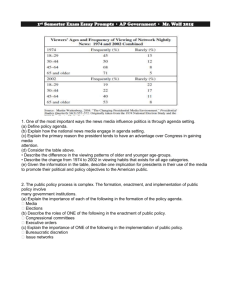
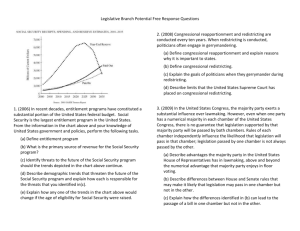
Congressional Redistricting Process Vocabulary
advertisement

The Congressional Redistricting Process Vocabulary Census- an official, periodic procedure for systematically gathering information and counting a population; the U.S. Constitution requires a decennial census to adjust the number of delegates each state receives in the House of Representatives to ensure adequate representation based on population changes Compactness- a redistricting requirement defined by the tight or unified geometric shape and interior of a district, such as a square; strange or irregularly shaped districts are often challenged in court as examples of race-based gerrymandering Contiguity- a redistricting requirement defined by a single, unbroken, physically connected district; a contiguous district permits one to travel to all parts without crossing its boundaries while a district comprising of two or more separate areas is not contiguous “Covered jurisdictions”- states, counties, or towns that have a history of continued discrimination against minority voters, and must gain preclearance (preliminary approval) for voting or election-related changes from the U.S. Justice Department or the U.S. District Court in Washington, D.C. under Section 5 of the Voting Rights Act of 1965 (Public Law 89-110) Decennial- occurring every ten years Disenfranchise- to deprive a citizen of the right to vote Electoral College- a body of electors chosen by the voters in each state to elect the President and Vice President of the United States; states lose or gain Electoral Votes based on reapportionment Gerrymandering- a process that occurs when redistricting is undertaken for the benefit of a particular group, such as members of one political party or race Majority-minority district- a district comprised mostly of members of the same racial minority group Per curiam opinion- a decision issued by a multiple-judge appellate court where a judgment is issued collectively and is often unsigned Political subdivision- the geographic boundary of a state, county, city, town, or municipality; respect for political boundaries is encouraged by many state constitutions during the redistricting process; redistricting plans that excessively split local subdivisions among many Congressional districts are typically found to be evidence of gerrymandering Preclearance- an approval requirement of Section 5 of the Voting Rights Act of 1965 (Public Law 89-110); “covered jurisdictions” must gain approval from the U.S. Justice Department or the U.S. District Court in Washington, D.C. prior to implementing redistricting plans Reapportionment- the reallocation of seats in a legislature; for example, Congressional reapportionment results in some states gaining and other states losing seats in Congress Redistricting- the redrawing of Congressional districts that takes place every 10 years following the decennial census Section 5 of the Voting Rights Act of 1965 (Public Law 89-110)- a provision of the Voting Rights Act which requires jurisdictions with a history of racial discrimination in voting (“covered jurisdictions”) to gain preclearance (preliminary approval) from the U.S. Justice Department or the U.S. District Court in Washington D.C., for proposed changes to election laws, including new redistricting plans Strict scrutiny- a policy or law must demonstrate that it is justified because of a compelling government interest, the highest standard of judicial review used by federal courts to determine if a government policy or law is constitutional; the Supreme Court applies strict scrutiny to redistricting on the basis of race under the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment Suffrage- the right to vote Voting Rights Act of 1965 (Public Law 89-110)- a U.S. federal statute enacted to enforce the Fifteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution by outlawing discriminatory voting practices that were historically responsible for denying African Americans the right to vote