Biology 110 Student Self Assessment Chapter 4
advertisement

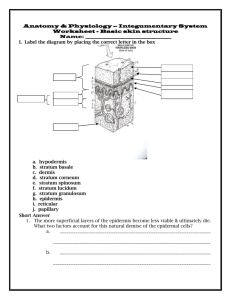
Biology 110 Student Self Assessment Chapter 4 1. The categories of epithelial tissue membranes are ______ membranes. a. synovial, cutaneous, and mucous b. synovial, cutaneous, and serous c. synovial, mucous, and serous d. synovial, mucous, and cutaneous e. mucous, cutaneous, and serous 2. Which of the following is a connective tissue membrane? a. synovial membrane b. cutaneous membrane c. mucous membrane d. serous membrane e. pleural membrane 3. The skin is a _____________ membrane. a. synovial b. cutaneous c. mucous d. serous e. basement 4. An example of a mucous membrane is the ______________. a. lining of the respiratory tract b. parietal peritoneum c. visceral peritoneum d. parietal pericardium e. visceral pericardium 5. Which of the following is a vital function of the skin? a. It converts modified epidermal cholesterol to vitamin D. b. It aids in the transport of materials throughout the body. c. The cells of the epidermis store glucose as glycogen for energy. d. It absorbs vitamin C so that the skin will not be subject to diseases. e. It aids in dessication. 6. The most external skin region is composed of ______. a. simple columnar epithelium b. stratified squamous epithelium c. adipose tissue d. areolar tissue e. dense fibrous connective tissue 7. Which layer insulates deeper tissue from extreme temperature changes that occur outside the body? a. epidermis b. dermis c. subcutaneous connective tissue d. the papillary layer e. the reticular layer 8. Which of the following is the correct sequence in layers of the epidermis going from outermost to innermost layer? a. stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum germinativum b. stratum granulosum, stratum, germinativum, stratum lucidum, stratum spinosum, stratum corneum c. stratum germinativum, stratum corneum, stratum spinosum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum d. stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum germinativum 9. Which of the following homoeostatic imbalances is caused by a virus? a. athlete’s foot b. cold sores c. impetigo d. contact dermatitis e. cyanosis 10. The “tanning” effect (darkening of the skin) that occurs when a person is exposed to the sun is somewhat protective due to ______. a. increased production of melanin that helps to block ultraviolet light b. an increased concentration of keratin that “toughens” the skin c. added layers of epidermis that thicken the skin d. an increased blood supply that carries the heat of the sun away e. a decreased blood supply that blocks melanocyte activity 11. Melanocytes are found in the ________. a. stratum spinosum b. stratum lucidum c. stratum corneum d. stratum basale e. stratum granulosum 12. Which of the following is found in the dermis? a. melanocytes b. keratin c. stratum corneum d. pain and touch receptors e. adipose cells 13. Epidermal cells that are actively mitotic and replace superficial cells that are continually rubbed off are ___________ cells. a. stratum granulosum b. stratum corneum c. stratum lucidum d. stratum spinosum e. stratum germinativum 14. Acne is a disorder associated with inflammation of the ______. a. apocrine glands b. sebaceous glands c. eccrine glands d. hair follicles e. sudoriferous glands 15. The papillary layer of the dermis has structures called ______. a. dermal papillae b. hair follicles c. Pacinian corpuscles d. adipose cells e. hair bulbs 16. When the body temperature rises, which of the following takes place? a. Eccrine glands become active. b. Arrector pili muscles contract. c. Pacinian corpuscles are stimulated. d. Blood is prevented from reaching skin capillary beds e. vitamin D synthesis is blocked 17. Fingernails are _______. a. a modification of the epidermis b. derived from osseous tissue c. extensions of the carpal bones d. formed from a different embryonic layer e. genetically controlled by a “delayed action” gene 18. The secretions of the eccrine glands are ______. a. primarily uric acid b. 99 percent water, sodium chloride, and trace amounts of wastes, lactic acid, and vitamin C c. fatty substances, proteins, antibodies, and trace amounts of minerals and vitamins d. solely metabolic wastes e. basic 19. Apocrine glands are __________. a. found all over the body b. found in the axillary and genital areas c. found on the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet d. are far more numerous than eccrine glands e. are an important and highly efficient part of the body’s heat regulating equipment 20. Mrs. Widget has an allergy to certain chemicals that cause itching, redness, and swelling of her skin. Her condition is termed ___________. a. impetigo b. alopecia c. erythema d. cyanosis e. contact dermatitis 21. What is the first threat to life from a massive third-degree burn? a. infection b. dehydration c. unbearable pain d. loss of immune function e. blood loss 22. A physician estimates the volume of fluid lost in a severely burned patient by ______. a. measuring urinary output and fluid intake b. observing that tissues are continually moist c. blood analysis d. using the “rule of nines” e. performing enzyme studies 23. Which of the following is an indication of melanoma? a. a symmetrical mole b. a pigmented spot that has smooth borders c. a spot on skin smaller than a pencil eraser d. a pigmented spot that is black e. a pigmented spot that contains areas of different colors