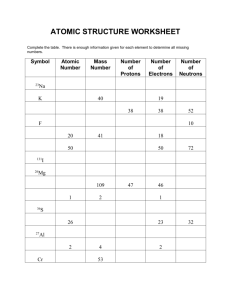
I. Chemical Reactions – An Introduction
advertisement

Name: ___________________________ Block: ________ Date: __________ Chemistry Midterm Exam Review A. Measurements and Calculations accuracy precision scientific notation dimensional analysis percent error qualitative quantitative SI Units significant figures (counting, multiplying, dividing, adding, subtracting, averaging) uncertainty in measurement 1. Determine the number of significant figures in the following numbers. a. 0.00007690 g ______ c. 90070 km _______ b. 0.00978 mm ______ d. 9.10 cg _______ 2. Record your answer with the correct number of significant figures and units. a. 41.6 g + 3.259 g = __________ c. (26.2 cm)(1.234 cm) = __________ b. 0.00134 mL - 0.000233 mL = ________ d. (32.20 kg) / (4.0 kg) = _________ c. Convert the following numbers from scientific notation to ordinary notation. a. 3.02 x 10-3 g = _________________ b. 5.791 x 105 m = ______________ d. Convert the following numbers from ordinary notation to scientific notation. a. 4560 cm = ______________ b. 0.0076 g = ______________ 3. How many centigrams are in 234 mg? 4. How many meters are in 0.000325 km? 5. What is the percent error if you measure the density of a substance to be 3.679g/ml but the known true density of that material is 4.115g/mL 6. What is the difference between accuracy and precision? B. Density and C. Matter matter phases physical property chemical property density volume mass displacement element molecule monatomic/diatomic compound mixture homogenous mixture heterogeneous mixture pure substance solution melting point boiling point conductivity luster malleability ductility magnetism chromatography filtration distillation chemical/physical change 7. The density of Mercury is 13.0 g/mL. If you have 24.3 mL of Mercury, what is its mass? 8. A cube of wood that weighs 23.5 g measures 224.21 cm by 1.45 cm by 7.34 cm. What is the density of the wood? 9. You measure 23.6 mL of water into a graduate cylinder. You place a 56.56 g chunk of metal into the cylinder and the volume increases to 29.3 mL. What is the density of the chunk of metal? 10. Classify the following as a chemical or physical property. a. Color b. Flammability c. Solubility 11. Classify the following as a chemical or physical change. a. Tearing paper b. Burning wood c. Boiling water 12. Classify the following as an element or a compound. a. Phosphorus b. Carbon dioxide c. Water 13. Classify the following as a mixture or pure substance. a. A multivitamin tablet b. distilled water c. tap water 14. Classify the following as a homogeneous or heterogeneous mixture. a. chunky peanut butter b. a solution of copper (II) sulfate c. a bag of trail mix 15. What would you use to separate two liquid solvents from each other? a. Chromatography c. Distillation b. Filtration d. Nuclear separation D. Chemical Foundations atom atomic mass atomic number proton neutron electron ion cation/anion average atomic mass isotope half-life α (alpha) radiation β (beta) radiation γ (gamma) radiation 16. Give the symbols for the following elements a. Iron b. Fluorine e. Helium f. Hydrogen Democritus Dalton Thomson Millikan Rutherford Bohr c. Beryllium g. Silicon d. Boron h. Vanadium 17. Write the formula for the compound containing a. a two to three ratio of Manganese to sulfur b. six carbon, twelve hydrogen and six oxygen 18. Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the following. p n e p n e a. 42 Ca0 d. 62 b. 6 Li+1 e. 30 -3 c. 52 f. 124 -1 Cr Co+3 P I 19. If element X consists of 78.7% of atoms with a mass of 24.0 amu, 10.1% of atoms with a mass of 25.0 amu, and 11.2% of the atoms with a mass of 26.0 amu, what is the atomic mass of element X? 20. The average atomic mass of rubidium is 85.47 amu. There are two naturally occurring isotopes of rubidium: 85Rb, mass of 84.91 amu and 87Rb, mass of 86.92 amu. What is the percent abundance of each of the isotopes? 21. What is the half-life of a sample if 5.00 kg decays to 0.63kg in 27 days? 22. If the half-life of a chemical is 25 years and you have 1.000 gram, how much will be left in 100 years? E. Modern Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table electron configuration excited state ground state orbital Principle energy level sublevel Aufbau Order Pauli Exclusion Principle Hund’s Rule Bohr Planck Heisenberg De Broglie element group/family period metal nonmetal metalloid alkali metal alkaline earth metal transition metal halogen noble gas Mendeleev Moseley atomic radius electronegativity ionization energy shielding effect ion oxidation state cation anion 23. Define the following terms: a. principle energy level b. orbitals c. sublevel 24. Write the complete electron configuration and the orbital diagram for Aluminum Chlorine Argon Copper 25. Using your periodic table, write the noble gas configurations for Fluorine Silicon Cesium Lead Iodine 26. Explain the following rules: Aufbau Order Pauli Exclusion Principle Hund’s Rule F. Chemical Bonding ionic bond covalent bond polar covalent bond electronegativity polyatomic ion molecule 27. chemical formula molecular formula structural formula Lewis structure monatomic diatomic intramolecular force VSEPR linear bent tetrahedral trigonal planar trigonal pyramidal For each of the following pairs of bonds, choose the bond that will be more polar. a. H-P or H-C b. O-F or O-I c. N-O or S-O d. N-H or Si-H 28. Draw the Lewis structure for each of the following a. CO2 g. CF4 b. N2 h. NO+ c. NH3 i. NO3- d. NH4+ j. H2S e. SO4-2 k. ClO3- f. NF3 l. BeF2 29. Determine the molecular shape for each of the previous drawings: Tetrahedral, Trigonal pyramid, bent, trigonal planar, linear. 30. Determine if the previous drawings (#26) were Polar or Nonpolar G. Chemical Nomenclature polyatomic ions cation anion common charges acids molecules ionic compounds binary covalent molecules metals/non-metals “-ate/-ic acids” “-ite/-ous acids” “-hydro_____-ic acids” 31. Identify the following elements as a metal, a nonmetal or a semi-metal a. Strontium c. Antimony e. Selenium b. Cadmium d. Silicon f. Manganese 32. Write the name for the following compounds. a. AgBr b. Ni(CN)3 c. Sr3(PO4)2 d. HF e. NH3 f. Au2SO4 g. Ca(OH)2 h. PF5 33. Write the formula for the following compounds. a. Barium chloride e. tetraphosphorus decoxide b. Cesium sulfite f. Manganese (II) acetate c. Sodium chlorite g. Nitric acid d. tricarbon hexanitride h. hydronitric acid H. Chemical Composition and the Mole Atomic mass unit (amu) Mole Avagadro’s Number Molar Mass Molecular Weight Formula Unit Percent composition Empirical formula Molecular formula 34. Calculate the molar mass of the following compounds? (these will be used in #35-38) a. AgBr e. Ni(CN)3 b. HNO2 f. Sr3(PO4)2 c. HF g. CO2 35. How many moles are in 7.23 grams of the following compounds? a. Ni(CN)3 b. HNO2 c. Sr3(PO4)2 36. How many moles are in 3.02 x 1023 formula units of the following? a. AgBr b. Sr3(PO4)2 c. HF 37. How many grams are in 7.2 x 1026 formula units or molecules of the following? (two steps) a. Ni(CN)3 b. HNO2 c. CO2 38. How many particles are in 3.45 grams of the following? (two steps) a. AgBr b. HNO2 c. HF d. Ni(CN)3 e. Sr3(PO4)2 f. CO2 39. A compound used as an additive in gasoline is 71.65% Cl, 24.27% C, and 4.07% H. The molar mass is 98.96 g. Determine the empirical formula and the molecular formula. 40. What is the percent composition of sodium, phosphorous, and oxygen in sodium phosphate? I. Chemical Reactions – An Introduction Chemical Equation Reactants Products Coefficients Subscripts Solid (s) Liquid (l) Gas (g) Aqueous (aq) Diatomic elements 41. Balance the following equations. a. ___ C2H6 + ___ O2 ___ CO2 + ___ H2O b. ___ CaCl2 + ___ H2O ___ Ca(OH)2 + ___ HCl c. ___ Cl2 + ___ NaI ___ NaCl + ___ I2 d. ___ NH3 + ___ Cl2 ___ NH4Cl + ___ NCl3 e. ___ AuCl2 + ___ K2SO4 ___ AuSO4 + ___ KCl 42. Write and balance the following equations and include state symbols. a. Solid iron (III) oxide is heated strongly in carbon monoxide gas; it produces elemental iron and carbon dioxide gas. b. Acetylene gas (C2H2) is burned in oxygen to produce carbon dioxide gas and water vapor. c. Calcium metal is added to water to produce hydrogen gas and the solid calcium hydroxide. J: Chemical Reaction Types Precipitate Soluble/Insoluble Dissociation Solubility Rules Activity Series Double Replacement Single Replacement Decomposition Synthesis Combustion (Complete and Incomplete) Acid Base Neutralization Reaction (same as double displacement acid/base reaction) Write Out the Generic Reaction Formula for the Following Reaction Types - Synthesis - decomposition - single replacement (metal cation exchange) - double replacement - neutralization (a type of double replacement) - combustion - complete - combustion - incomplete 43. Determine whether the following compounds are soluble or insoluble. a. sodium acetate c. silver hydroxide b. lithium sulfide d. colbalt (II) sulfate 44. Balance the following equations. Include physical state symbols. Classify the reactions in as many ways as possible. a. 2 C4H10 (g) + 13 O2 (g) ___ CO2 ( ) + ____ H2O ( b. ___ Ca (s) + ____ H2O (l) ____ Ca(OH)2 ( ) ) + ____ H2 ( ) Will this reation go? Why or why not? c. ____ AgC2H3O2 (aq) + _____ KBr (aq) ___ KC2H3O2 ( ) + ___ AgBr( Will this reation go? Why or why not? d. ____ SO2 (g) + ___ H2O (l) ____ H2SO3(aq) e. ____ KClO3 (s) _____ KCl (s) + _____ O2 ( f. ____ NaOH(aq) + ____ H2SO4(aq) ) ____ Na2SO4(aq) + ____ HOH(l) )