Training and Developing the Sales Force
advertisement
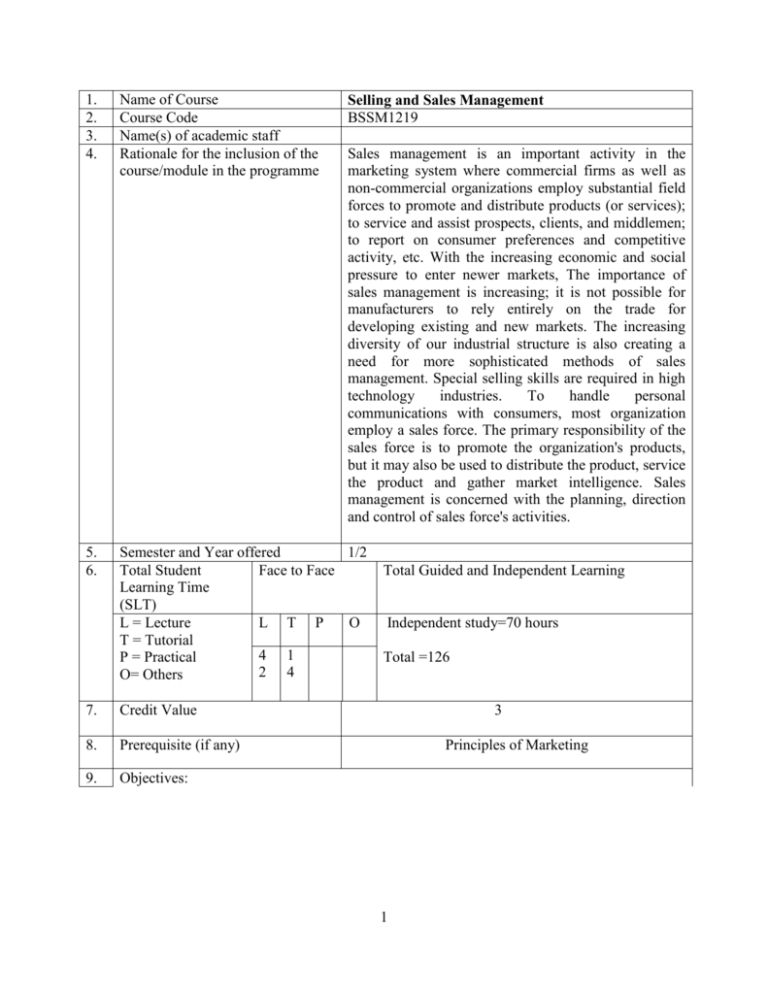
1. 2. 3. 4. Name of Course Course Code Name(s) of academic staff Rationale for the inclusion of the course/module in the programme 5. 6. Semester and Year offered 1/2 Total Student Face to Face Learning Time (SLT) L = Lecture L T P O T = Tutorial 4 1 P = Practical 2 4 O= Others 7. Credit Value 8. Prerequisite (if any) 9. Objectives: Selling and Sales Management BSSM1219 Sales management is an important activity in the marketing system where commercial firms as well as non-commercial organizations employ substantial field forces to promote and distribute products (or services); to service and assist prospects, clients, and middlemen; to report on consumer preferences and competitive activity, etc. With the increasing economic and social pressure to enter newer markets, The importance of sales management is increasing; it is not possible for manufacturers to rely entirely on the trade for developing existing and new markets. The increasing diversity of our industrial structure is also creating a need for more sophisticated methods of sales management. Special selling skills are required in high technology industries. To handle personal communications with consumers, most organization employ a sales force. The primary responsibility of the sales force is to promote the organization's products, but it may also be used to distribute the product, service the product and gather market intelligence. Sales management is concerned with the planning, direction and control of sales force's activities. Total Guided and Independent Learning Independent study=70 hours Total =126 3 Principles of Marketing 1 10. To provide an introduction to personal selling as a systematic process. To provide insights into how people are motivated - both salespeople and prospective buyers. To provide and introduction to the basic activities of sales management: evaluation, compensation, forecasting, budgeting, time and territory management Learning outcomes: At the completion of the subject, students should be able to perform the following tasks: Identify key trends affecting sales organization and sale managers in the current era. Understand the attraction and benefits of the sales profession Understand the process of motivation and various career phases of sales personnel that influence motivation Understand the key issues that drive the recruitment and selection of salespeople, how selection criteria and the selection procedure are determined. Identify the key issues in sales training objective of sales training. Understand the various methods of training and to measure the cost and benefits of sales training. Understand how a sales manager can make the performance review process more productive and valuable for the salesperson 11. Transferable Skills: To enhance the student's ability in applying demand analysis and segmentation techniques in Sales and Marketing. To develop the student's ability for managing the firm's marketing efforts directed to Sales and Marketing Provide a framework for understanding business marketing strategy development and, thereby, provide the student with decision-making capabilities in the field. 12. Teaching-learning and assessment strategy A variety of teaching and learning strategies are used throughout the course, including: Lecture sessions Tutorial sessions Case Studies Student-Lecturer discussion Collaborative and co-operative learning Workshops and Training Seminars Independent study Assessment strategies include the following: Ongoing quizzes Midterm tests Performance Assessment (Participation, project, Assigned exercises) Case Presentations 2 13. Synopsis: The goal of the Sales Management course is to examine the elements of an effective sales force as a key component of the organization's total marketing effort. The course will extend student’s understanding of marketing's reach and potential impact in achieving its overarching goals. Course objectives include understanding the sales process, the relationship between sales and marketing, sales force structure, customer relationship management (CRM), use of technology to improve sales force effectiveness, and issues in recruiting, selecting, training, motivating, compensating and retaining salespeople. Students learn to apply the discussion topics through an interactive project worked on throughout the course. 14. Mode of Delivery: Face to Face Lecture sessions Tutorial sessions 15. Assessment Methods and Types: The assessment for this course will be based on the following: Coursework 50% Quizzes Assignments Project Mid-Semester Exam Final Examination 16. 10% 10% 10% 20% 50%. Total 100% Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims The individual course is mapped to the programme aims using a scale of one to five where (One being the least relevant/related and five being the most relevant/ related). 17. A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 4 3 4 3 4 3 Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes The learning outcomes of this course are mapped to the eight MQF domains using a scale of one to five where (one being the least relevant/related and five being the most relevant/ related). LO1 LO2 LO3 LO4 LO5 LO6 LO7 LO8 3 4 4 2 2 2 2 2 LO9 2 LO10 LO11 2 2 18. Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic WEEK Details SLT 3 LO12 4 WEEK 1 Introduction to Sales Management The Sales Strategy Selling Approached Selling Process Sales Leaders Ethics in Sales Management WEEK 2 Sales Functions and Multi-Sales Channels Selling in a Multi-channel Environment Aligning the Sales Organisation Outsourcing of Sales Personnel Global Sales Management WEEK 3 Leadership and Sales Executive Leadership versus Managing Identifying leaders in Global Marketplace Situational Approaches Contemporary perspective of Leadership WEEK 4 B2B Sales and Customer Relationship and Management Understanding the B2B Purchasing Decisions B2B Customer Relationship Management Customer Lifetime Value Risk and Organisational Buyer WEEK 5 Technology and Sales Management Sales Management Software Sales Force Automation Systems Implementing CRM and SFA Systems Salesperson/Sales Managers Issues WEEK 6 Designing and Organising the Sales Force Size of the Sales Force Geographical, Market and Product Structure Key Account Structure Reporting Relationship within a Firm’s Sales Force Span of Control 4 Total Indep. L T 3 1 5 9 3 1 5 9 3 1 5 9 3 1 5 9 3 1 5 9 3 1 5 9 WEEK 7 Recruitment and Selection of the Sales Force Planning to Hire Job Analysis and Description Finding and Recruiting Applicants WEEK 8 Training and Developing the Sales Force Importance of Sales Training The Training Process Identifying the Firm’s Sales Training Needs Designing and Developing the Sales Training Programme Delivery of the Training Programme WEEK 9 Motivating and Rewarding Sales Personnel What motivates Salespeople Generational Motivational Issues Financial and Non-Financial Rewards Components of a Reward Programme Managing the Sales Force Leading the Sales Force Leadership Competencies for Sales Personnel WEEK 10 Importance of Customer Knowledge and Information Knowledge generated by the Firm’s Sales Force Sales Forecasting Estimating Market Potential and Demand Forecasting Methods Limitation of Forecasting WEEK 11 Performance Appraisal of the Sales Force Sales Analysis Cost Analysis Profit Analysis Ratio Measures for Evaluating the Sales Force Leveraging Technology to Manage Sales Rep. Performance Ratio Measures for Performance Appraisals The Four—Factor Model of Evaluation Qualitative Performance Measures 5 3 1 5 9 3 1 5 9 3 1 5 9 3 1 5 9 3 1 5 9 WEEK 12 WEEK WEEK 13 14 19. Factors Affecting a Firm’s Sales Performance Influence of Corporate Culture Influence of Social Culture Components of Corporate and Social Culture 3 Managing the Global Sales Force Changing Demographics and Diversity in the Sales Force Evaluation and Control of the Sales Programme Cost Analysis Behaviour and Other Performance Analyses Sales Presentations by Students in classroom Group presentation of Project Total Main references supporting the course: 1 5 9 3 1 5 9 3 1 5 9 42 14 70 126 Churchill/Ford/Walker’s, Sales Force Management, (Latest Edition) McrawHill Additional references supporting the course: 1. Darymple, D.J. & Cron, W.L., Sales Management, (Latest Edition) John Wiley 2. Tanner, Honeycutt, Erffmeyer, Sales Management, Shaping Future Sales Leaders, (Latest Edition), Prentice Hall. 20. Other additional information All related subject materials will be available to the students during the period of the course 6











