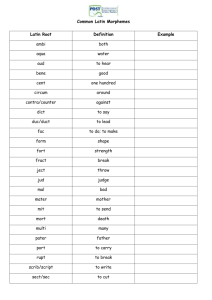
Pearson_AP_Quizzes_files/Ch 7 216
advertisement

Chapter 7 PRACTICE 216-233 Name___________________________________ Period________ Date_________ MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The linguistic relativity hypothesis suggests that ________. A) one's language determines the pattern of one's thinking and view of the world B) we decide which objects belong to a concept according to what is most probable or sensible, given the facts at hand C) perception of surface structure precedes deep structure in understanding a sentence D) one's thinking and view of the world determines the structure of one's language 1) 2) The belief that thought and experience are determined by language is known as linguistic ________. A) absolutism B) determinism C) relativism D) exclusivity 2) 3) Which of the following experimental results BEST refutes the linguistic relativity hypothesis? A) People retrieved the word “brown” faster than “muddy brown.” B) People who had to rotate a consonant 90 degrees to compare it to a prototype recognized it more quickly than people who had to rotate it 180 degrees. C) Members of a primitive tribe whose language has no words for colors could still think about a wide variety of colors. D) Members of a primitive tribe who were asked to perform a task using top-down processing completed it more quickly than those using bottom-up processing. 3) 4) Researchers have found that ________ influenced by culture. A) both language and thought are B) language, but not thought, is C) thought, but not language, is D) neither language nor thought are 4) 5) Hyde's research found that female workers were likely to be rated most positively when the term ________ was used to describe workers in general. A) “he” B) “he or she” C) “she” D) “they” 5) 6) According to Whorf, language affects ________. A) how we think and what we think about B) what we think about but not how we think C) neither how we think nor what we think about D) how we think, but not what we think about 6) 7) In a recent study that required men and women to respond to gender-neutral and genderspecific pronouns, ________ responded more quickly to stimuli that contained traditional gender stereotypes than to stimuli that contained nontraditional stereotypes. A) women, but not men B) both women and men C) men, but not women D) neither men nor women 7) 12/09/2011 Walker_Maryann Friday, December 9, 2011 4:41:18 PM ET 1 TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 8) People cannot think about things for which they have no words in their language. 8) 9) The idea that patterns of thinking are determined by the specific language one speaks is called the linguistic fixedness hypothesis. 9) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 10) Problem representation is ________. A) a specific type of heuristic C) a specific type of decision making 10) B) an alternative to using algorithms D) interpreting or defining a problem 11) The first step in solving a problem is to ________. A) eliminate functional fixedness B) conduct a means-end analysis C) create a representation of the problem D) decide on using either an algorithm or heuristic strategy 11) 12) Belinda sits down to take a psychology test and finds that it is an essay test requiring creative writing to construct hypothetical situations. What type of thinking will be MOST important to her to do well on the test? A) divergent thinking B) convergent thinking C) functional thinking D) circular thinking 12) 13) The type of thinking required to solve problems requiring a creative, flexible, or inventive solution is ________ thinking. A) convergent B) divergent C) functional D) circular 13) 14) Creative problem solving typically involves ________. A) circular thinking B) convergent thinking C) divergent thinking D) logic 14) 15) Belinda sits down to take a psychology test and finds that it is a multiple-choice test. What type of thinking will be necessary for her to do well on the test? A) functional thinking B) divergent thinking C) circular thinking D) convergent thinking 15) 16) An important aspect of problem representation is ________. A) use of an algorithm B) conceptual relativity C) choice of a decision-making strategy D) proper categorization of the problem 16) 17) After problem interpretation, the next step in problem solving is ________. A) a means-end analysis B) a short period of trial and error C) selection of a solution strategy D) creation of subgoals 17) 2 Walker_Maryann Friday, December 9, 2011 4:41:18 PM ET 18) A similarity between hill-climbing and means-end analysis is that both ________. A) are always forward looking B) use compensatory modeling C) necessitate the creation of subgoals D) take into account problems of set 18) 19) Your car is not operating correctly. The mechanic opens the hood and says “We've been seeing lots of cars recently with fouled plugs or dirty fuel filters. Let's start there and see if that's your problem, too.” The mechanic is using a(n) ________. A) compensatory decision model B) algorithm C) noncompensatory decision model D) heuristic 19) 20) A problem-solving strategy in which an individual or a group produces numerous ideas and evaluates them only after all ideas have been collected is called ________. A) convergent thinking B) brainstorming C) critiquing D) functional analysis 20) 21) Failing to see that a wrench can also be used to hammer a nail is an example of ________. A) positive transfer B) learned helplessness C) reproductive thinking D) functional fixedness 21) 22) A seemingly arbitrary flash “out of the blue” where the solution to a problem suddenly becomes apparent to you, but you do not consciously know how you “figured it out,” is called ________. A) a mental set B) brainstorming C) priming D) insight 22) TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 23) A technique that is always forward looking and does not allow for digression is hill-climbing. 23) 24) Heuristics are rules of thumb that guarantee a solution if properly carried out. 24) 25) Heuristics are problem-solving methods that guarantee a solution if they are appropriate for the problem and are properly carried out. 25) 26) Means-end analysis is very similar to working backward in that it is always forward looking. 26) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 27) Margo can't close the window in her office, and a strong wind has come up. She complains to John that her papers are blowing and she can't find a paperweight. John takes the empty stoneware coffee mug from her bookshelf and puts it on top of her papers to anchor them. Margo has been suffering from ________. A) inadequate means-end analysis B) working backward C) functional fixedness D) noncompensatory modeling 27) TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 28) Mental set and functional fixedness are both obstacles to effective problem solving. 3 Walker_Maryann Friday, December 9, 2011 4:41:18 PM ET 28) 29) In some cases, the solution to a problem may be as simple as retrieving information from memory. 29) 30) Trial and error is a more effective problem-solving technique than using heuristics. 30) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 31) A strategy that involves analyzing the difference between the current situation and the desired goal, and then reducing the discrepancy, is called ________. A) means-end analysis B) a problem-solving set C) compensatory modeling D) creating subgoals 31) 32) Gary is assigned to write a history paper. Instead of writing it all in one sitting, he breaks the assignment up into a series of separate tasks that include choosing a topic, doing the research, preparing an outline, writing the first draft, editing, etc. His strategy is BEST described as ________. A) using algorithms B) hill-climbing C) creating subgoals D) means-end analysis 32) 33) The first step in solving a problem is ________, which means interpreting or defining the problem. A) problem representation B) working backward C) hill climbing D) counterfactual thinking 33) 34) A formula is an example of a(n) ________. A) response set B) heuristic 34) C) logarithm 35) Problem-solving methods that guarantee solutions if appropriate and properly executed are called ________. A) algorithms B) noncompensatory models C) prototypes D) heuristics 35) 36) An example of an algorithm is a ________. A) compensatory model C) linguistic elaboration 36) B) nim game D) mathematical formula 37) The three most important building blocks of thought are ________. A) language, images, and concepts B) semantics, phonemes, and morphemes C) concepts, algorithms, and heuristics D) cognitions, feelings, and language 37) 38) Language is a flexible system of ________ that enables us to communicate our ideas, thoughts, and feelings. A) echoes B) sets C) icons D) symbols 38) 4 Walker_Maryann D) algorithm Friday, December 9, 2011 4:41:18 PM ET 39) A uniquely human capability that has long been thought of as separating us from all other animals is ________. A) language B) emotion C) problem solving D) color vision 39) 40) Spoken language is based on units of sound units called ________. A) registers B) phonemes C) morphemes 40) D) semantics 41) The basic sound units of any language are called ________. A) sound bytes B) morphemes C) phonemes D) semantics 42) The sounds of “t,” “th,” and “sh” are ________. A) semantics B) sound bytes C) morphemes D) phonemes 43) By themselves, phonemes are ________. A) units of meaning C) meaningless B) syntactical D) units of prototypes 41) 42) 43) 44) Which of the following would be considered a phoneme? A) “Book at the look” (instead of “Look at the book”) B) “I missed my mife (wife)” C) “B” D) “Dog” 45) Phonemes are grouped together to form ________. A) morphemes B) semantics 45) C) registers D) sound bytes 46) The smallest meaningful units in a language are ________. A) phonemes B) morphemes C) semantics D) processors 47) Prefixes, suffixes, and words are examples of ________. A) morphemes B) subjugations C) phonemes D) semantics 46) 47) 48) According to your text, each of the following is a distinguishing feature of language EXCEPT ________. A) meaningfulness B) productivity C) novelty D) displacement 48) 49) The language rules that determine how sounds and words can be combined and used to communicate meaning within a language are collectively known as ________. A) morphemes B) grammar C) linguistic relativity D) phonemes 49) 50) The underlying meaning of a sentence is its ________ structure. A) deep B) surface C) simple 50) 5 Walker_Maryann 44) Friday, December 9, 2011 4:41:18 PM ET D) complex 51) A flexible system of communication that uses sounds, rules, gestures, or symbols to convey information is called ________. A) language B) morphology C) syntax D) code 51) TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 52) Syntax is the system of rules that governs how we combine words to form grammatical sentences. 52) 53) Most concepts are simple and clear cut. 53) 54) We must form a new concept for every new experience. 54) 55) Language is based on universal sound units called morphemes. 55) 56) Semantics describes how we assign meaning to the morphemes we use. 56) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 57) Before Jane enrolled in a college course on introductory psychology, she thought the study of psychology was the study of how unconscious needs and desires affect our actions. Now that she is almost halfway through the course and she has studied the same areas your text has covered, ________. A) her concept of psychology is not currently modifiable B) her concept of psychology has changed C) her image of psychology has changed D) she no longer thinks about psychology abstractly 57) 58) Which of the following statements is true? A) Concepts and images are basically synonymous. B) Concepts give meaning to new experiences. C) Basic concepts do not change over time. D) We form new concepts for each new experience. 58) 59) Use of a pie chart, in which each item receives a piece of the pie according to its percentage of total budget, is an example of a(n) ________. A) classification prototype B) concept C) algorithm D) image 59) 60) An image is a ________. A) mental category for classifying specific people, places, or events B) mental representation of a sensory experience C) way of grouping experiences so that each new perception is not surprising D) conceptual prototype 60) 6 Walker_Maryann Friday, December 9, 2011 4:41:18 PM ET 61) Jane's first child was born a month ago, and like many other new mothers, she often exclaims that she had no idea that an infant could be so much work. Which of the following is true? A) Jane can no longer think about an infant abstractly. B) Jane is applying the language relativity hypothesis. C) Jane's concept of an infant has been modified. D) Jane's concept of an infant is not currently modifiable. 61) 62) When you wish to understand a sentence, you must start with listening to the speech sounds that make up the words and phrases, decipher the meaning of each of the words and phrases, and eventually interpret the idea conveyed by the sentence. This is sometimes called a(n) ________. A) heuristic B) interpolation C) transformation D) transaction 62) 63) The person whose work has most greatly contributed to our understanding of the way grammar works is ________. A) Louis P. Leakey B) Harry Harlow C) George Lakoff D) Noam Chomsky 63) 64) Researchers who taught a gorilla named Koko to use sign language found that through age 5 her vocabulary was ________ the spoken vocabulary of a human 5-year-old and was ________ than the vocabulary of a deaf 5-year-old child using sign language. A) about the same as; larger than B) smaller than; about the same as C) smaller than; smaller than D) smaller than; larger than 64) 65) The mirror test with animals has been used primarily to test for ________. A) light sensitivity B) depth perception C) self-awareness D) visual acuity 65) 66) Numerous studies indicate that animals ________. A) are capable of some primitive thought, but have no humanlike cognitive capacities B) are incapable of thought C) have some humanlike cognitive capacities D) have fully humanlike cognitive capacities 66) 67) Each of the following statements is true EXCEPT ________. A) at best, apes have reached the linguistic levels of a human child around age 2 to 2 ½ B) apes can develop vocabularies of hundreds of words using sign language and computer keyboards C) the ability of some primates to use signs to refer to an object is proof of their mastery of human-like language D) chimps can learn signs without extensive training or rewards from human trainers 67) 68) In the mirror test, which of the following animals is the only one that shows signs of self-recognition and awareness? A) orangutans B) dogs C) dolphins D) elephants 68) 7 Walker_Maryann Friday, December 9, 2011 4:41:18 PM ET TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 69) All animals communicate. 69) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 70) Human infants first demonstrate mirror-recognition at ________ months of age. A) 6 to 12 B) 1 to 6 C) 18 to 24 D) 12 to 18 70) 71) In the mirror test, which of the following animals is the only one that shows signs of self-recognition and awareness? A) cats B) dogs C) dolphins D) chimpanzees 71) 72) Researchers who taught a gorilla named Koko to use sign language found that by age 5, she had a vocabulary of about ________ words. A) 500 B) 1,000 C) 100 D) 5,000 72) 73) The communication of honeybees is unlike human language in that ________. A) it is more dependent on external reinforcement than human language B) it is more flexible than human language C) involves a wider variety of sounds than human language D) it is not characterized by semantics, displacement, and productivity 73) 74) Nonhuman animals communicate primarily through ________. A) phonemes B) signs C) images 75) Honeybees communicate through the use of ________. A) the sounds made by vibrating their wings B) an intricate dance C) pheromones D) their stingers, to touch other bees in the hive 8 Walker_Maryann Friday, December 9, 2011 4:41:18 PM ET 74) D) morphemes 75) Answer Key Testname: CH 7 216-233 PRACTICE 1) A 2) B 3) C 4) A 5) C 6) A 7) B 8) FALSE 9) FALSE 10) D 11) C 12) A 13) B 14) C 15) D 16) D 17) C 18) A 19) D 20) B 21) D 22) D 23) TRUE 24) FALSE 25) FALSE 26) FALSE 27) C 28) TRUE 29) TRUE 30) FALSE 31) A 32) C 33) A 34) D 35) A 36) D 37) A 38) D 39) A 40) B 41) C 42) D 43) C 44) C 45) A 46) B 47) A 48) C 49) B 12/09/2011 Walker_Maryann Friday, December 9, 2011 4:41:18 PM ET 9 Answer Key Testname: CH 7 216-233 PRACTICE 50) A 51) A 52) TRUE 53) FALSE 54) FALSE 55) FALSE 56) TRUE 57) B 58) B 59) D 60) B 61) C 62) C 63) D 64) B 65) C 66) C 67) C 68) A 69) TRUE 70) C 71) D 72) A 73) D 74) B 75) B 10 Walker_Maryann Friday, December 9, 2011 4:41:18 PM ET