AP Biology
advertisement
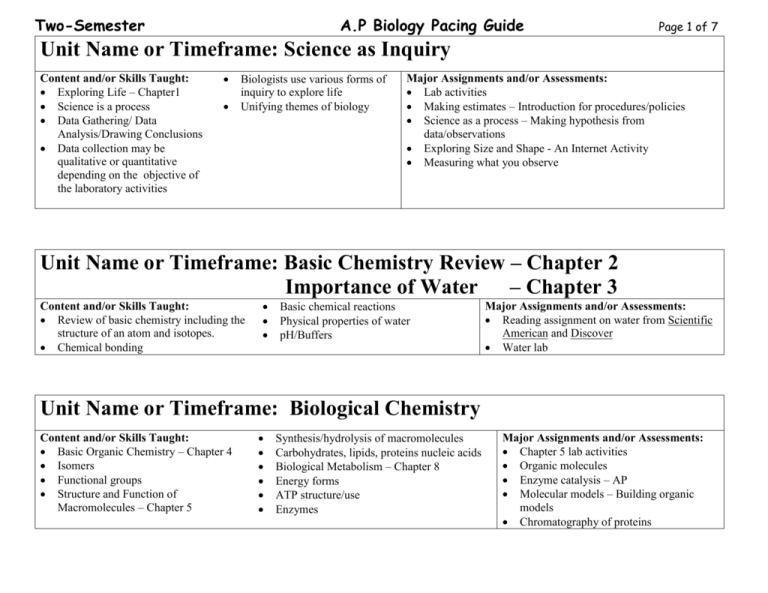
Two-Semester A.P Biology Pacing Guide Page 1 of 7 Unit Name or Timeframe: Science as Inquiry Content and/or Skills Taught: Exploring Life – Chapter1 Science is a process Data Gathering/ Data Analysis/Drawing Conclusions Data collection may be qualitative or quantitative depending on the objective of the laboratory activities Biologists use various forms of inquiry to explore life Unifying themes of biology Major Assignments and/or Assessments: Lab activities Making estimates – Introduction for procedures/policies Science as a process – Making hypothesis from data/observations Exploring Size and Shape - An Internet Activity Measuring what you observe Unit Name or Timeframe: Basic Chemistry Review – Chapter 2 Importance of Water – Chapter 3 Content and/or Skills Taught: Review of basic chemistry including the structure of an atom and isotopes. Chemical bonding Basic chemical reactions Physical properties of water pH/Buffers Major Assignments and/or Assessments: Reading assignment on water from Scientific American and Discover Water lab Unit Name or Timeframe: Biological Chemistry Content and/or Skills Taught: Basic Organic Chemistry – Chapter 4 Isomers Functional groups Structure and Function of Macromolecules – Chapter 5 Synthesis/hydrolysis of macromolecules Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins nucleic acids Biological Metabolism – Chapter 8 Energy forms ATP structure/use Enzymes Major Assignments and/or Assessments: Chapter 5 lab activities Organic molecules Enzyme catalysis – AP Molecular models – Building organic models Chromatography of proteins Two-Semester A.P Biology Pacing Guide Page 2 of 7 Unit Name or Timeframe: Cells/ Cell Structure Content and/or Skills Taught: Tour of the Cell – Chapter 6 Prokaryotic/eukaryotic Cellular organelles – Structure and function Plant/animal cell differences Membranes – Chapter 7 Structure of and movement across including passive/active transport Major Assignments and/or Assessments: Lab activities Cells and the microscope Cells and their membranes Cellular organelles Cell structure and function Diffusion and osmosis – AP Unit Name or Timeframe: Energy Transformations Content and/or Skills Taught: Photosynthesis – Chapter 10 General process, chloroplast structure, redox in biological systems Light dependent/light independent reactions, Calvin cycle C3/C4 plants Cellular respiration – Chapter 9 Glycolysis, citric acid cycle, oxidative, phosphorylation, chemiosmosis Fermentation Major Assignments and/or Assessments: Lab activities Plant pigments and photosynthesis- AP Leaf anatomy Fermentation Cell Respiration - AP Unit Name or Timeframe: Cell Cycle Content and/or Skills Taught: The Cell Cycle - Chapter 12 Chromosome structure Cell division and production of genetically identical daughter cells Mitosis Phases Molecular control, cancer Meiosis and the Sexual life cycle – Chapter 13 Fertilization and meiosis Meiosis and reduction division Stages of Meiosis Comparing mitosis/meiosis Crossing over/ independent assortment/ random fertilization Major Assignments and/or Assessments: Lab activities Mitosis and meiosis - AP Two-Semester A.P Biology Pacing Guide Page 3 of 7 Unit Name or Timeframe: Mendel and the Gene Content and/or Skills Taught: Mendel and the Gene Idea – Chapter 14 Mendel’s experimental approach Development of Mendel’s Three Laws of Inheritance Dominance, segregation and independent assortment Testcross Laws of Probability Inheritance patterns Incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, pleiotropy, epistasis Polygenic inheritance Pedigree analysis The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance – Chapter 15 Morgan and Drosophila Linked genes and recombination Gene mapping Sex linked inheritance X and Y chromosomes Alteration of chromosome number Major Assignments and/or Assessments: Lab activities Mendelian Genetics: A Monohybrid Cross with Bean Seeds Human genetic traits Genetics of drosophila Unit Name or Timeframe: Molecular Genetics Content and/or Skills Taught: Molecular Basis of Genetic Inheritance – Chapter 16 Evidence for DNA as the genetic material Basic DNA/RNA structure Model development with Watson and Crick DNA replication Proofreading and repair From Gene to Protein – Chapter 17 Molecular dogma Genetic code Transcription M-RNA splicing and processing Translation t-RNA structure and ribosome Building a polypeptide/ stages of Types of mutations Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria – Chapter 18 Viral structure Reproductive cycles: Lysogenic vs. Lytic RNA as the genetic material/ Reverse transcription Bacterial structure Nucleoid region/ plasmids Methods of reproduction Transduction, conjugation, transformation Transposons Gene expression and the operon Inducible and repressible Eukaryotic Genomes: Organization, Regulation and Evolution – Chapter 19 Chromatin structure and DNA packing Histones and nuclesome structure and methylation Levels of control DNA Technology and Genomics – Chapter 20 DNA cloning Restriction enzymes Gene libraries and DNA and hybridization Gene amplification (PCR) RFLP analysis with gel electrophoresis DNA sequencing and functioning (RNAi) Comparing gene sequences of different organisms Application of DNA technology: medical, pharmaceutical, forensic, environmental and agricultural Ethics of genetic engineering Major Assignments and/or Assessments: Lab activities DNA Structure: Simulation of Bacterial Genome Protein synthesis DNA isolation Molecular biology – AP ‘CATS’ lab CIBT Bacterial Transformation– BioRad Two-Semester A.P Biology Pacing Guide Page 4 of 7 Unit Name or Timeframe: Evolution Content and/or Skills Taught: Descent with Modification: A Darwinian Perspective – Chapter 22 Before Darwin Origin of Species Descent with modification Natural selection and adaptation Homologies Biogeography Content and/or Skills Taught The Evolution of Populations – Chapter 23 Population genetics Gene pools and allele frequencies Hardy-Weinberg Theorem Mutation and sexual recombination Content and/or Skills Taught Genetic drift and gene flow Bottleneck and Founder effect Adaptive evolution The Origin of Species - Chapter 24 Biological species concept Allopatric and sympatric speciation Adaptive radiation Macroevolution Major Assignments and/or Assessments: Lab activities Population genetics and evolution – AP Population dynamics Unit Name or Timeframe: Taxonomy and the Three Domains (Five Kingdoms) Content and/or Skills Taught: • Phylogeny and Systematics– Chapter 25 • Phylogenies based on common ancestors inferred from fossil, morphological and molecular evidence • Systematics and evolutionary history • Binomial nomenclature • Cladistics • Molecular clocks and evolutionary time • Introduction to Biological Diversity Chapter 26 • Origins of early life • Synthesis of organic compounds • Extraterrestrial sources of organic compounds • Abiotic synthesis of polymers • Protobionts • The “RNA” world (ribozymes) • Fossil dating • Rocks and organic material • Geologic record • Prokaryotic evolution • Eukaryotic evolution Endosymbiosis Multicellularity an the colonization of land Continental drift Prokaryotes – Chapter 27 Symbiosis Protists – Chapter 28 Fungi –Chapter 31 Heterotrophic nutrition Decomposers Lichens Major Assignments and/or Assessments: Lab activities Cladogram: A Molecular Connection Two-Semester A.P Biology Pacing Guide Page 5 of 7 Unit Name or Timeframe: Plants Content and/or Skills Taught: How Plants Colonized the Land – Chapter 29 Evolution from green algae Derived terrestrial adaptations Apical meristems, alternation of generations, walled spores, multicellular gametangia, multi-cellular dependent embryos Life cycles of mosses, ferns and seedless vascular plants The Evolution of Seed PlantsChapter 30 Heterospory Ovules and the production of eggs, pollen and the production of sperm Evolutionary advantage of seeds Gymnosperms Angiosperms Flowers, fruits and life cycles Diversity Monocots and dicots Plant Structure, Growth and Development – Chapter 35 Plant body and the hierarchy of organs, tissues and cells Roots, stems and leaves Three tissues systems: dermal, vascular and ground Differentiated plant cells Meristems and cambium Transport in vascular plants – Chapter 36 Physical forces driving transport of materials in plants Membrane selective permeability Proton pumps Water potential Symplast and apoplast Endodermis Transport in xylem Sap ascent, root pressure, Transpiration-Cohesion-Tension Theory Adhesion Stomata and water regulation Organic material translocation in phloem Bulk flow Plant Nutrition – Chapter 37 Nitrogen availability Nitrogen fixation and symbiosis Carnivorous plants and epiphytes Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology – Chapter 38 Flower structure Pollination Double fertilization Ovules into seeds and ovaries into fruit Seed germination Vegetative propagation Plant biotechnology Plant Responses to Internal/External Signals – Chapter 39 Signal transduction Plant hormones and tropisms Responses to light (photoperiodism) Environmental stresses Major Assignments and/or Assessments: Lab activities Plant structure: Roots and Stems Transpiration -AP Two-Semester A.P Biology Pacing Guide Page 6 of 7 Unit Name or Timeframe: Animals Content and/or Skills Taught: Introduction to Animal Diversity – Chapter 32 Nutritional modes, cell structure and specialization, reproduction and development Animal body plants Symmetry, tissues, body cavities Pseudocoelomates and coelomates Protostome and deuterostome development Fate of blastospore Phylogenic tree Invertebrates – Chapter 33 Vertebrates – Chapter 34 Notochords Jaws, limbs and feet, amniotes, mammals Animal From and Function – Chapter 40 Size and shape/environmental constraints Tissue structure and function Epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous Homeostatic regulation Endotherms vs. ectotherms Heat exchange Animal Nutrition – Chapter 41 Food processing Ingestion, digestion, absorption, elimination Intracellular vs. extracellular digestion Human digestive system Circulation and Gas Exchange – Chapter 42 Circulatory systems and Phylogeny Open vs. closed systems Vertebrate circulatory system Mammalian Heart Blood flow/pressure Capillary exchange Lymphatic system Blood composition Gas exchange Gills, tracheal systems, lungs Mammalian lungs Respiratory pigments and oxygen transport Immune System – Chapter 43 Innate immunity External defenses Internal defenses and chemical defenses Inflammatory response Acquired immunity and lymphocytes Humoral and cell mediated immunity Antigens and antibodies Self vs. non-self Allergy, autoimmune disease, immunodeficiencies Osmoregulation and Excretion – Chapter 44 Water balance and osmosis Fresh and marine organisms Land animals Nitrogenous waste systems in organisms Neprons and the human kidney Countercurrent system Hormones and the Endocrine System Chapter 45 Overlap between hormone and nervous regulation Hormones: Their transport and physiological effects Animal Reproduction – Chapter 46 Asexual and sexual Gamete production and fertilization Human male and female reproductive anatomy Human female reproductive cycles (menstrual) Conception and birth Animal Development – Chapter 47 Fertilization, cleavage, gastrulation, organogenesis (differentiation) Morphogenesis: Changes in cell shape, position and adhesion Nervous Systems – Chapter 48 General nervous system organization Neuron structure Resting potential Action potentials Synaptic communication Neurotransmitters Vertebrate cephalization Central/peripheral system Brain structure Injury and stem cell research Motor Mechanisms – Chapter 49 Animal skeletons Muscles for moving skeletal parts Sarcomere structure and function Muscle types Major Assignments and/or Assessments: Lab Activities Animal Tissues Physiology of the circulatory system – AP Earthworm dissection Fetal pig dissection Perch dissection Food Forensics: Lab activity in immunology Two-Semester A.P Biology Pacing Guide Page 7 of 7 Unit Name or Timeframe: Ecology Content and/or Skills Taught: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere – Chapter 50 Organisms and their environment Subfields or organismal ecology Biotic factors/ abiotic factors/ climate Aquatic biomes/terrestrial biomes Behavioral Ecology – Chapter 51 Behavioral traits and evolution Predator/prey Foraging behavior Mate selection Population Ecology – Chapter 52 Population density, dispersion and demography Population growth in idealized environment Logistic growth Caring capacity Population cycles and interdependence Community Ecology – Chapter 53 Interactions at the community level Competition, predation, parasitism, disease, mutualism, commensalism Trophic structures Food chains and food webs Disturbances and ecological succession Biogeographic factors effecting biodiversity Equatorial/polar gradients, islands Ecosystems – Chapter 54 Energy flow and chemical cycling Trophic relationships and decomposition Limitations Light and nutrient Trophic efficiencies and pyramids Biogeochemical cycles Water/ carbon/ nitrogen phosphorus cycles Humans and the environment Acid rain, habitat destruction, toxins, greenhouse effect, rising CO2 levels Conservation ecology and restoration Major Assignments and/or Assessments: Lab activities Behavior: Habitat Selection -AP Dissolved Oxygen and Aquatic Primary Productivity –AP Behavior of pill bugs