Remedies for Breach of Contract pages 210-214
advertisement

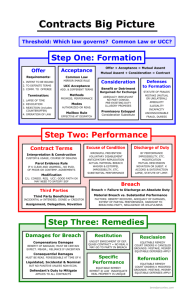
Remedies for Breach of Contract pages 210-214 By Lauren Conroy Remedies for Breach of Contract • The law divides breaches of contract into two categories: the major breach and the minor breach. • Different remedies are granted for injuries caused by minor and major breaches • Remedy: action or procedure followed to enforce a right or to compensate for an injury Basic Remedies for Major Breach 1. Rescission and restitution- cancelling the contract and returning whatever has been received under it. 2. Money damages- the payment of money to compensate for injury. 3. Specific performance- a court order commanding the breaching party to perform what was promised in the contract. Minor Breaches • The party injured by a minor breach must generally continue to perform the duties defined by the contract • Only remedy generally available is money damages • Offset: deducting the cost of completing or fixing a minor breach from payment of the contract price to the breaching party Rescission and Restitution • Restitution permits the injured party to recover money or property • When rescission is granted, all the contractual obligations of the parties are extinguished Types of Money Damages • Compensatory: seeks to place injured parties in the same financial position they would have been in if there was no breach • Consequential: the court tries to place injured parties in the same financial position they would have been in if the contract was performed Types of Money Damages • Liquidated: damages agreed upon before a possible breach of contract • Punitive: the purpose is to punish and make an example of the defendant (occurs when there is an intentional tort) • Nominal: small amount of award money when no injury has occurred Remedies for Breach of Contract • Money damages are not always an adequate remedy for breach of contract • Decree for Specific Performance: the court orders the defendant to do exactly what was promised in the contract.