Introduction to Economics (4 weeks)
advertisement

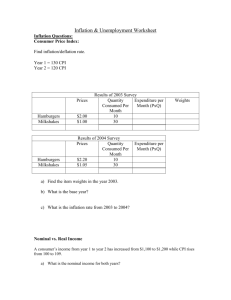
AP ECONOMICS Final Exam Review by Unit Final Exam Format: When: Importance: 60 multiple choice & 3 Free Response Questions 1st: Tuesday Dec 15th 2nd: Wednesday Dec 16th 25% of Grade UNIT #1 Introduction to Economics and Supply & Demand 5th: Thursday Dec. 17th Textbook Chapters: 1, 2 & 3 Topic I: Basic Economic Concepts: Economics, scarcity, trade-offs, opportunity cost, opportunity benefit, explicit costs, implicit costs, marginal cost, marginal benefit, property rights, incentives, Economic Systems, 3 basic questions, economic goals, Circular Flow of Economy, macroeconomics, microeconomics, externality, assumptions, “it depends”, long run, short run, efficiency, positive statement, normative statement Trade: Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF), Specialization, comparative advantage, absolute advantage, David Ricardo Textbook Chapter 4 Topic II: Supply & Demand Supply, Demand, Utility, Equilibrium, Determinants of Demand (TIPSEN), Determinants of Supply (TINE-TP) , Complements, Substitutes, normal good, inferior good, Invisible Hand, Price Ceilings, Price Floors, Surplus, Shortage, Change in Demand, Change in Quantity Demanded, Complements, Substitutes, Marginal Utility, Diminishing Marginal Utility, Intro questions: 1) Draw the Circular Flow of the Economy 2) What 3 questions must every economic system answer? 3) Draw a PPF curve and label points above, below & on the curve (constant cost PPF vs. increasing cost PPF) 4) What is the long run goal of an economy in regard to a PPF curve? 5) Why do countries trade? (absolute vs. comparative advantage) 6) How is trade mutually beneficial Supply & Demand Questions: 7) What is the difference between a change in quantity demanded & a change in demand 8) What causes the Demand Curve to shift? The Supply Curve? 9) When BOTH curves shift: when is the effect on price & quantity indeterminate 10) What do price ceilings above market equilibrium lead to? Below market equilibrium 11) Same thing for Price Floors… Key points: Know all the terms listed above Be prepared for Free Response questions on Free Trade and Supply/Demand curve shifts Understand Floors/Ceilings & shifting Supply/Demand Qty Food 10 . ---------- B ----------- 5 5 10 Qty Shelter UNIT #2 Measuring Economic Growth Topic I: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) & National Income Chapter 23 GDP, GDP deflator, Real GDP, Nominal GDP, What counts in GDP calculation, Final Goods, GDP = C + I + G + (X-M) Topic II: Inflation Chapter 24 Real vs. Nominal, Consumer Price Index (CPI), base year, market basket, cost-push inflation, demand-pull inflation Topic II: Unemployment & Business Cycle Chapter 28 Theory of Full Employment, 4-types of unemployment: seasonal, frictional, structural, cyclical, Business Cycle, Determinants of long run economic growth Make sure you: o o o o o o o o o o o Understand how to compute GDP from base year calculations What counts in GDP? What does not? GDP = C + I +G + NX What does GDP not measure (think Bhutan) Understand the difference between nominal & real interest rates Understand who is helped & hurt by inflation CPI vs. GDP deflator….(what counts in each one…) Understand 4-types of unemployment Why can’t the natural rate of unemployment fall to zero Understand how human/physical capital is critical to productivity Understand the Determinants of Long Run Economic Growth UNIT #3 Aggregate Demand & Supply Topic I: Aggregate Demand & Supply Chapter 33 (739-772) Aggregate Demand (AD), Aggregate Supply (AS), Long Run Aggregate Supply (LRAS), natural rate of output, stagflation, sticky-wages, sticky-prices, interest rate effect, wealth effect, exchange rate effect, Determinants of AD, Determinants of AS, 3 models of AS/AD: Keynesian, Classical & New Classical Topic II: Savings & Investment Chapter 26 (575-592) Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS), Marginal Propensity Consume (MPC), Autonomous Consumption, Savings Function, Dissaving, Loanable Funds market, Deficit, Debt, Crowding Out, Topic III: Fiscal Policy Chapter 34 (only pgs 787-797) Expansionary Fiscal Policy, Contractionary Fiscal Policy, Money Multiplier, Crowding Out, Supply Side Topic IV: Short Run Trade Offs: Inflation & Unemployment Chapter 35 (801-825) Short-Run Phillips Curve, Long-Run Phillips Curve, Supply Shock LRAS1 Price Level SRAS1 Real Interest Rate -------------- ------------- R1 S1 AD1 Real GDP 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) E1 Q1 D1 Qty Loanable Funds Explain why the SRAS is upward sloping & the LRAS is vertical Explain why the AD is downward sloping. What shifts both the LRAS & SRAS What only shifts the SRAS What is the loanable funds market? (sum of private & public savings) Explain the difference between a government deficit and a government debt. a. b. Which is more dangerous What are the current levels in the USA today 7) Why does Savings = Investment in a closed economy (T = Taxes) • Y=C+I+G • National saving: income left after paying for consumption & government purchases: Y– C–G=I • So, S=I (savings = investment) • Public Savings = T – G • Private Savings = Y – T - C Inflation Rate Inflation Rate (percent per year) B 6 A 2 Long-run Phillips curve High inflation B Low inflation A 2. . . . but unemployment remains at its natural rate in the long run. Phillips curve 0 4 7 Unemployment Rate (percent) 0 Natural rate of unemployment Unemployment Rate UNIT #4 Money & Monetary Policy Terms by Chapter: Topic I: Money Growth & Inflation Chapter 29 (641-658) Federal Reserve, money, medium of exchange, unit of account, store of value, liquidity, fiat money, currency, demand deposits, central bank, money supply, required reserves, excess reserves, fractional-reserve banking, money multiplier, open market operations, reserve requirements, discount rate, reserve ratio, M1, M2, M3, federal funds rate, T-account, assets, liabilities Topic II Monetary Policy Chapter 34 (only pages 777-786) Expansionary Monetary Policy, Contractionary Monetary Policy, Quantity Theory of Money, Theory of liquidity preference, Milton Friedman, Money Market Model, Topic II: Money Growth & Inflation Chapter 30 (661-685) Monetary neutrality, velocity of money, equation of exchange MV = PQ, inflation tax, Fisher effect, nominal interest rates, real interest rates, quantity theory of money What you need to be successful: Nominal Interest Rate i2 Understand & be able to draw the AD/AS model Understand & be able to draw the Money Market Model Understand what a Fractional Reserve Banking System is and how this leads to money creation o T-account calculations Understand the 3-functions of Money Understand the components of M1, M2, & M3 Understand the money multiplier theory Understand the 2-conflicting goals of monetary policy Understand the 3-tools of monetary policy & how the Fed implements each tool Understand the equation MV = PQ & the quantity theory of money Understand the difference between nominal & real interest rates MS2 --------MD Qty of $ UNIT #5 International Economics Topic I: International Economies Chapter 31 (pages 691-713) Open Economy, Closed Economy, Current Account, Capital Account, Official Reserves, Net Capital Outflow, Exchange Rates, Purchasing Power Parity, Trade Deficit, Trade Surplus, appreciation, depreciation, NX = NCO 1) 2) 3) 4) What is included in the current account? What is included in the capital account? In theory, why must they equal How can an open economy all the U.S. to consume more than it produces? a. recall that in a closed economy this would not be possible: Savings = Investment 5) Market for exchange rates: a. Think of the market below as located in the middle of the ocean b. You must go to the “House of Money” to get (demand) currency or to give (supply) c. Someone living in France would Supply Euros if they needed (demanded) dollars S1 Dollar Price of a Euro -------------- -------------- 1.3 Dollars Q1 D1 Qty of Euros • Y = C + I + G + NX • National saving: income left after paying for consumption & government purchases: Y – C – G = I + NX • So, • Then: S = I + NX S = I + NCO • Savings = Id + If (d= domestic f = foreign)