International Economics
advertisement
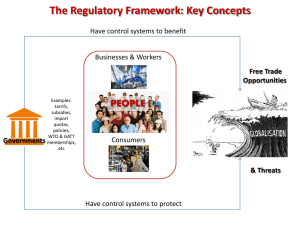
India’s way- a case study in state planning and protectionism The infant industry argument for protectionism is often used as part of a wider theory based on import substitution industrialisation (ISI). After India achieved independence the country embarked on a series of measures designed to encourage economic development. India was keen to reduce its dependence on trade ties and imports form its old Colonial master, Britain. Therefore it started a series of reforms designed to encourage import substitution and self-sufficiency. Most of these reforms were state- led and involved state ownership and control of key industries (socialism) and PROTECTIONISM. TASK Apply the following criteria to evaluate the theory of import substitution- as applied to India. Because of the overlapping nature of the criteria, they do not have to be applied separately. Criteria for evaluation What are the long run implications of protectionism as opposed to the short run? Consider the argument from the points of view of the different stakeholders, e.g. domestic producers, domestic workers, consumers, government, foreign producers, foreign workers, etc. Does the infant industry argument have more validity for a developing country than for a developed country? References: Video clips from Commanding Heights for real world examples (esp. on India): Episode 1Battle of Ideas: chapter 10 http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/commandingheights/lo/story/ch_menu.html Episode 2 – The Agony of Reform: chapters 4, 5, 17 & 21 http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/commandingheights/lo/story/ch_menu_02.html Handout on protectionism See also http://www.tutor2u.net/economics/content/topics/trade/import_controls.htm