How does cigarette smoke affect the growth of plants
advertisement

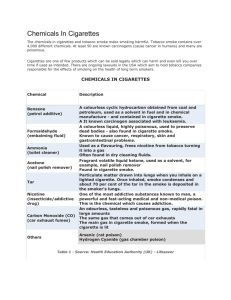
How does cigarette smoke effect the growth of plants? Emily Stahl and Jackie Bossman Mrs. Hawks 9th grade science November 16, 2009 2 How does cigarette smoke effect the growth of plants? It is a proven fact that cigarettes have negative effects on the human body, but little research has been done on the effect of cigarette smoke on plants. Some research indicates that cigarette smoke can have postitive effects on a plant by helping it during photosynthesis. Other research shows that cigarette smoke has negative effects on a plant because it clogs its pores. Smoke is a combination of gases, organic compounds and particulate matter. Cigarette smoke contains over 4,000 chemicals in it. These include 43 known cancercausing compounds, metals, and 400 other toxins (Biology and Politics). The cancer causing compounds are Nitrosamines, cadmium, TSNA, benzodiazepine, crysenes, pyrene, polonium 210, nickel, P.A.H., diberiz acidine, Bnaphthylamine, urethane, N.Nitrosonornicotine, and Toluidine. The metals in cigarette smoke are aluminum, magnesium, zinc, mercury, silicon, titanium, lead, and copper. Some of the other toxins that make up cigarette smoke are acetone, acetic acid, ammonia, arsenic, butane, cadmium, carbon monoxide, DDT, Dieldrin, ethanol, formaldehyde, hexamine, hydrogen cyanide, methane, methanol, naphthalene, nicotine, nitrobenzene, nitrous oxide phenols, stearic acid, toluene, and vinyl chloride (Biology and Politics). Acetone is used as a sanitary cleaner and it is an active ingredient in nail polish remover. It is also used as paint thinner. Acetic Acid is what gives vinegar its taste and odor. It is also used in the production of soft drink bottles, photography film, wood glue, and synthetic fibers and fabrics (Biology and Politics). Ammonia is used in the production of liquid fertilizer, water and wastewater treatment, and as a refrigerant. Weak ammonia solutions are also used as household cleaners and detergents (Uses of 3 ammonia). Arsenic is extremely poisonous and causes death from organ failure. Butane is used as a fuel for cooking and cigarette lighters and as a propellant in aerosol sprays. Cadmium is used in the production of batteries, as a pigment in paint, and is sometimes added to plastic as a stabilizer. Carbon Monoxide is best known as the exhaust fumes that come from a vehicle. DDT and Dieldrin are used as insecticides. Ethanol is found in alcoholic beverages and psychoactive drugs, which are drugs or medication that have a significant effect on mood or behavior. Ethanol is also used in modern thermometers. Formaldehyde is found in many products used to make furniture, cabinets, wall paneling, shelves, and counter tops and can be found in dyes, textiles, plastics, paper products, fertilizer, and cosmetics. It is also used to kill germs or as a body preservative. Hexamine is used as an antibiotic and as fuel tablets used mainly by military organizations and campers. Hydrogen Cyanide is a deadly chemical that causes cells to die by preventing them from using oxygen properly. Methane is used in energy production and is considered as a greenhouse gas that has contributed to global warming. Methanol is used as a fuel, antifreeze, and helps make formaldehyde. Naphthalene is used in mothballs, tanning leather applications, insecticide, antiseptic, dye, and plastics. Nicotine was used as an insecticide and is a very addictive drug. Nitrobenzene is used in pesticides, dyes, explosives, and pharmaceuticals, and shoe and floor polishes. Nitrous Oxide Phenols are used in rocket motors, cooking sprays as a propellant, and as “laughing gas” at a dentist office. Stearic Acid is used in candles, soaps, plastics, and cosmetics (Biology and Politics). Toluene is used in paints, paint thinners, fingernail polish, varnish, adhesives, and rubber (Toluene). Vinyl Chloride is used to produce PVC (Biology and Politics). 4 Plants are complex organisms that can be affected by cigarette smoke in a variety of ways. The major parts of a plant are stomata, guard cells, roots, stem, leaves, epidermis, xylem, phloem, Sclerenchyma, and Collenchyma. Stomata are tiny pores found in the epidermis (Botany). Guard cells are located on the undersurface of leaves and our used for controlling water loss and gas exchange (Guard cell). Roots are the underground portion of a plant that serve as support and draw minerals and water from the surrounding soil. The stem is the main trunk of a plant. The leaf is the main foodmanufacturing organ of a plant. The epidermis is the outer skin layer of a plant. The xylem and phloem are the transport tissues of a plant (Botany). The sclerenchyma and collenchyma are the protective tissues of a plant that are composed of thickened, dry, and hardened cells (Collenchyma). According to studies, cigarette smoke can have a variety of effects on plants. The carbon dioxide in cigarette smoke helps the plant during photosynthesis, but if the cigarette smoke coats the leaves of a plant the absorption of light will be stopped and the plant will not be able to perform photosynthesis (Effects of cigarette smoke on plants). Photosynthesis is the process of converting light energy to chemical energy and storing it in the bonds of sugar (Photosynthesis). Other chemicals in cigarette smoke cause the plant to suffer from foliar necrosis, which is the premature death of the cells in a leaf. Exposing a plant to cigarette smoke may also cause its leaves to fall off, or cause the plant to suffer from epinasty (Does smoke effect house plants). Epinasty is the outward and downward bending of a plant part resulting from different growth rates on the upper and lower sides (Epinasty). This is 5 caused by the ethylene content in cigarette smoke. Ethylene is used to hasten the ripening of a fruit, but when exposed to a plant it causes swelling and makes the leaves unable to grow upward (Does smoke effect house plants). The chemicals can also modify the response of the plant to other environmental stresses, usually causing unfavorable outcomes (Effects of cigarette smoke on plants). Cigarette smoke can help a plant to grow during photosynthesis because of the carbon dioxide in cigarette smoke. However, it may cause a plant to have reduced or abnormal growth, or even cause it to die because of the chemicals in the smoke. It has varied effects on plants, but usually has more negative effects than positive. 6 Works cited "Does Smoke Affect House Plants." Professor's House. 2007. Professor's House, Web. 25/11/09. <http://www.professorshouse.com/your-home/gardening-plants/doessmoke-affect-house-plants.aspx>. "Does Smoke Affect House Plants." Professor's House. 2007. Professor's House, Web. 25/11/09. <http://www.professorshouse.com/your-home/gardening-plants/doessmoke-affect-house-plants.aspx>. "Guard Cell." Tiscali. 2009. Helicon Publishing, Web. 30 Nov 2009. <http://www.tiscali.co.uk/reference/encyclopaedia/hutchinson/m0035144.html>. "Photosynthesis." 02/11/2004. J. Stein Carter, Web. 30 Nov 2009. <http://biology.clc.uc.edu/Courses/bio104/photosyn.htm>. Habeck, Mike. "Toluene." Eco USA. May 1994. Mike Habeck, Web. 30 Nov 2009. <http://www.eco-usa.net/toxics/chemicals/toluene.shtml>.\ Lawerence, Alexis. "Effects of Cigarette Smoke on Plants." Garden Guides. 2009. Demand Media, Web. 25 Nov 2009. <http://www.gardenguides.com/79934effects-cigarette-smoke-plants./>. Lemke, Dr. David E. "Collenchyma." Biology 1410. 13/9/1999. Texas State University, Swarthout, Debbie. "Botany." The encyclopedia of earth. 25/08/08. National Council for Science and the Environment, Web. 25/11/09. <www.eoearth.org/>. Swarthout, Debbie. "Botany." The encyclopedia of earth. 25/08/08. National Council for Science and the Environment, Web. 25/11/09. <www.eoearth.org/>. Web. 25 Nov 2009. <http://www.bio.txstate.edu/~dlemke/botany/1410lab/lab_exercises/lab3/tissues/c ollenchyma.html>.