Perfect Competition - Business-TES
advertisement

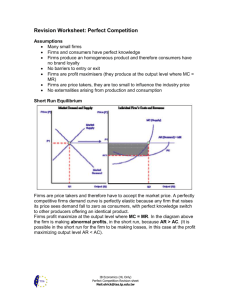
Perfect Competition We now move on to study the economics of different market structures. The spectrum of competition ranges from perfectly competitive markets where there are many sellers who are price takers to a pure monopoly where one single supplier dominates an industry and sets price. We start our analysis of market structures by looking at perfect competition. Perfect competition – a pure market Perfect competition describes a market structure whose assumptions are extremely strong and highly unlikely to exist in most real-time and real-world markets. The reality is that most markets are imperfectly competitive. Nonetheless, there is some value in understanding how price, output and equilibrium is established in both the short and the long run in a market that holds true to the tough assumptions of a world of perfect competition. Economists have become more interested in pure competition partly because of the rapid growth of ecommerce in domestic and international markets as a means of buying and selling goods and services. And also because of the popularity of auctions as a rationing device for allocating scarce resources among competing ends. Basic assumptions required for conditions of pure competition to exist • • • • • • Many small firms, each of whom produces an insignificant percentage of total market output and thus exercises no control over the ruling market price. This means buyers have plenty of choice. Many individual buyers, none of whom has any control over the market price – i.e. there is no monopsony power. This means firms can sell all that they want. Perfect freedom of entry and exit from the industry. Firms face no sunk costs - entry and exit from the market is feasible in the long run. This assumption ensures all firms make normal profits in the long run Homogeneous products are supplied to the markets that are perfect substitutes. This leads to each firms being passive “price takers” and facing a perfectly elastic demand curve for their product. Perfect knowledge – consumers have readily available information about prices and products from competing suppliers and can access this at zero cost – in other words, there are few transactions costs involved in searching for the required information about prices No externalities arising from production and/or consumption which lie outside the market The real world of imperfect competition! Clearly the assumptions of pure competition do not hold in the vast majority of markets. Some suppliers may exert some control over market supply and seek to exploit their monopoly power. On the demandside, some consumers may have monopsony power against suppliers because they purchase a high percentage of total demand. There are nearly always some barriers to the contestability of the market (see revision notes on barriers to entry) and far from being homogeneous, most markets are full of heterogeneous products due to product differentiation. Consumers nearly always have imperfect information (for example information gaps) and their preferences and choices can be influenced by the effects of persuasive marketing and advertising. In every industry there is always asymmetric information where the seller knows more about quality of good than buyer. The real world is one in which negative and positive externalities from both production and consumption are numerous – both of which can lead to a divergence between private and social costs and benefits. Finally there may be imperfect competition in related markets such as the market for essential raw materials, labour and capital goods. We can come fairly close to a world of perfect competition but in practice there are nearly always barriers to pure competition. Currency markets - taking us closer to perfect competition IB Economics notes Perfect Competition Neil.elrick@tes.tp.edu.tw “As perfect competition is a theoretical absolute, there are no pure examples of a perfectly competitive market.” (Source: Wikipedia) It is often said that the most competitive market possible is at best rare and probably does not exist at all in its purest form. Perhaps the vast market in global currencies takes us as close as we might reasonably get to a world of perfect competition? Brief background on currency dealing The foreign exchange market is where all buying and selling of world currencies takes place. There is 24-hour trading, 5 days a week (about 9pm London Sunday to 10pm London Friday. Trade volume in the Forex market is around $1.2 trillion per day. This compares with to the New York Stock Exchange which trades ‘only’ $25 billion per day. 31% of global currency trading takes place in London. Well over ninety per cent of trading in currencies around the world is speculative rather than the buying and selling of currencies to enable people and firms to conduct business in the real economy. The main players in the currency markets are as follows: • • • • • Banks both as “market makers” dealing in currencies and also as end users demanding currency for their own operations). These banks include investment banks and commercial “high street” banks Hedge funds and other institutions (e.g. funds invested by asset managers, pension funds) Central Banks (including occasional currency intervention in the market) Corporations (mostly defensive hedging of exposures to risk) Private investors / market speculators / tourists Why does a currency market come close to perfect competition? Homogenous output: The "goods" traded in the foreign exchange markets are homogenous - a US dollar is a dollar whether someone is trading it in London, New York or Tokyo. Many buyers and sellers meet openly to determine prices: There are large numbers of buyers and sellers each of the major banks has a foreign exchange trading floor which helps to "make the market". Indeed there are so many sellers operating around the world that the global currency exchanges are open for business twenty-four hours a day. No one agent in the currency market can influence the price on a persistent basis - all are ‘price takers’. Currency values are determined solely by demand and supply factors. IB Economics notes Perfect Competition Neil.elrick@tes.tp.edu.tw High quality information: Most participants in the market - be they buyers or sellers - are well informed, in most cases with access to real time information and also plenty of background analysis on the factors driving the prices of each individual national currency. Technological progress has made much more information more immediately available at a fraction of the cost of just a few years ago. This is not to say that information is cheap - an annual subscription to a Bloomberg or a Reuter’s news terminal will normally cost several thousand dollars. But the market is rich with information and transactions costs for each batch of currency bought and sold have come down. Seeking the best price: The buyers and sellers in foreign exchange only deal with those who offer the best prices. What are the limitations of currency trading as an example of a near-perfectly competitive market? Firstly the market can be influenced by official intervention via buying and selling of currencies by governments or central banks operating on their behalf. There is a huge debate about the actual impact of intervention by policy-makers in the currency markets. Those who are sceptical about the effects of intervention buying and selling to move currencies in anything other than the short term talk of governments not being able to "buck the market". Others conceded that intervention does change the ruling price for a currency especially if there is concerted and coordinated intervention by a number of countries acting in unison. Secondly there are costs involved in a bank or other financial institution when establishing a new trading platform for currencies. They need the capital equipment to trade effectively; the skilled labour to employ as currency traders and researchers. Despite these limitations, the foreign currency markets take us close to a world of perfect competition. Much the same can be said for trading in the equities and bond markets and also the ever expanding range of future markets for financial investments and internationally traded commodities. IB Economics notes Perfect Competition Neil.elrick@tes.tp.edu.tw Establishing price and output in the short run under perfect competition The previous diagram shows the short run equilibrium for perfect competition. In the short run, the twin forces of market demand and market supply determine the equilibrium “market-clearing” price for the industry. In the diagram below, a market price P1 is established and output Q1 is produced. This price is taken by each of the firms. The average revenue curve (AR) is their individual demand curve. Since the market price is constant for each unit sold, the AR curve also becomes the Marginal Revenue curve (MR). For the firm, the profit maximising output is at Q2 where MC=MR. This output generates a total revenue (P1 x Q2). The total cost of producing this output can be calculated by multiplying the average cost of a unit of output (AC1) and the output produced. Since total revenue exceeds total cost, the firm in this example is making abnormal (economic) profits. This is not necessarily the case for all firms. It depends on their short run cost curves. Some firms may be experiencing sub-normal profits if average costs exceed the market price. For these firms, total costs will be greater than total revenue. Short run losses IB Economics notes Perfect Competition Neil.elrick@tes.tp.edu.tw The adjustment to the long-run equilibrium If most firms are making abnormal (or supernormal) profits, this encourages the entry of new firms into the industry, which if it happens will cause an outward shift in market supply forcing down the ruling market price. The increase in supply will eventually reduce the market price until price = long run average cost. At this point, each firm in the industry is making normal profit. Other things remaining the same, there is no further incentive for movement of firms in and out of the industry and a long-run equilibrium has been established. This is shown in the next diagram. IB Economics notes Perfect Competition Neil.elrick@tes.tp.edu.tw We are assuming in the diagram above that there has been no shift in market demand, i.e. we are considering an outward shift in market supply brought about by the entry of new competing firms each of whom is supplying a homogeneous product to the market. The effect of increased supply is to force down the market price and cause an expansion along the market demand curve. But for each supplier, the price they “take” is now lower and it is this that drives down the level of profit made towards the normal profit equilibrium. In an exam you may be asked to trace and analyse what might happen if • • There was a change in market demand (e.g. arising from changes in the relative prices of substitute products or complements) There was a cost-reducing innovation affecting all firms in the market or an external shock that increases the variable costs of all producers. Effects of a change in market demand We now consider how a competitive market adjusts to a change in market demand in both the short and the long run. In the short run, businesses are operating with at least one fixed factor. Therefore the elasticity of the supply curve depends on the amount of spare capacity, the level of existing stocks and also the time scale of the production process – in other words how fast and at what cost the industry can expand supply when demand changes. In the long run, because of freedom of entry and exit into and out of the industry, we supply curve to be more elastic in response to a change in demand. The diagram below shift of demand with short run market supply deemed to be relatively inelastic (in which adjustment in the market drives prices higher) but where long run market supply downward pressure on price as market output increases. IB Economics notes Perfect Competition Neil.elrick@tes.tp.edu.tw expect the market shows an outward case the short run is elastic, putting Pure competition and economic efficiency Perfect competition can be used as a yardstick to compare with other market structures because it displays high levels of economic efficiency. 1. Allocative efficiency: In both the short and long run in perfect competition we find that price is equal to marginal cost (P=MC) and thus allocative efficiency is achieved. At the ruling market price, consumer and producer surplus are maximised. No one can be made better off without making some other agent at least as worse off – i.e. the conditions are in place for a Pareto optimum allocation of resources. 2. Productive efficiency: Productive efficiency occurs when the equilibrium output is produced with average cost at a minimum. This is not achieved in the short run, but is attained in the long run equilibrium for a perfectly competitive market. 3. Dynamic efficiency: We assume that a perfectly competitive market produces homogeneous products – in other words, there is little scope for innovation designed purely to make products differentiated from each other and thereby allow a supplier to develop and then exploit a competitive advantage in the market to establish some monopoly power. Some economists claim that perfect competition is not an optimal market structure for high levels of research and development spending and the resulting product and process innovations. Indeed it may be the case that monopolistic or oligopolistic markets are more effective in creating the environment for research and innovation to flourish. A cost-reducing innovation from one producer will, under the assumption of perfect information, be immediately and without cost transferred to all of the other suppliers. That said, a “competitive market” (i.e. a contestable market) provides the discipline on firms to keep their costs under control, to seek to minimise wastage of scarce resources and to refrain from exploiting the consumer by setting high prices and enjoying high profit margins. In this sense, a more competitive market can stimulate improvements in both static and dynamic efficiency over time. It is certainly one of the main themes running through the recent toughening-up of UK and European competition policy as this introductory passage to a competition white paper demonstrates: Gains from competition Competitive markets provide the best means of ensuring that the economy's resources are put to their best use by encouraging enterprise and efficiency, and widening choice. Where markets work well, they provide strong incentives for good performance - encouraging firms to improve productivity, to reduce prices and to innovate; whilst rewarding consumers with lower prices, higher quality, and wider choice. By encouraging efficiency, competition in the domestic market - whether between domestic firms alone or between those IB Economics notes Perfect Competition Neil.elrick@tes.tp.edu.tw and overseas firms Source: www.dti.gov.uk - also contributes to our international competitiveness. The long run of perfect competition, therefore, exhibits optimal levels of economic efficiency. But for this to be achieved all of the conditions of perfect competition must hold – including in related markets. When the assumptions are dropped, we move into a world of imperfect competition with all of the potential that exists for various forms of market failure. The next diagram shows how when price and output is not at the competitive equilibrium, the result is a deadweight loss of economic welfare. The competitive price and output is P1 and Q1 respectively. IB Economics notes Perfect Competition Neil.elrick@tes.tp.edu.tw