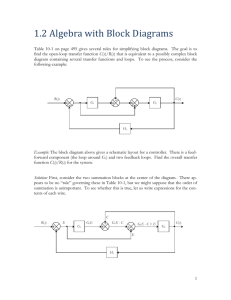
I Can't Swallow!
advertisement

The Steakhouse Syndrome Mazer R. Ally, M.D. Case • 24yo male presents to the ER with a meat impaction • 3hrs ago he was eating a NY strip steak at Morton’s Steakhouse • Midway into the meal he felt a piece of meat get stuck. He immediately drinks some water but that doesn’t help. • He points to the sternal notch where he feels this sensation of impaction • His airway is intact, but noticing that he cannot tolerate secretions Case (cont) • The patient has no significant medical history, no reflux symptoms and is not on any medications. • He reports occasional episodes where food gets “hung up”, but usually can wash it down with water. • The patient is taken to the ER – Glucagon is given but ineffective • GI is called for help… Endoscopy • Is this Eosinophilic Esopahgitis (EoE)? Outline • • • • • • • Definition Epidemiology Pathogenesis Clinical Presentation Endoscopic findings Diagnosis Management What is Eosinophilic Esophagitis? • Chronic, immune/antigen mediated esophageal disease • Clinically associated with symptoms related to esophageal dysfunction AND • Histologically associated with eosinophil-predominant inflammation. • Seen in both children and adults J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011 Publications Eosinophilic Esophagitis PubMed Citations 1978-2009 Epidemiology: Incidence of EE at University of Pennsylvania (1994-2003) Liacouras CA et al. Clinical Gastro Hep 2005 Epidemiology: The Prevalence of EE Who gets EoE? Young Caucasian Males Moawad et al. Gastroenterology 2009; 136 (Suppl 1):S1857 Clinical Presentation (N=127) Clinical Presentation Endoscopic Findings: 1. Concentric rings Trachealization Concentric rings: not always EE Endoscopic Findings: 2. Longitudinal furrows Endoscopic Findings: 3. White lesions Endoscopic Findings: 4. Friability/Crepe-like Endoscopic Findings: 5. Narrow lumen esophagus EoE does not always have endoscopic features • 10% of patients demonstrate a normal appearing esophagus Pathogenesis Moawad et al. Dig Dis Sci 2009 Food Allergens Associated with EE in Children • Skin prick test performed on 42 subjects with EE plus 4 controls • Positive reactions for 62% of the EE group and 25% of the control group Number of patients testing positive 15 14 12 11 10 10 7 5 4 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 Almond Beef Chicken Corn Potato Rye 0 Milk Peanut Egg Soybean Wheat Codf ish Pea Baxi S, et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006 Richter J. Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology Current Hot Topics 2008 Seasonal Variation Peds EE Adult EE Wang et al. J Clin Gastroenterol 2007 Almansa et al. Am J Gastroenterol 2009 Aeroallergens and EE EoE(%Pt) Trees * Grass** Weed** 15 40 33% 12 30 20 27% 24% 16% 9 6 10 3 0 0 Jan-­‐Mar Apr-­‐Jun Jul-­‐Sep Oct-­‐Dec Moawad et al. Gastroenterology 2009; 136 (Suppl 1):S1857 Mean Pollen Count (Grains per m3) Mean Pollen Count (Grains per m3/10) * ** * History of Atopic Diseases Walter Reed Population Atopic dermatitis 6% Asthma 12% Food allergies 13% 33% Seasonal allergies 0 10 20 % EE Patients (n=127) 30 40 Does Acid Exposure Play a Role? Eosinophilic Esophagitis Oct 2 1997 Erosive Esophagitis March 4 2009 EoE and GERD have a complex association • GERD causes esophageal injury with eosinophilic infiltration • GERD and EE coexist but are unrelated • EE causes GERD • GERD causes EE Spechler et al. Am J Gastroenterol 2007 Diagnosis • Made by multiple biopsies from the proximal and distal esophagus • Histologic findings: – Increase number of eosinophils (>15 eos) – Microabscesses – Spongiosis – Basal zone hyperplasia – Degranulation – Subepitheilial fibrssis is characteristic Odze RD. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009 Nutrients 2013, 5 Number of biopsies to establish diagnosis Gonsalves N et al. Gastrointest Endoscop 2006 Management • Pharmacologic therapy – Proton pump inhibitors – Corticosteroids (topical and systemic) – Leukotriene receptor antagonists • Dietary – Elemental – Six-food elimination (Eggs, Wheat, Peanuts, Seafood, Soy, Milk) – Elimination based on testing • Mechanical – Dilation PPI therapy • A trial of PPI therapy is recommended for patients with EoE even if the diagnosis is clear cut • PPI responsive esophageal eosinohilia – Have typical EoE symptoms and histology – Do not have GERD by endoscopy or pH monitoring – Exhibit a clinical and histological response to PPI’s PPI-REE • Pathogenesis – Patients have GERD causing esophageal eosinophilia (Non-erosive reflux disease) – Patients have EoE that responds to an anti-inflammatory effect of PPIs PPI Response in Children with EoE (N=43) Dranove JE et al. J Pediatr. 2009 Approaches to Diet therapy • Elemental diet – Amino acid based formulas – Gold standard • Empiric Elimination Diet (Six Food Elimation Diet) – Avoidance of milk, soy, eggs, wheat, nuts, seafood • Direct Elimination Diet – Skin prick testing – 75% success in children Elemental Diet • Amino-acid based formula • Effective in children but costly • >95% success in children, not studied in adults Introduction to Elemental Diet Kelly KJ et al. Gastroenterology 1995 6 food elimination diet 50 patients Dysphagia Symptom Score Effect of a SFED for weeks on Effect of Six-Food Elimination Diet (SFED) for 6 Dysphagia Symptom Score Weeks on Dysphagia Symptom Score in 50 Adults 16 14 12 12 10 8 6 4 3.5* 2 0 Pre-SFED Post-SFED Gonsalves N. Gastroenterology 2012;142:1451. Elemental vs. Six Food Elimination Diet Six foods 60 EoE patients Wheat Eggs Milk Soy Peanuts 35 SFED* 25 elemental diet 6 weeks Seafood 26/35 with < 10 eos/hpf 74% 22/25 < 10 eos/hpf 88% Kagalwalla et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006 Pre and Post Eosinophil Counts SFED Kagalwalla et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006 Elemental Diet What can we eat? Salad without croutons Water Elimination Diet Based on Skin Prick Testing (N=75) Liacouras CA et al. Clinical Gastro Hep 2005 Topical Steroids- Fluticasone • Fluticasone 440 mcg twice daily • Treatment given for 6-8 weeks • Ensure delivery to esophagus by removing spacer • Rinse mouth with water and avoid food for 2 hours • Side effects include candidiasis • Effective in inducing remission Esophageal Candidiasis Topical Steroids Konikoff et al. Gastroenterology 2006 Oral Viscous Budesonide Eos 0-7 Eos 8-23 Eos ≥ 24 Children < 10 – 1mg/day Children > 10 – 2mg/day Aceves S et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007 Systemic Steroids • 21 children found to have EoE • Treated with 1.5mg/kg oral methylprednisolone for 4 weeks • 20/21 had clinical improvement within 7 days and histology within 4 weeks Liacouras et al. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1998 Targeting Degranulation Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists • • • • • • 12 patients with EoE (mean age 40) Mean eosinophil count 56/HPF Treated with Singulair for 14 months 7/8 with improvement in symptoms No change in eosinophilia 6/8 with recurrence of symptoms once treatment discontinued Attwood et al. Gut 2003 Dilation in EoE • Generally used when medical therapy “fails” • When initially reported was felt that dilation led to increased complications – Reports of spontaneous esophageal perforations – Perforations during endoscopy – Tears with dilation Dilation: Initial Description • 10/11 patients successfully treated • Symptoms recurred in 8 months on average • Perforation has been reported, but mucosal wall disruption more common Straumann et al. Gastroenterology 2003 Dilation in EoE • No single dilator type has proved superior to another in safety or efficacy • Esophageal strictures are dilated progressively rather than abruptly – Rule of 3’s Improvement in Symptoms Following Dilation Moawad FJ et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010 (submitted) CRE vs Bougie • Controlled radial expansion – Dilate dominant or focal stricture – Limit esophageal wall disruption – Allows direct visualization • Bougie – Dilate entire esophagus – No visualization (Maloney) Dilation Complications with Dilation (N=36) Cohen et al. Clin Gastro Hep 2007 Recommendations for Dilation • Perform carefully and gradually • Begin small (8-10 mm bougie) • 2 consecutive dilators in 1mm increments • 3 consecutive dilators if no resistance encountered Back to that case… • Patient had biopsies takenmax was 63 EOS/ HPF • Started on a PPI • Plan for repeat EGD in 8 weeks Key Points • EoE is a common disease in adults and children • EoE is a clinicopathologic disease • The prevalence appears to be increasing • Food impaction and dysphagia are the most common presenting symptoms in adults • EoE should be considered in all patients with dysphagia • Treatments are effective but relapse is common Questions