Energy & Waves Unit Test Study Guide
advertisement

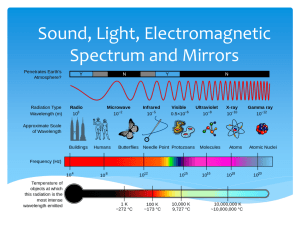
Study Guide Due 1/11/13 Date of Unit Test 1/15/13 Energy & Waves Unit Test Study Guide Your Unit Test will consist of 50 multiple choice questions to be answered on a scan-tron sheet. You will not be able to use any notes or your textbook. Please remember to bring a #2 pencil to the test. Chapter 1, Unit B – Energy (pages 9-28B) 1. The ability to cause change is called __________________. 2. How is kinetic energy increased? 3. The energy stored in food is a form of ___________________ energy. 4. Which type of energy is stored in the nucleus of atoms? 5. X-rays are a form of _____________________ energy. 6. Sunlight is changed into electric energy by what device? 7. When a rock falls from a cliff potential energy changes into _____________ energy. Chapter 2, Unit B – Temperature and Heat (pages 37 – 55B) 8. Temperature is usually measured in degrees with what device? 9. Why are steel joints often used to separate sections of concrete bridges? 10. According to the kinetic theory of matter, how do particles in a gas move? 11. Heat is a flow of energy caused by ______________________________. 12. The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1°C is called _______________. 13. A metal spoon is used to stir a pot of hot soup. The spoon is warmed by which type of heat transfer? 14. Suppose that you are at the beach. Energy from the Sun reaches you mainly through which type of heat transfer? 15. Many people wear hats in the winter. Are hats insulators or conductors of heat? Chapter 1, Unit C – Waves (pages 9 – 28C) 16. How do forces cause waves? 17. Give at least two examples of a longitudinal wave. 18. The number of crests that reach the shore in a given time is called ____________. 19. What do you measure to find wavelength? 20. An echo is an example of what type of wave movement? 21. Describe refraction. 22. Give an example of diffraction. 23. How does a mechanical wave transfer energy? Chapter 2, Unit C – Sound (pages 37 – 63C) 24. What causes sound waves? 25. How is the sound of your voice produced? 26. To make the pitch of a sound wave lower, frequency has to _________________. 27. When an ambulance passes, how does the sound of the siren change? 28. The intensity of a sound is determined by what measurement of the wave? 29. If the frequency of a sound wave is increased, the sound's ______________ is also increased. 30. By turning up the volume on a stereo, you are increasing the ______________ of the sound wave. 31. What type of sounds can damage hearing? 32. How is ultrasound used in the medical field? Chapter 3, Unit C – Electromagnetic Waves (pages 73 – 99C) 33. Where do most of the visible electromagnetic waves on Earth come from? 34. Unlike mechanical waves, electromagnetic waves can transfer energy through _______________. 35. Which EM waves have the highest frequencies? 36. A fire produces light by ______________________. 37. Sunblock and some kinds of sunglasses are designed to protect against which type of EM waves? 38. A regular light bulb creates light by heating a filament until it glows. This way of producing light is called ___________________. 39. How do bioluminescent animals produce light? 40. The light that hits a clear window will mostly be ____________________ through the window. 41. What do polarized sunglasses do? 42. The apparent color of an object depends on what two factors? Chapter 4, Unit C – Light and Optics (pages 113- 138C) 43. What is the study of light and tools that use light? 44. In what direction are parallel light rays that hit a concave mirror reflected? 45. A ray of sunlight moves from the air into the denser medium of a pond. How will the light ray's speed change? 46. Why can a laser beam travel great distances without spreading? 47. What does the law of reflection state? 48. Where do images focus in the eye? 49. If a mirror reflects light rays and brings them together at a focal point, then the mirror must be _______________. 50. How does a refracting telescope enlarge images?