated Remedies 27 Version: 02/2004 IB CP 2 CG TABLE OF CONTENTS Content Section 4 Breach of Contract and Associated Remedies Page 27 Overview 29 4.1 30 Assisting the Learners with this Section 28 Version: 02/2004 IB CP 2 CG Overview Learning Outcome The following is the Learning Outcome of this Section: 4. Have an Overview of Breach of Contract and the Associated Remedies. Learning Objectives The Learning Objectives are as follows: On completion of this Section, the Learner must be able to: 4. Assessment Criteria Have an overview of breach of Contract and the associated remedies by: Comprehending the different forms of breach of Contract Realising the remedy of execution of a Contract Realising the remedy of cancellation of a Contract Realising the remedy of damages of a Contract To demonstrate the achievement of the Learning Objectives, Learners are required to meet the criteria and/or provide the following evidence: Comprehending the different forms of breach of Contract Identify the different forms of breach of Contract Realising the remedy of execution of a Contract Describe the remedy of execution of a Contract. Identify the legal remedies available to the innocent party Realising the remedy of cancellation of a Contract Describe the remedy of cancellation of a Contract Realising the remedy of damages of a Contract Describe the remedy of damages of a Contract 29 Version: 02/2004 IB CP 2 CG 4. Breach of Contract and the associated remedies 4.1 Assisting the Learners with this Section Overview of the main concepts of this Section When creating Contracts, one envisage their fulfillment or discharge by due and proper performance. However, this is not always the case. Where the intended result is not achieved because of the fault of one of the parties, the party commits breach of Contract. This Section discusses the different types of breach of Contract and the remedies associated therewith. Summary of key learning points Below is a summary of the key learning points of this Section. Where the intended result is not achieved because of the fault of one of the parties, the party commits breach of Contract The forms of breach of Contract are: Default by the debtor Default by the creditor Positive malperformance Repudiation Prevention of performance A debtor commits breach of Contract in the form of default (failure to pay), if he/she does not perform at the agreed time and the delay is due to his/her own fault Default of the creditor occurs where the creditor causes the debtor’s performance to be delayed Positive malperformance occurs when the debtor commits an act, which is contrary to the terms of the Contract Repudiation (denial) is any behaviour by a party to a Contract indicating that he/she does not intend to honour the obligations under the Contract A debtor commits breach of Contract in the form of prevention of performance where he/she culpably (deserving blame) renders his/her own performance impossible The creditor commits breach of Contract if he/she renders the debtor’s performance impossible When a party commits breach of Contract, the law of Contract protects the innocent party’s personal rights and grants him/her redress in the form of a legal remedy, which can be enforced through an action in a court of law 30 Version: 02/2004 IB CP 2 CG 4. Breach of Contract and the associated remedies Summary, continued The legal remedies available to the innocent party are: Execution of the Contract Cancellation of the Contract Payment of damages 31 Version: 02/2004 IB CP 2 CG 4. Breach of Contract and the associated remedies Content covered in the Learner Guide The following is covered in this Section of the Learner Guide. Included is a list of topics as well as the page numbers relevant to the Learner Guide. TABLE OF CONTENT Content Page Outline of the Learning Outcomes and Objectives covered in this Section 85 Forms of breach of Contract Introduction Default by the debtor Default by the creditor Positive malperformance Repudiation Prevention of performance by a debtor Prevention of performance by a creditor 86 86 86 88 89 90 91 91 The remedy of execution of a Contract Introduction Execution of the Contract Specific performance Reduced performance Interdicts 92 92 92 92 92 93 The remedy of cancellation of a Contract Introduction Cancellation and default of the debtor Cancellation and default of the creditor Cancellation and defective performance Cancellation and repudiation Cancellation and prevention of performance Act of cancellation Consequences of cancellation The remedy of damages Introduction Patrimonial loss Foreseeable loss Mitigation of damages Proof of loss and the calculation of damages 95 95 95 95 96 96 96 96 96 Summary 101 Conclusion 103 98 98 98 99 99 99 32 Version: 02/2004 IB CP 2 CG 4. Breach of Contract and the associated remedies Activities covered in the Learner Guide The following activities are covered in this Section of the Learner Guide. Page Activity 87 Activity: The Learner needs to list 2 examples from his/her workplace where breach of Contract took place and the cause/s thereof. 88 Activity: The Learner needs to investigate the possibility of THE BANK being responsible for the delay of performance of a client and give reasons therefore. If this is not possible, he/she needs to motivate why. 89 Activity: The Learner needs to relate the examples of malperformance given on page 89 of the Learner Guide back to his/her own workplace and give an example of each. 90 Activity: The Learner needs to give an example of repudiation from the workplace. He/she needs to investigate if it is possible that a client could deny that he/she concluded an agreement. 7492 Activity: The Learner needs to list an example where a client committed breach of Contract where the client is liable for prevention of performance. The Learner needs to investigate if it is possible that THE BANK can prevent a client from performance. 94 Activity: The Learner needs to discuss the remedies with his/her manager and investigate if there are additional remedies/procedures/ systems in place in the event of breach of Contract. 97 Activity: The Learner needs to investigate under what circumstances the remedy of cancellation will take place and if a Contract can be cancelled because of the non-performance on the side of THE BANK. 100 Activity: The Learner needs to discuss the remedy of damages with his/her manager and investigate the procedure for the claiming of damages on breach of Contract. The Learner needs to investigate when, and under what circumstances claiming of damages will take place, and if it is at all possible that damages can be claimed as a remedy on the breach of Contract. 102 Activity: Self-explanatory. The Learner needs to note additional learning points or draw a mind-map of the learning points in the space provided. 33 Version: 02/2004 IB CP 2 CG