Wanganui High School
advertisement

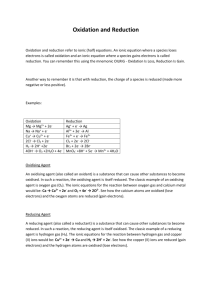
Definition Definition Definition Definition Addition of oxygen OR removal of hydrogen Addition of hydrogen OR removal of oxygen Loss of electrons OR increase in oxidation number Gain of electrons OR decrease in oxidation number oxidation reduction oxidation reduction GER!!!! Oxidation number of an element eg Zn, O2, S8 or C is Sum of the oxidation numbers in a “molecule” eg H2O, CH4, NaCl, is Leo (loss of electrons oxidation) Ger (gain of electrons reduction zero zero Sum of oxidation numbers in a polyatomic ion, eg SO42-, Cr2O72-, NH4+, is… Oxidation number of a simple ion, eg S2-, Cr3+, Fe3+, is… The oxidation number of O in compounds is… The oxidation number of H in compounds is… the charge on that ion the charge on that ion -2 (unless a peroxide, -1) +1 (unless metal hydride, -1) I AM LEO The oxidation number of F in compounds is… -1 RIG(e) OIL(e) reduction is gain (of electrons) oxidation is loss (of electrons) Balance atoms – that are not H or O Balance O – add water Balance H – add H+ Balance charge – add eto more positive side balancing half equations Oxidising agent Oxidising agent Oxidising agent Oxidising agent Acidified orange dichromate H+/Cr2O72- is reduced to Acidified purple permanganate H+/ MnO4- is reduced to Colourless hydrogen peroxide, H2O2 is reduced to Very pale orange iron(III) ion Fe3+ is reduced to green chromium(III) ion Cr3+ “colourless” manganese ion, Mn2+ colourless water, H2 O very pale green iron(II) ion Fe2+ Oxidising agent Oxidising agent Oxidising agent Oxidising agent Pale greeny-yellow chlorine Cl2 is reduced to Orange brown iodine I2 is reduced to Oxygen gas, O2 is reduced to Hydrogen ion, H+, eg from acids like HCl or H2SO4 is reduced to colourless Cl- ion (& pungent smell disappears) colourless I- ion oxide ion O2- colourless hydrogen gas, H2 Reducing agent Reducing agent Reducing agent Reducing agent Metals, eg Mg, Zn or Cu are oxidised to Black carbon, C, is oxidised to Colourless carbon monoxide gas, CO, is oxidised to Colourless hydrogen gas, H2, is oxidised to metal ions, Mg2+, colourless CO2 gas colourless CO2 gas Zn2+ or Cu2+ colourless H+ ion Reducing agent Reducing agent Reducing agent Reducing agent Very pale green Colourless iron(II) ion Fe2+ is bromide ion, Br-, is oxidised to oxidised to Colourless iodide ion, I-, is oxidised to Colourless, pungent smelling sulfur dioxide gas, SO2 is oxidised to very pale orange iron(III) ion Fe3+ orange-brown solution of iodine, I2 (or grey solid) reddish brown bromine, Br2 colourless sulfate, SO42- Reducing agent Increase in oxidation number is Decrease in oxidation number is No change in oxidation number eg Cr2O72- CrO42-, (Cr +6 in both) means that colourless sulfate, SO42- oxidation reduction it is NOT a redox reaction Redox reaction in which the same element is both oxidised and reduced is called Oxidising agent is another name for an Reducing agent is another name for a Oxidising agents _____ electrons and are _____ in the process disproportionation oxidant reductant gain reduced Halogens as oxidants Halogens as oxidants Colourless, hydrogen sulphite, HSO3- is oxidised to Reducing agents _____ electrons and are _____ in the process To combine balanced half equations x by factors so that lose oxidised the electrons will cancel out Halogens as oxidants Halogens as oxidants Cl2, Br2 & I2 react with water H2O to make F2 , v. strong oxidant, reacts with H2O to make HCl + HOCl i.e. HX + HOX HF + O2 Oxidising strength Will oxidise other is F > …. elements eg Fe + Cl2 forms Cl > Br > I FeCl3 Test for chlorine gas (starch-iodide paper) Test for chlorine gas (moist litmus paper) Turns starchiodide paper black (I2 made) Turns red and then is bleached by HOCl Halogens as oxidants Halogens as oxidants Halogens as oxidants Halogens as oxidants Reaction with halides Reaction with halides Cl2 + Br- or I- Br2 + I- Br2 is not a strong enough oxidising agent to oxidise… I2 is not a strong enough oxidising agent to oxidise… produces Cl- & Br2 or I2 produces Br- & I2 chloride chloride or bromide Oxidising agents _______ other species and in the process they become _____ Reducing agents _______ other species and in the process they become _____ Colour change Colour change Mix H+/ MnO4- & Fe2+ Mix H+/ Cr2O72- & Fe2+ oxidise reduced reduce oxidised purple to colourless (slight pale orange) orange to green Electrolysis Electrolysis Electrolysis Electrolysis Anions (-) are Cations (+) are Electrolyte is ionic attracted to the attracted to the compound that is positively charged negatively charged either _____ or electrode, the … electrode, the … _____ Oxid Ation occurs at the… anode cathode aqueous or molten anode! Electrolysis Electrolysis Electrolysis Electrolysis Redu Ction occurs at the… cathode! Used to extract In Al extraction In Al extraction aluminium from its the carbon anodes the Al2O3 is mixed ore, alumina…. have to be with cryolite to replaced as they aluminium oxide Al2O3 react with O2 to make CO2 gas lower the m.pt. and so save $$$ Electrolysis is used to electroplate metal items which are made the… cathode Electrolysis Is used to purify copper by making an impure ___, pure ___ and using CuSO4(aq) Electrolysis of NaCl solution produces Electrolysis of CuCl2 solution produces Cu anode Cu cathode H2 & Cl2 (and NaOH solution) Cu & Cl2 Electrolysis Electrolysis of molten PbBr2 produces ___ at cathode and ___ at anode Electrolysis If the solution of NaCl or CuCl2 is very dilute you will get ___ instead of Cl2 ionic compound must be (aq) or molten (l) so that the ions are Electrolysis of molten NaCl produces ___ at cathode and ___ at anode oxygen, O2 free to move sodium metal chlorine gas lead metal bromine Electrolysis ___ conduct in solution / molten liquid, ___ carry the charge in the wire Oxidation No. / state of N in N2O4 is Electrolysis of acidified water Electrolysis of acidified water @ anode @ cathode 2OH– O2 + 2H+ + 4e– 2H+ + 2e– H2 ions electrons +4 Other colours to know… copper(II) ion Cu2+ is Nitrogen dioxide gas, NO2, is Oxidation No. / state of N in NO3- is Oxidation No. / state of N in NH4+ is blue brown +5 -3