PHYSICS 203 Introduction to Astronomy Lab Lab 7: Optics and Telescopes
advertisement

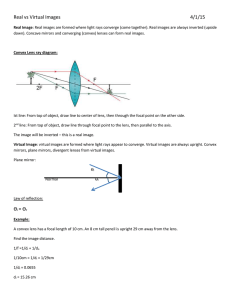
PHYSICS 203 Introduction to Astronomy Lab Lab 7: Optics and Telescopes Name________________ The focal length of a convex lens determines the position where an image is formed. In astronomical telescopes, the object to be viewed (star, planet, etc) is very far from the lens; roughly at infinity. In this case the image is formed at the focal point of the objective lens. As with all converging lenses when the object is far away, the image is smaller than the object and inverted. A second convex lens (the eyepiece) is positioned such that its focal point is just beyond the focal point of the objective lens. This lens takes the image from the objective and produces a virtual image that is larger than the image produced by the objective (see diagram). Thus, the focal length of the objective in a refracting telescope is of importance. 1. We will determine the focal length of a convex lens using the equation 1 = f 1 + d0 1 di where f is the focal length do is the distance from the lens to the object di is the distance between the lens and the image (note that if the object is at infinity the image occurs at the focal length) Set the lens some distance from the light source and move the screen until the image is as sharp as possible. Measure d0 and di and record those values. Repeat the process for two different distances between the light source and the lens. Note whether the image is larger or smaller than the arrow of the light source. For each set of numbers calculate the focal length using the equation above. do di focal length trial 1 trial 2 trial 3 ave. focal length ___________ 2. Now, look at the telescope. The length of the telescope will be the focal length. Magnification in a refracting telescope can be found as the ratio of the focal length of the objective to the focal length of the eyepiece (M = fo/fe). The maximum useful magnification depends of the aperture of the telescope and can be estimated by 2x per mm of aperture. (Note that shorter focal length eyepieces result in higher magnification) Focal length of telescope ______________cm Aperture of telescope _______________cm Maximum useful magnification _______________x Minimum useful focal length for eyepiece ___________cm Ray diagram for an astronomical telescope.