Kingdom Animalia
advertisement
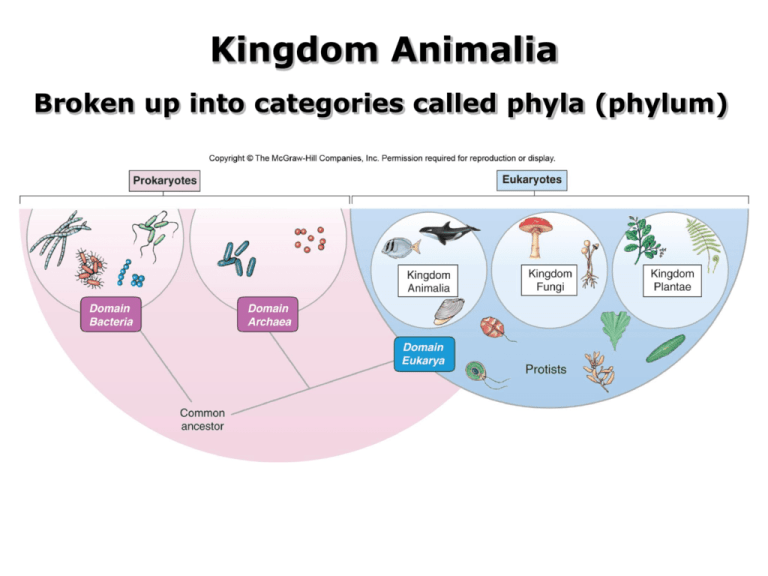
Kingdom Animalia Broken up into categories called phyla (phylum) Kingdom Animalia - Multicellular organisms - Do not make own food, obtain it from others 2 major groups of animals: 1. Vertebrates – have backbone (vertebrae) 2. Invertebrates – lack backbone - at least 97 % of all species of animals are invertebrates Invertebrates Hierarchy of Organization Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata Class Mammalia Order Primates Family Hominidae Genus Homo species sapiens Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia Phylum Porifera Class Order Family Genus species Phylum Porifera – “pore bearers” How do sponges feed? Sponge Body Calcareous Spicules Siliceous Spicules Spongin Importance of Sponges - May have been the first multicellular animals - Simple colonies in which certain cells became specialized for certain functions Phylum Cnidaria Body Plan Cnidarian Body Forms Cnidarians occur in 1 of 2 basic forms How Do Cnidarians Feed? Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia Phylum Cnidaria Class Hydrozoa Scyphozoa Cubozoa Anthozoa Order Family Genus species Types of Cnidarians Class Hydrozoa – wide range of forms & life histories - Some lack polyp stage (have tiny medusa stage), some lack medusa stage - ex. Siphonophores, Portuguese man of war (colonies) Class Hydrozoa - Obelia Class Scyphozoa - larger jellyfish - Medusa stage is dominant, polyp stage is very small or absent Class Cubozoa - box jellyfishes - Medusa stage is small & cube shaped, polyp stage is very small - Extremely toxic Class Anthozoa – sea anemones, corals, gorgonians - Solitary or colonial polyps that lack medusa stage Read “The Case of the Killer Cnidarians” Phylum Ctenophora http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G7WT81ukHZE Phylum Platyhelminthes Body Plan Do they have true tissues & organs? Marine Flatworms Marine Flatworms Phylum Annelida Body Plan Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia Phylum Annelida Class ? Order Family Genus species Phylum Annelida Class Polychaeta – marine segmented worms Adaptations to living in the water? Adaptations to living in the water? Class Polychaeta –marine worms http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JQU7R-tjiNU http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_yn0uT7v6BU http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kIoN2PCvL4o Phylum Mollusca Basic Mollusc Body All molluscs have this basic body plan but is often greatly modified Symmetry? Soft or hard body? Shell? Functions of Mollusc Body Parts 1. Muscular foot? 2. Mantle? 3. Radula? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mLVDwlrSq5U http://www.oceanfootage.com/video_clips/NZ39b_ 040 Basic Mollusc Reproduction Trochophore veliger Domain Eukaryota Kingdom Animalia Phylum Mollusca Class ? Class ? Class ? Order Family Genus species Class Gastropoda Snails, limpets, abalone, nudibranchs Body? Foot? Shell? Radula? Nudibranchs (sea slugs) Where’s their shell? Class Bivalvia – Clams, mussels, oysters - Where’s their body? - Head? Radula? What are their gills use for? What is their foot used for? Bivalve Burrowers Bivalves Attached to Substrate - Mussels Foot secretes byssal threads (attachment threads) Class Cephalopoda Octopuses, squids, cuttlefish, nautilus Class Cephalopoda Active or sedentary? Complex or very basic nerve & sensory system? Where is the foot? Where is the radula? Beak-Like Jaws Where’s Their Shell? Nautilus? Cuttlefish? - shell - modified shell = cuttlebone Where’s Their Shell? Squid? Modified shell = pen Where’s Their Shell?! Where’s Their Shell? Octopus? - No shell http://www.ted.com/index.php/talks/view/id/206





