Exercise 18 Revision on Optical Instrument(I)
advertisement

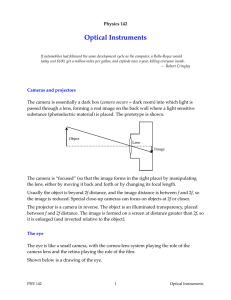
CK Cheung Revision on Optical Instrument (I) 95’ 16. An astronomical refracting telescope consists of A. 0.06 m two converging lenses of focal lengths 100 cm B. 0.69 m and 5 cm. Under normal adjustment, it is used C. 0.81 m to observe a distant object which subtends an D. 1.35 m angle of 0.2º when viewed directly. Which of E. 16.7 m the following statements is/are correct? 82’ (1) The lens with focal length 5 cm should be the 15. A near-sighted person’s greatest distance of objective. distinct vision is 0.9 m. His sight is improved (2) The height of the first image formed by the by telescope is 3.5 mm. wearing spectacles which increase his greatest distance of distinct vision to 18 m. (3) The angle subtended by the final image seen What is the magnitude of the focal length of the by the observer is 4º. spectacle lenses? A. (1) only A. 0.86 m. B. (3) only B. 0.90 m. C. (1) and (2) only C. 0.95 m. D. (2) and (3) only D. 17.1 m. E. (1), (2) and (3) E. 92’ 81’ 17. The sun subtends an angle of 0.5º at the surface 10. 18.9 m. of the Earth. A convex lens of focal length 100 15 cm cm is used to form an image of the sun onto a screen. The diameter of the image is about object A. 1 mm B. 3 mm C. 5 mm D. 9 mm A converging lens of focal length 15 cm is used 50 mm as a magnifying glass with the final image at E. infinity. If the least distance of distinct vision is 91’ 25 cm, the angular magnification achieved is 28. A simple two-convex lens refracting telescope has a magnifying power of 12.5 when the A. 0 telescope is in normal adjustment. B. 1 The C. 5/3 separation between the objective and the eye D. 15 The focal length of the objective is 0.75 m. piece is E. 1 infinite CK Cheung 94’IIB(2). (a) eyepiece objective lens object ho P Q Fo hi Fo FE FE final image Figure 2.1 A student uses two converging lenses to set up a compound microscope in normal adjustment. Figure 2.1 shows two light rays, P and Q, form the top of an object falling on the objective lens of the microscope. The foci of the objective lens are denoted by FO and the foci of the eyepiece are denoted by FE. (i) On Figure 2.1, complete the ray paths for P and Q as they pass through the microscope, showing how the final image is formed. (ii) (2 marks) Indicate on Figure 2.1 the visual angle subtended by the final image at the eye of an observer using the microscope. (iii) (1 mark) Distinguish between linear magnification and angular magnification. (2 marks) (iv) Find the angular magnification of the microscope in terms of the height of the object, ho, and the height of the final image, hi. Show your working. (Take the least distance of distinct vision to be D) (2 marks) (b) Figure 2.2 shows four light rays from an object passing through a microscope in normal adjustment. R and S come from the top of the object, T and U come from the bottom. R and T pass through the top of the objective lens, S and U pass through the bottom. R object T S U objective lens eyepiece X Figure 2.2 (i) On Figure 2.2, X is the best position for the eye to view the image. With reference to the ray diagram, briefly explain the advantage(s) of choosing X as the viewing position. (3 marks) (ii) Why should 2 mm? the diameter of the beam at 2 X be no wider than about (1 mark)