Energy Engineering B.S. Academic Plan
advertisement

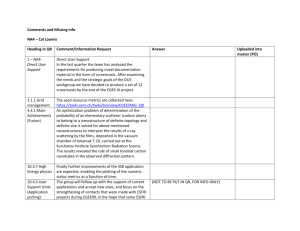
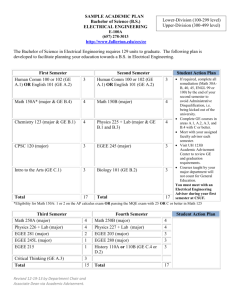
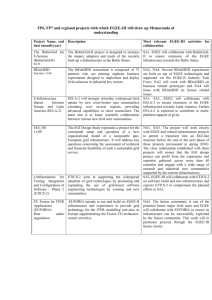
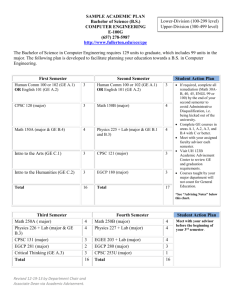
Recommended Academic Plan for B.S. in Energy Engineering (effective spring 2014) Bachelor of Science in Energy Engineering Program 1 Semester 2nd Semester CHEM 110 (GN) Chemical Principles CHEM 111 (GN) Experimental Chemistry 3 1 CHEM 112 (GN) Chemical Principles MATH 141 (GQ) Calculus With Analytic Geometry II 3 4 MATH 140 (GQ) Calculus With Analytic Geometry I ECON 102/014 or EBF 200 (GS) Economics (GA/GH/GS Elective 1) EM SC 100S (GWS) Freshman Seminar * Health and Physical Activity (GHA) 4 PHYS 211 (GN) General Physics: Mechanics 4 3 ENGL 015 (GWS) Rhetoric and Composition or ENGL 030 (GWS) GA/GH/GS Elective 2 3 3 1.5 15.5 3rd Semester CHEM 202 Organic Chemistry MATH 251 Ordinary and Partial Differential Equations PHYS 212 (GN) General Physics: Electricity And Magnetism GA/GH/GS Elective 3 GA/GH/GS Elective 4 3 17 4th Semester 3 4 4 3 3 EE 211 Electrical Circuits and Power Distribution* MATH 231 Calculus of Several Variables CMPSC 201 or 201C or CMPSC 201F PHIL 103 (GH) Ethics (GA/GH/GS Elective 5) GA/GH/GS Elective 6 Health and Physical Activity (GHA) 17 5th Semester 3 2 3 3 3 1.5 15.5 6th Semester EGEE 012 Energy Engineering Lectures 1 EGEE 304 Heat and Mass Transfer 3 MATSE 201 Intro. to Material Science EME 301 Thermodynamics EME 303 Fluid Mechanics of Energy Systems EGEE 302 Principles of Energy Engineering 3 3 3 3 3 3 ENGL 202C (GWS) Technical Writing 3 EGEE 430 Intro. to Combustion FSC 431 Chemistry of Fuels- coal, petroleum, gas, biomass EGEE 437 Design of Solar Energy Conversion Systems EGEE 438 Sustainable Energy Options 16 7th Semester EME 460 Geo-resource Evaluation and Investment Analysis / IE 302 Engineering Economy FSC 432 Petroleum and Natural Gas Processing EGEE 441 Electrochemical Energy Conversion EGEE 451 Energy Conversion Processes Professional Elective 1 EGEE 411 Energy Science and Engineering Laboratory Credits for Graduation 3 3 15 3 8th Semester EGEE 494A Research Projects/ EGEE 295/395/495 Industrial Internship 2 3 3 3 3 Technical Elective 1 EGEE 464W Energy Design Project EGEE Elective Technical Elective 2 3 3 3 3 3 Professional Elective 2 3 18 131 17 * For Students at Campus Colleges Students at campuses where EM SC 100S (GWS) and EE 211 are not offered should take CAS 100 (GWS) in place of EM SC 100S and an appropriate or equivalent electrical circuits course in place of EE 211. The curriculum has been designed to enable students who start at campus locations other than University Park to transfer to University Park and seamlessly transition into the program in their fifth semester. ELECTIVES Students may select their EGEE, professional, and technical electives from the lists below. The technical electives are energy-related courses outside the major that are offered by various colleges across Penn State. Substitutions must be made by petition. The electives marked with an asterisk have prerequisites that only students pursuing concurrent degrees may be able to satisfy. EGEE ELECTIVES EGEE 412 Green engineering and environmental compliance EGEE 420 Hydrogen and fuel cells EGEE 436 Modern thermodynamics for energy systems EGEE 455 Materials for energy applications EGEE 470 Air pollution from combustion sources ENVSE 427 Pollution Control in the Process Industries PROFESSIONAL ELECTIVES ACCTG 211 Financial and Managerial Accounting for Decision Making (4) EBF 301 Global Finance for the Earth, Energy, and Materials Industries (3) EBF 304W Global Management for the Earth, Energy, and Materials Industries EBF 401 Strategic Corporate Finance for the Earth, Energy, and Materials Industries (3) EBF 473 Risk Management in Energy Industries (3)* EBF 484 Energy Economics ENGR 310 Entrepreneurial Leadership ENGR 312 Sustainable Energy Entrepreneurship ENGR 407 Technology-Based Entrepreneurship ENGR 408 (US) Leadership Principles (2) ENGR 409 (US) Leadership in Organization ENGR 425 New Venture Creation ENTR 300 Principles of Entrepreneurship* ERM 411 Legal aspects of resource management* B LAW 243 Legal Environment of Business B LAW 340 Business Law BA 250 Small Business Management I B 303 International Business Operations MGMT 301 Basic Management Concepts MGMT 426 Invention Commercialization MGMT 427 Managing an Entrepreneurial Start-up Company TECHNICAL ELECTIVES BE 497B Biomass energy systems AE 456 Solar energy building system design AE 498D Photovoltaic systems design and construction CE 370 Introduction to environmental engineering CE 371 Water and wastewater treatment* CE 475 Water quality chemistry* CE 476 Solid and hazardous wastes* CH E 320 Phase & chemical equilibria CH E 410 Mass transfer operations* CH E 430 Chemical reaction engineering* CH E 438 Bioprocess engineering* CH E 446 Transport phenomena* EE 387 Energy conversion* ENGR 294H Resource Sustainability: Biodiesel Production and Use (3) ENVSE 406 Sampling and Monitoring of the Geo-Environment* ESC 313 Introduction to Principles, Fabrication Methods, and Applications of Nanotechnology E SC 417 (MATSE 417) Electrical and Magnetic Properties E SC 481 Elements of Nano/Micro-electromechanical Systems Processing and Design E SC 482 Micro-Optoelectromechanical Systems (MOEMS) and Nanophotonics E SC 483 (MATSE 483) Simulation and Design of Nanostructures E SC 414M Elements of Material Engineering GEOG 430 (currently 406): Human use of environment* ENVSE 400 Safety Engineering (3)* ENVSE 430 Industrial health and safety program management (3) ENVSE 445 Industrial hygiene and toxicology (3) MatSE 259 Properties and processing of engineering materials* MatSE 412 Thermal properties of materials* Meteo 473 Application of computers to meteorology Meteo 474 Computer methods of meteorological analysis and forecasting* ME 402 Power Plants* ME 403 Polymer Electrolyte fuel cell engines* ME 404 Gas turbines* ME 408 Energy systems* ME 410 Heat Transfer ME 401 Refrigeration and air conditioning ME 411 Heat exchanger design ME 431 Internal combustion engines MNG 401 Mining operations MNG 410 Underground coal extraction* MNG 441 Surface mining systems and design* MN PR 301 Elements of mineral processing NucE 301 Fundamentals of reactor physics* NucE 310W Issues in nuclear engineering NucE 401 Introduction to nuclear engineering NucE 405 Nuclear and radio-chemistry* NucE 420 Radiological safety* NucE 428 Radioactive waste control* PNG 405 Rock and fluid properties PNG 411 Introduction to Petroleum and Natural Gas Extraction (1) PNG 410 Applied Reservoir Engineering (3)* PNG 480 Production process engineering Agricultural and biological, chemical, civil, electrical, environmental, mechanical, mining, nuclear and petroleum engineering, materials science and engineering, industrial health and safety, and energy business and finance students will be able to substitute by petition some of their courses for some of the minor and dual or concurrent degree requirements. Students in chemical, mechanical, and nuclear engineering in particular may make the following substitution of courses: EGEE Course EMSC 100S (3) EGEE 012 (1) EME 301 (3) EME 303 (3) EGEE 302 (3) EGEE 304 (3) EGEE 420 (3) EGEE 430 (3) EGEE 464 (3) EGEE 470 (3) Substitute/equivalent course CAS 100 (3) CH E 300 (1) CH E 220 (3) or ME300 (3) CH E 330 (3) or ME 320 (3) CH E 210 (3) CH E 350 (3) or ME 410 (3) ME 403 (3) ME 430 (3) CH E 470 (3)# ME 433 (3) # the capstone design project needs to be energy related and must be approved by the ENENG program chair prior to taking the course. Energy Engineering Majors are not allowed to take equivalent courses from other department without the permission of the ENENG program chair. The program goal is to ensure a broad-based energy engineering education for Penn State students with special interest in energy. For example, in the required capstone design course EGEE 464W, the program intends to participate and work with the Learning Factory program in the College of Engineering to provide students an opportunity to work on industrial energyrelated problems in teams composed of students from multiple energy-related disciplines. The proposed energy engineering program is consistent and in line with the recent Penn State University Energy Task Force report and recommendations. In particular, it fulfills the recommendation to develop an exciting new undergraduate curriculum in energy. Courses for Energy Engineering Minor Select 3 courses (9 credits) from the following EME 301 Thermodynamics in energy and mineral engineering EME 303 Fluid mechanics in energy and mineral engineering EGEE 302 Principles of energy engineering EGEE 304 Heat and mass transfer EGEE 411 Energy Science and Engineering Laboratory or EGEE 494A Research projects EGEE 430 Introduction to combustion or ME 416 Introduction to combustion EGEE 420 Hydrogen and fuel cells or ME 408 Fuel cell engines Select 3 courses (9 credits) from the following FSC 431 Chemistry of fuels FSC 432 Petroleum and natural gas processing EGEE 433 Physical processes in energy engineering EGEE 437 Design of solar energy conversion systems EGEE 438 Sustainable energy options EGEE 441 Electrochemical energy conversion EGEE 451 Energy conversion processes EGEE 464W Energy design project or CH E 470 or ME 442W (2) and ME 443W (1) EGEE 470 Air pollution from combustion sources or ME 470 Fundamentals of air pollution The approved course substitutions should make it attractive for students in chemical, mechanical, and nuclear engineering, in particular, to be able to readily work towards a minor, option, or dual or concurrent degree in energy engineering. The prerequisites for the above courses or their substitutes would have been met for most engineering students within their major. Students in disciplines such as agricultural and biological, civil, electrical, environmental, mining, and petroleum engineering; materials science and engineering; and energy business and finance (EBF) should seek advice from the Energy Engineering program chair on the substitutions and technical elective choices for minors, options or dual degrees.