Lecture Eight The Subjunctive Mood
advertisement

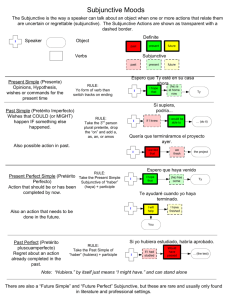
Lecture Eight The Subjunctive Mood Teaching hours: 2 Teaching aims: 1. Students can understand the structure and formation of subjunctive mood. 2. Students can comprehend the meaning in the subjunctive mood sentence. Key points of teaching: types of subjunctive mood and their presentations; the basic verb forms of the subjunctive mood Time allotment: the basic concepts of mood(10ms): types of subjunctive mood and their presentations(50ms). the basic verb forms of the subjunctive mood(20ms). homework assignment(20ms). Teaching contents: I. Lead-in It is possible that Lincoln might not have been as angered as he was by the proposal if it had not been made by Stephen A. Douglas, the senior Senator from Lincoln’s own states — Illinois. (but the fact is that proposal was made Stephen A. Douglas, the senior Senator from Lincoln's own states — Illinois so Lincoln was greatly angered.) If I hadn’t been defeated, I probably never would have become President. I used to joke with Hillary that if my father hadn’t lost his life on that rainy Missouri highway, I would have grown up a few miles from her and we probably never would have met. It made me laugh to think how happy the Republicans would have been if they could have seen their party’s mascot watering me (an elephant). If these men had rowed Andre back that night, perhaps the traitorous plot would never have been discovered and West Point and George Washington would have fallen into the hands of the enemy. Mr. Powell now says he might not have recommended attacking Iraq had he known there were no weapons stockpiles. Some say Mr. Gore would have won the election if Ralph Nadir had not been a candidate. Before Abraham Lincoln was elected president, his rival, Stephen A. Douglas said that Lincoln was two-faced,Lincoln replied: If I were two-faced, would I be wearing this one? 幽默注释:美国总统林肯(Abraham Lincoln)长得比较丑,他幽默地嘲笑自己长得不好看。 It’s important that our Judiciary be full. (George W. Bush, President of the U.S. A. 2002-05-09) For instance, in the TOEFL test of November 2000, one example in the section of listening comprehension is as follows: I wish that the professor were in his office. Question: What is the problem with the speaker? (The correct answer is that she couldn't find the professor in his office.) I wish I were an Oscar Mayer wiener. That is what I'd really like to be. 'Cause if I were an Oscar Mayer wiener, everyone would be in love with me. (Advertisement, 1930s) II. Introduction Question: What is subjunctive mood? It is a form of verb used to express doubts, desires, and conditions contrary to fact. It has a present and past form. The present form is identical to the base form of the verb, so you only notice it in the third person singular, which has no final -s, and in the case of the verb be, which has the form be instead of am, is, and are. The past subjunctive is identical with the past tense except in the case of the verb be, which uses were for all persons: If I were rich …, If he were rich …, If they were rich…. The terms present subjunctive and past subjunctive can be misleading, as they describe forms rather than meanings: the past and present subjunctives are so called because they resemble the past and present indicatives, respectively, but the difference between them is a modal one, not a temporal one. For example, in “I asked that it be done yesterday,” be done (a present subjunctive) has no present-tense sense; and likewise, in "If that were true, I'd know it," were (a past subjunctive) has no past-tense sense. Question: When is the subjunctive used? The subjunctive mood is used in these instances: 1. In “if” clauses to express condition contrary to fact. Examples: If I were a rich man... Were he alive, he would be proud of his son. 2. In “that” clauses expressing a wish, request, recommendation or command. Examples: The president requested that the emissary be treated fairly. The attorney general demanded that the Congress come to a decision immediately. The committee recommended that the rules be changed. 3. In set phrases expressing a wish, hope, prayer, request or recommendation. Examples: when someone sneezes, we say, “God bless you,” Heaven help the working woman. Long live the Queen! Long live the bride and groom! III. Types of subjunctive There are two forms of the subjunctive: be-subjunctive and were-subjunctive. The present lecture will dwell on the uses of these two subjunctive forms-remnants of Old English-expressing hypothetical and non-factual meanings. 1. BE-subjunctive The be-subjunctive,like the imperative,is realized by the base form of the verb.Whatever the person of the subject,the predicator invariably takes the base form.Consequently,where the clause has a plural subject,there is normally no distinction between indicative and subjunctive forms,except for the verb be.The subjunctive form of be is be for all persons.The be-subjunctive is used: 1)In certain that-clause The be-subjunctive is commonly used in that-clauses to express a command, decision, suggestion, etc. These that-clauses usually occur: a) after such verbs as decide, decree, demand, insist, move, order, prefer, propose, recommend, request, require, suggest, vote, etc, eg: He ordered that all the books be sent at once. We propose that somebody neutral take the chair. b) after such adjective as advisable, appropriate, desirable, essential, fitting, imperative, important, impossible, necessary, obligatory, proper, etc,egg: It is essential that al!the facts be examined first. It is necessary that he come back without delay. c) after such nouns as decision, decree, demand, instruction, order, requirement, resolution, etc, eg: The board has given instructions that the agent fly to Boston. We were faced with the demand that this tax be abolished. This use of the be-subjunctive is quite common in formal style, especially in American English. This subjunctive form can sometimes be replaced by "should + infinitive" or to-infinitive, eg, He ordered that the books be sent at once. =He ordered that the books should be sent at once. =He ordered the books to be sent at once. 2)In certain adverbial clauses The be-subjunctive is also used in adverbial clauses introduced by if, though, whatever, so long as, whether, lest, etc. eg: If the rumour be true,everything is possible. Quietly we sat on the river bank lest the fish swim away. Whatever be his defense,we cannot tolerate his disloyalty. This-use of the be-subjunctive is limited to formal, while in informal style the indicative mood or “should/may+ infinitive” are used instead. Compare: If tile rumour is true,everything is possible. He hid himself in the bush lest he should be seen. Whatever his defense may be,we can't tolerate his disloyalty. 3)In certain formulaic expressions The be-subjunctive is also used in some formulaic expressions to express a wish,prayer,curse, etc.The formulaic use of the be-subjunctive tends to be formal and old-fashioned in style, eg: Long live the People's Republic of China! God bless you! So be it. Far be it from me to spoil the fun. 2. WERE-subjunctive The were-subjunctive has only one form were, which applies to subjects of - all persons, but which formally contrasts with the indicative form was only when it is used with first and third person singular subjects. The were-subjunctive is hypothetical or unreal in meaning and is-used: 1) In certain adverbial clauses The were-subjunctive is-commonly used in adverbial clauses introduced by if, if only, as if, as though, etc to denote an unreal condition or concession, eg: If I were you, t should wait till next week. If only I were not so nervous. He behaves as though he were better than us. Though the whole world were against me, I would do what I consider as right. 2) In certain nominal clauses The were-subjunctive is also used in nominal clauses after verbs like wish would rather, suppose, imagine, etc to denote a hypothetical situation, eg: I wish it were spring all the year round. I'd rather I were not at the site of the accident. Suppose the earth were flat. It must be noted that in present-day English, the were-subjunctive with first and third person subjects is often replaced by the indicative was in less formal style. Compare: I wish it was spring all tile year round. I'd rather I wasn’t at the site of tile accident. The were-subjunctive is obligatory, however, in the set expressions "as it were" (= so to speak) and "if I were you", as well as in non-introduced conditional clauses with inverted word order, eg: He is my best friend. my second self, as it were. Were I to do it, I should rely on you. 3. Some few notes on ways of expressing hypothetical meanings Modern English has a number of devices for expressing hypothetical meanings. In addition to the be-subjunctive and the were-subjunctive, we can use past tense forms of verbs and past tense modals for the same purpose. 1) Use of past tense forms of verbs The past tense forms of verbs are usually used to express hypothesis in the following contexts. a) It is time (that)...: It is time (that) we left this place. It is high time (that) you made up your mind. b) I would rather (that) you / lie ... I'm sure lie is keeping something back: I'd rather lie told me the truth. They offered me this expensive wine, but frankly I'd rather they had offered me some. beer. c) If only …: . If only 1 knew her address. If only she had listened to my advice. d) ... as if / as though ... : He behaves as if lie owned this place. The woman talked eloquently about the accident as though she lout witnessed the whole thing. They are staring at me as if I was / were crazy. e) I wish (that)...: I wish the sun was shining at this moment. I wish I hadn't eaten so much last night. 2) Use of past tense modals The past tense modals are commonly used to express hypothesis in the following contexts. a) In conditionals: If I were you l would not miss this opportunity. If he be found guilty lie is-ould be sent to prison. If she had been invited,she would have attended the meeting. If they had caught the early train,they would have been here by now. if you should change your mind,do let me know. If lie should refuse to appear in court,he might be held guilty. b) In implied conditionals: But for his help,I couldn't have achieved anything. Anyone who should do that would be laughed at. In different circumstances,I might have agreed. This same tiling happening in wartime would amount to disaster. c)In other contexts: That she should forget me so quickly was rather a shock. That I should see a college student arrested for stealing! oh that I could sec him again! =I wish that I could see him again· Would that she could see her son now! =If only she could see her son now! Would that the flood might never come again! To think that he would marry such a nasty woman! To think that he should have deserted his wife and children! Who would have thought that things should come to such a tragic end? Who would have thought that the man living next door should be a hidden terrorist? The door was pushed open;who should come in but the woman they were talking about. He stepped into a cave and what should lie sec but a tigress with her baby tigers. IV. 1. Present subjunctive Present subjunctive is used in a such a clause introduced by a verb like propose, suggest, recommend, or demand, by an adjective like imperative, important, adamant, or necessary, or by a noun like insistence or proposal. 1) Verbs used with the subjunctive Verbs that are commonly used with the Simple Present Subjunctive are: advise, ask, beg, decide, decree, desire, dictate, insist, intend, move, order, petition, propose, recommend, request, require, resolve, suggest, urge, and vote. e.g. The manager insisted that he finish the work. I propose that we take a break. 2) Nouns used with the subjunctive There are also nouns that can be used in the same way: advice, condition, demand, directive, intention, order, proposal, recommendation, request, suggestion, and wish. e.g. My advice is that we leave at once. His deep wish is that his daughter go to university. I make a proposal that we (should) hold a meeting next week. 3) Adjectives used with the subjunctive Some adjectives can be used with the Simple Present Subjunctive in the following construction: It is advisable/desirable/essential/important/imperative/necessary/urgent/vital + that It is essential that you be present. e.g. It is necessary that everyone leave now. It was necessary that we (should) make everything ready ahead of time. It is required that nobody (should) smoke here. 2. Past subjunctive When 'if clauses' describe an unreal or hypothetical situation, the subjunctive mood is used with would, could, might, or should in the main clause and were in the dependent clause. 1) Forms of the verb used in the main clause When a sentence contains a condition which is considered false or improbable, the verb in the main clause is usually in the Simple or Perfect conjugation with the auxiliary would. a. Referring to present or future time In a sentence containing a false or improbable condition, if the main clause refers to present or future time, the Simple conjugation with the auxiliary would is usually used. e.g. If he were ready, I would accompany him. If she came, I would lend her my bicycle. If I didn’t love you, I wouldn’t want to be with you. In these examples, the use of the Simple conjugation with would indicates that the main clauses “I would accompany him” and “I would lend her my bicycle” refer to present or future time. In the case of a continuous, ongoing action, the Continuous conjugation with would may be used. e.g. If they were here, he would be speaking to them now. If they arrived tomorrow, he would be giving them a tour of the city. b. Referring to past time In a sentence containing a false or improbable condition, if the main clause refers to past time, the Perfect conjugation with the auxiliary would is usually used. e.g. If it had snowed, I would have skied in the park. In this example, the use of the Perfect conjugation with would indicates that the main clause I would have skied in the park refers to past time. The use of the Perfect conjugation with would, combined with the use of the Past Perfect in the subordinate clause, indicates that the condition it had snowed is false, and that the action of skiing did not take place. In the case of a continuous, ongoing action, the Perfect Continuous conjugation with would may be used. e.g. If they had been here, he would have been speaking to them. 2) Forms of the verb used in the subordinate clause a. Referring to present or future time In a sentence containing a false or improbable condition, if the subordinate clause refers to present or future time, the Simple Past Subjunctive is usually used. e.g. If it snowed, I would ski in the park. If he were here, I would give him the books. In these examples, the use of the Simple Past Subjunctive indicates that the subordinate clauses if it snowed and if he were here refer to present or future time. In the case of a continuous, ongoing action, the Past Continuous Subjunctive may be used. If she were staying here now, I would let her ride my horse. snowed If it were to snow tomorrow, I should (would) stay at home. should b. Referring to past time In a sentence containing a false or improbable condition, if the subordinate clause refers to past time, the Past Perfect Subjunctive is usually used. e.g. If he had wanted to come, he would have called us. c. Omission of “If” Sometimes the word if is omitted from a subordinate clause expressing a condition. When the word if is omitted, the verb (in the case of the Simple tenses of to be), or the first auxiliary, must be placed before the subject. The following pairs of sentences illustrate the change in word order which occurs when the word if is omitted from a clause expressing a condition. e.g. If I were braver, I would challenge him. Were I braver, I would challenge him. Were they to get married, they would be happy. If I had not received your message, I would have left. Had I not received your message, I would have left. Should I have time, I would call on her. d. Clauses after “wish” Wishes for the past When the subordinate clause refers to an earlier time than the main clause, the Past Perfect Subjunctive is usually used in the subordinate clause. e.g. I wish you had called earlier. They will wish they had listened to us sooner. The perfect conjugation with could can be used too in this situation. e.g. I wish I could have helped you yesterday. In the case of a continuous, ongoing action, the Past Perfect Continuous Subjunctive may be used instead of the Past Perfect Subjunctive. e.g. She wishes she had been staying with us last week. Wishes for the present When the subordinate clause refers to the same time as the main clause, the Simple Past Subjunctive is usually used in the subordinate clause. e.g. I wish I didn't love you so much. (From the movie, Casablanca, 1942) She wishes her boyfriend were here. When she was at the party, she wished she were at home. Now that he is in China, he wishes he understood Chinese. The simple conjugation with could also works here. e.g. I wish I could help you now. In the case of a continuous, ongoing action, the Past Continuous Subjunctive may be used instead of the Simple Past Subjunctive. e.g. They wish they were traveling now. Wishes for the future When the subordinate clause refers to a later time than the main clause, the Simple conjugation with the auxiliary would and could are usually used in the subordinate clause. e.g. You wished she would arrive the next day. I wish she could change her mind. He will wish we would join him the following week. 3. Other Usage of Subjunctive Mood a. In the adverbial clauses led by “as if/ though”: Some degree of conjecture (after verbs like act, behave, talk, look ) that may be followed by as if/ as though in clauses of manner. The Simple Past Subjunctive and the Past Perfect Subjunctive are usually used in the subordinate clauses. She behaves as if/though she were the Queen. (She obviously isn't the Queen) He walks as if/though he were an old man. (But in fact he's a young man) They talk as if/though the world were coming to an end. (Of course it's not) He looks as if/though he's sick. (He is sick) He talks as if/though he were sick. (But actually he's well) b. In the sentence type “It is (about, high) time that…”: It is time we went to bed. c. In the sentence type “If only…” For representing wishes, imaginary future situations, willingness, regrets and blame for past events. If only she would marry me. If only I were young again. If only I had followed your advice then. d. In the object clauses following “would rather, would prefer, had rather, would just as soon…” I would rather that you posted the letter. (indicating the present time) I had hoped that she would go to the U.S. and study there, but she said she liked to stay in China. e. In the clause after for fear that, in order that, so that, in case that, lest to express purposes: I reminded her twice of it lest she should forget. I will not make a noise for fear that I should disturb him. He put his coat over his son in case he should catch cold. 4. Implied subjunctive a. Prepositional phrases introduced by with, without, under, but for: Plants would die without water on the earth. But for the fog, we would have reached our destination long ago. Under more favorable conditions we could have finished the task. b. In the clauses introduced by or, but, otherwise: Seize the chance, otherwise you would regret it. c. Infinitives: It would be a mistake not to help him. He would be stupid not to accept that offer. d. Participles: This same thing, happening in wartime, would amount to disaster. e. Attributive and adverbial clauses: Anyone who had married such a girl as she would have been regretful. Help was promised where it should become necessary. f. After suppose, imagine, what if: Imagine that we were on a desolate island now. Suppose you had not taken those measures, what would have happened? What if you came tomorrow instead of today? Negative, Continuous and Passive Forms of Subjunctive The subjunctive can be used in negative, continuous and passive forms. Negative Examples: The boss insisted that Sam not be at the meeting. The company asked that employees not accept personal phone calls during business hours. I suggest that you not take the job without renegotiating the salary. Passive Examples: Jake recommended that Susan be hired immediately. Christine demanded that I be allowed to take part in the negotiations. We suggested that you be admitted to the organization. Continuous Examples: It is important that you be standing there when he gets off the plane. It is crucial that a car be waiting for the boss when the meeting is over. I propose that we all be waiting in Tim's apartment when he gets home. Assignments: 1. Read Chapter 16.. 2. Do the exercises after the chapter. If I Were a Rich Man [TEVYE] "Dear God, you made many, many poor people. I realize, of course, that it's no shame to be poor. But it's no great honor either! So, what would have been so terrible if I had a small fortune?" If I were a rich man, Ya ha deedle deedle, bubba bubba deedle deedle dum. All day long I'd biddy biddy bum. If I were a wealthy man. I wouldn't have to work hard. Ya ha deedle deedle, bubba bubba deedle deedle dum. If I were a biddy biddy rich, Yidle-diddle-didle-didle man. I'd build a big tall house with rooms by the dozen, Right in the middle of the town. A fine tin roof with real wooden floors below. There would be one long staircase just going up, And one even longer coming down, And one more leading nowhere, just for show. I'd fill my yard with chicks and turkeys and geese and ducks For the town to see and hear. (Insert)Squawking just as noisily as they can. (End Insert) And each loud "cheep" and "swaqwk" and "honk" and "quack" Would land like a trumpet on the ear, As if to say "Here lives a wealthy man." If I were a rich man, Ya ha deedle deedle, bubba bubba deedle deedle dum. All day long I'd biddy biddy bum. If I were a wealthy man. I wouldn't have to work hard. Ya ha deedle deedle, bubba bubba deedle deedle dum. If I were a biddy biddy rich, Yidle-diddle-didle-didle man. I see my wife, my Golde, looking like a rich man's wife With a proper double-chin. Supervising meals to her heart's delight. I see her putting on airs and strutting like a peacock. Oy, what a happy mood she's in. Screaming at the servants, day and night. The most important men in town would come to fawn on me! They would ask me to advise them, Like a Solomon the Wise. "If you please, Reb Tevye..." "Pardon me, Reb Tevye..." Posing problems that would cross a rabbi's eyes! And it won't make one bit of difference if i answer right or wrong. When you're rich, they think you really know! If I were rich, I'd have the time that I lack To sit in the synagogue and pray. And maybe have a seat by the Eastern wall. And I'd discuss the holy books with the learned men, several hours every day. That would be the sweetest thing of all. If I were a rich man, Ya ha deedle deedle, bubba bubba deedle deedle dum. All day long I'd biddy biddy bum. If I were a wealthy man. I wouldn't have to work hard. Ya ha deedle deedle, bubba bubba deedle deedle dum. (Delete)If I were a biddy biddy rich, Yidle-diddle-didle-didle man. (End Delete) (Insert) Lord who mad ethe lion and the lamb, You decreed I should be what I am. Would it spoil some vast eternal plan? If I were a wealthy man. (End Insert, End Song)