Unit 10 Study Guide and Schedule
advertisement
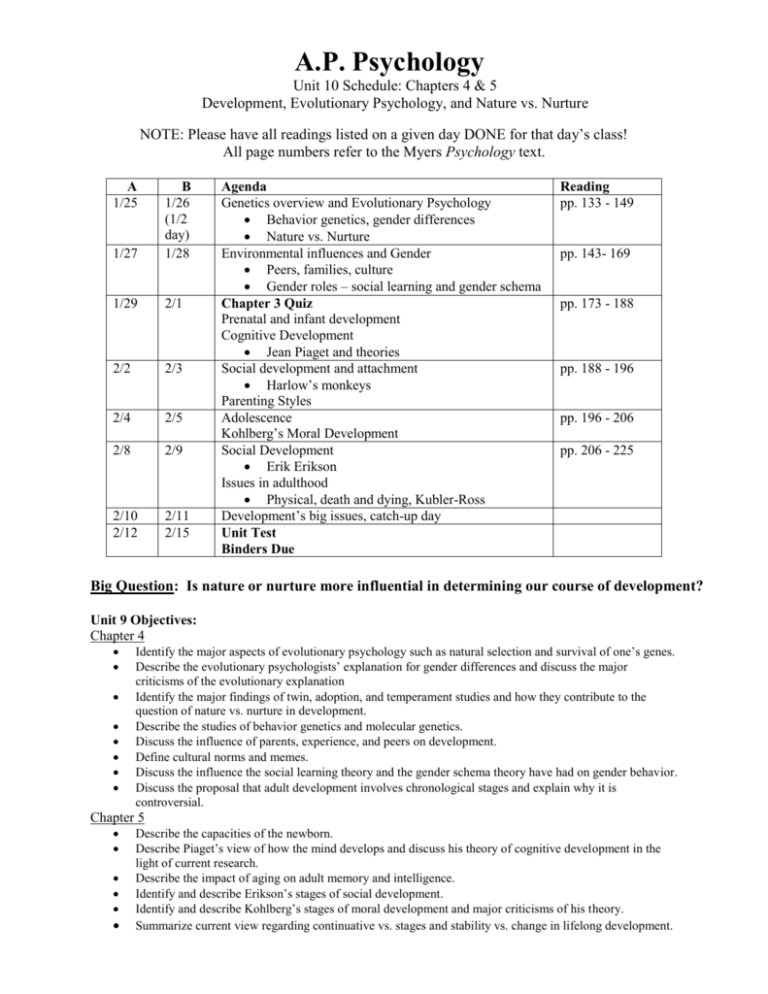
A.P. Psychology Unit 10 Schedule: Chapters 4 & 5 Development, Evolutionary Psychology, and Nature vs. Nurture NOTE: Please have all readings listed on a given day DONE for that day’s class! All page numbers refer to the Myers Psychology text. A 1/25 1/27 B 1/26 (1/2 day) 1/28 1/29 2/1 2/2 2/3 2/4 2/5 2/8 2/9 2/10 2/12 2/11 2/15 Agenda Genetics overview and Evolutionary Psychology Behavior genetics, gender differences Nature vs. Nurture Environmental influences and Gender Peers, families, culture Gender roles – social learning and gender schema Chapter 3 Quiz Prenatal and infant development Cognitive Development Jean Piaget and theories Social development and attachment Harlow’s monkeys Parenting Styles Adolescence Kohlberg’s Moral Development Social Development Erik Erikson Issues in adulthood Physical, death and dying, Kubler-Ross Development’s big issues, catch-up day Unit Test Binders Due Reading pp. 133 - 149 pp. 143- 169 pp. 173 - 188 pp. 188 - 196 pp. 196 - 206 pp. 206 - 225 Big Question: Is nature or nurture more influential in determining our course of development? Unit 9 Objectives: Chapter 4 Identify the major aspects of evolutionary psychology such as natural selection and survival of one’s genes. Describe the evolutionary psychologists’ explanation for gender differences and discuss the major criticisms of the evolutionary explanation Identify the major findings of twin, adoption, and temperament studies and how they contribute to the question of nature vs. nurture in development. Describe the studies of behavior genetics and molecular genetics. Discuss the influence of parents, experience, and peers on development. Define cultural norms and memes. Discuss the influence the social learning theory and the gender schema theory have had on gender behavior. Discuss the proposal that adult development involves chronological stages and explain why it is controversial. Chapter 5 Describe the capacities of the newborn. Describe Piaget’s view of how the mind develops and discuss his theory of cognitive development in the light of current research. Describe the impact of aging on adult memory and intelligence. Identify and describe Erikson’s stages of social development. Identify and describe Kohlberg’s stages of moral development and major criticisms of his theory. Summarize current view regarding continuative vs. stages and stability vs. change in lifelong development. Chapter 4 Overview Developmental psychologists study the life cycle, from conception to death, examining how we develop physically, cognitively, and socially. Chapter 3 covers prenatal, infant, and childhood development and introduces three major issues in developmental psychology: (1) the relative impact of genes and experience on behavior, (2) whether development is best described as gradual and continuous or as a discontinuous sequence of stages, and (3) whether the individual’s personality remains stable or changes over the life span. Chapter 5 Overview A key assumption of modern developmental psychology is that development is lifelong. Chapter 4 explores physical, cognitive, and social development during adolescence and adulthood. On the basis of this discussion, this chapter will revisit the issue of continuity in development. Although there are not too many terms to learn in this chapter, there are a number of important research findings to remember. Pay particular attention to the discussions regarding intellectual stability or decline and social changes during adulthood. A major challenge in this chapter is to become familiar with two stage theories: Kohlberg’s theory of moral development and Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development. Writing carefully prepared answers to the guided study items should be especially helpful in mastering the material of this chapter. Key Terms Using your own words, write a brief definition or explanation of each of the following. Do this after or while reading the assigned pages for class. 1. chromosomes – 2. evolutionary psychology – 3. behavior genetics – 4. DNA – 5. genes – 6. genome – 7. temperament – 8. molecular genetics – 9. heritability – 10. natural selection – 11. mutation – 12. gender – 13. norm – 14. individualism – 15. collectivism – 16. testosterone – 17. X and Y chromosomes – 18. gender role – 19. gender identity – 20. gender typing – 21. social learning theory – 22. developmental psychology – 23. zygote – 24. embryo – 25. fetus – 26. fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) – 27. teratogens – 28. habituation – 29. maturation – 30. schema – 31. assimilation – 32. accommodation – 33. object permanence – 34. egocentrism – 35. conservation – 36. theory of mind – 37. autism – 38. attachment – 39. critical period – 40. imprinting – 41. cross-sectional study – 42. longitudinal study – 43. crystallized intelligence – 44. fluid intelligence – 45. social clock – Developmental Psychology Unit Study Guide Complete the following study guide as you read the assigned pages for class. Chapter 3 Behavior Genetics: Predicting Individual Differences pp. 133 - 143 1. Explain the connection between DNA, genes, and chromosomes. How do these building blocks contribute to our understanding of human nature and behavior genetics? 2. Consider the two quotes in the column of pg. 135. What conclusion do you draw about animal and human genome research? 3. Explain the rationale for twin and adoption studies and discuss criticisms of them. Evolutionary Psychology: Understanding Human Nature pp. 143 – 149 4. How do evolutionary psychologists use natural selection to explain human behavior? How do they explain mutations? 5. What are some key criticisms of the evolutionary perspective in psychology? Parents and Peers pp. 149 – 152 6. After reading the scientific evidence for the impact of parents on their children, state your own perspective. How much credit (or blame) do you think parents deserve? Support your answer. Cultural Influences pp. 153 – 158 7. Identify and explain three examples of social norms. Gender Development pp. 159 - 169 8. Differentiate between gender and gender identity and explain two theories of gendertyping. Developing through the Life Span pg. 173 9. Identify and discuss the three major issues that developmental psychology centers on. Prenatal Development and the Newborn pp. 173 - 177 10. Outline the course of prenatal development. 11. Discuss the possible effects of teratogens on the developing embryo and fetus. 12. Describe the capacities of the newborn. Infancy and Childhood pp. 177 - 196 13. Describe brain development that occurs from infancy through childhood, including its impact on memory, and the role of experience. 14. Discuss Piaget’s view of how the mind develops and describe his cognitive stages. 15. Discuss the origins and effects of early attachment, and the roles of temperament and parenting on attachment throughout life. 16. Discuss how care giving, infant day care, and divorce influence attachment. 17. Explain how children’s behavior provides evidence of an emerging self-concept and discuss the possible effects of different parenting styles and culture on children. Adolescence pp. 196 - 206 18. Describe Kohlberg’s theory of moral development and its criticisms, and discuss the relationship of moral thinking to action. 19. Describe how Erikson viewed adolescence and the nature of social relationships during adolescence and explain adolescent’s changing relationships with parents and peers. Adulthood pp. 206 - 225 20. Identify the major physical changes that occur in middle adulthood and later life. 21. Describe the major cognitive changes that occur in adulthood and old age. 22. Compare and contrast cross-sectional and longitudinal studies. What are the pros and cons of using each to explain human development? 23. Discuss the importance of family and career commitments in adult development, and describe the sense of well being across the lifespan.







