Trigonometry Test: Chapter 4 - High School Math
advertisement
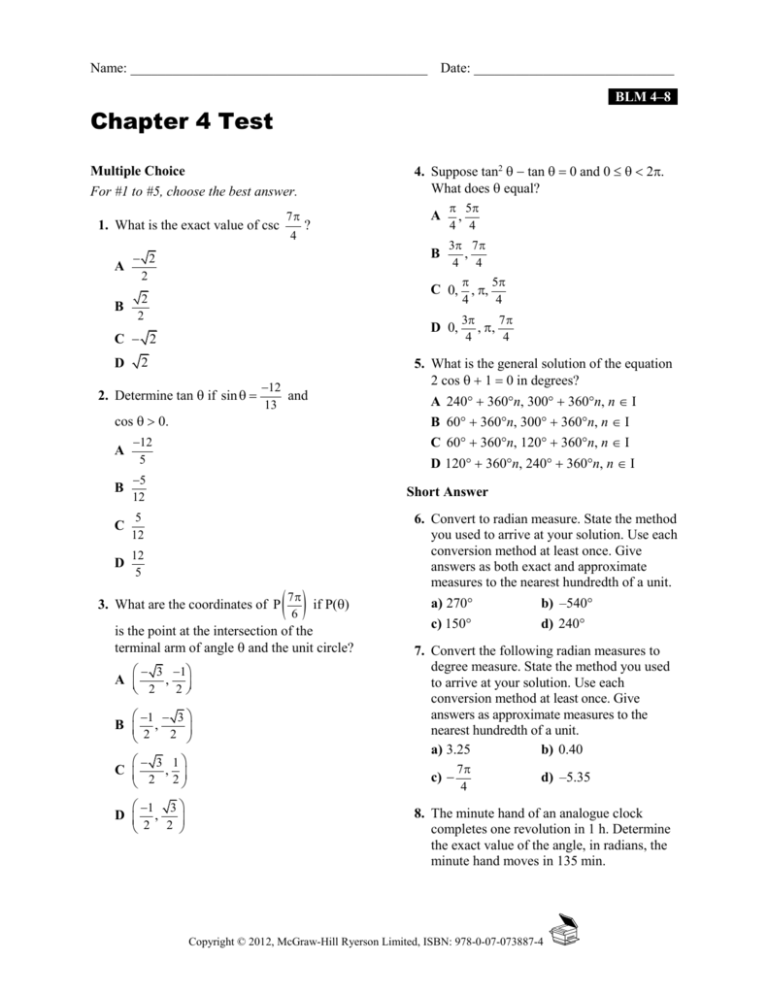
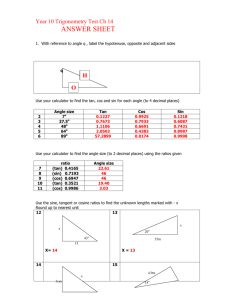
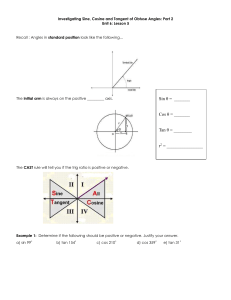
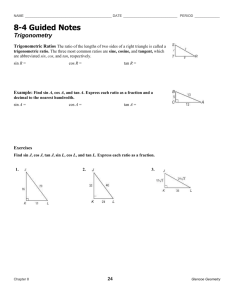
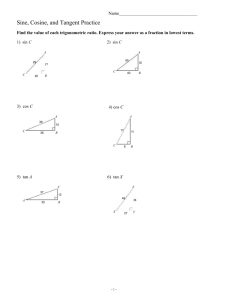
Name: ___________________________________________ Date: _____________________________ BLM 4–8 Chapter 4 Test 4. Suppose tan2 tan 0 and 0 2. What does equal? Multiple Choice For #1 to #5, choose the best answer. 1. What is the exact value of csc 7 4 ? 2 A 2 B 12 and 13 cos 0. B 5 12 C 5 12 D 12 5 if P() 7 6 is the point at the intersection of the terminal arm of angle and the unit circle? 3 1 , A 2 2 1 3 B , 2 2 1 3 D , 2 2 5 4 3 7 , , 4 4 5. What is the general solution of the equation 2 cos 1 0 in degrees? A 240 360n, 300 360n, n I B 60 360n, 300 360n, n I C 60 360n, 120 360n, n I D 120 360n, 240 360n, n I Short Answer 3. What are the coordinates of P 3 1 , C 2 2 3 7 , 4 4 D 0, 2. Determine tan if sin 12 5 B 4 2 A 5 , 4 4 C 0, , , 2 2 C 2 D A 6. Convert to radian measure. State the method you used to arrive at your solution. Use each conversion method at least once. Give answers as both exact and approximate measures to the nearest hundredth of a unit. a) 270 b) –540 c) 150 d) 240 7. Convert the following radian measures to degree measure. State the method you used to arrive at your solution. Use each conversion method at least once. Give answers as approximate measures to the nearest hundredth of a unit. a) 3.25 b) 0.40 c) 7 4 d) –5.35 8. The minute hand of an analogue clock completes one revolution in 1 h. Determine the exact value of the angle, in radians, the minute hand moves in 135 min. Copyright © 2012, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, ISBN: 978-0-07-073887-4 Name: ___________________________________________ Date: _____________________________ BLM 4–8 (continued) 9. Use the information in each diagram to determine the value of the variable. Give your answers to the nearest hundredth of a unit. a) 10. Determine the exact value of sin 2 2 cos (120) tan . 5 6 7 4 11. Given that sin 0.3 and cos 0.5, determine the value of tan to the nearest tenth. 12. If sin 3 , determine all possible 2 coordinates of P() where the terminal arm of intersects the unit circle. b) 3 1 13. If P() = , , what are the 2 2 ? coordinates of P 2 Extended Response 14. Consider an angle of c) 4 radians. 5 a) Draw the angle in standard position. b) Write a statement defining all angles that are coterminal with this angle. 15. The point (3a, 4a) is on the terminal arm of an angle in standard position. State the exact value of the six trigonometric ratios. 16. Solve the equation sec2 2 0, . d) 17. Consider the following trigonometric equations. A 2 sin 3 0 B 2 cos 1 0 C 2 2 sin cos 2 sin 6 cos 3 0 a) Solve equations A and B over the domain 0 . b) Explain how you can use equations A and B to solve equation C, 0 . Copyright © 2012, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, ISBN: 978-0-07-073887-4 c) Example: unit analysis; 315° d) Example proportion method; 306.53° Chapter 4 Test Answers 1. C 2. A 3. A 4. C 5. D 6. a) Example: unitary method; 8. 9 2 9. a) 133.69 or 2.33 b) a 31.85 cm c) r 6.99 m d) a 4.28 ft 3 ; 4.71 2 b) Example: proportion method; 3; 9.42 5 ; 2.62 6 4 d) Example: unitary method; ; 4.19 3 c) Example: unit analysis; 7. a) Example: proportion method; 186.21° b) Example: unitary method; 22.92° 10. 3 4 11. 0.6 1 3 1 3 12. , , , 2 2 2 2 1 3 13. , 2 2 BLM 4–9 (continued) 14. a) 4 2n, n I 5 15. sin 4 , cos 3 , tan 4 , 5 3 5 5 5 3 csc , sec , cot 3 4 4 16. , 4 4 2 17. a) Equation A: , ; Equation B: 3 3 4 b) b) Equation C is the product of Equation A times Equation B (i.e., AB C). Therefore, the solution to Equation C is the solutions to A and B: 2 , , . 4 3 3 Copyright © 2012, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, ISBN: 978-0-07-073887-4