Unit I – Levels of Organization Chapter 1 – Introduction to Human
advertisement

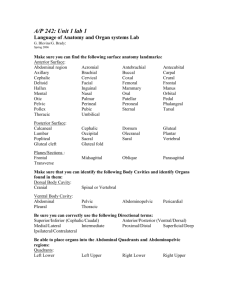
Unit I – Levels of Organization Chapter 1 – Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology - the basis for the language of anatomy and physiology is Greek & Latin. Anatomy – branch of science that deals with the structure (morphology) of body parts. (form and arrangement) Physiology – functions of body parts (what they do & how they do it) Characteristics of Life Movement – changing position or moving of internal parts Responsiveness – sense changes that occur Growth – increase in size Reproduction – producing offspring Respiration – obtaining oxygen Digestion – breaking down of substances Absorption – passing of substances across a membrane Circulation – movement of body fluids Assilimation – change of substances into a chemically different form Excretion – removal of wastes All of these together – working together – is your metabolism! All organisms need basic essentials: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Water – needed to transport fluids and substances throughout your body & to regulate body temp. Food – source of energy Oxygen – used to release energy from food Heat – related to metabolism (increased heat = increased metabolism) Pressure – pressure of gravity on body = atmospheric pressure – important to breathing - pressure of water on body = hydrostatic pressure – important to blood pressure Homeostasis – maintaining a balance between the inside and outside. Hypertonic – more concentration inside than outside - concentration will move out - eating salty peanuts Hypotonic – more concentration outside than inside - concentration will move in - drinking water when cells are dehydrated Isotonic – some concentration inside as outside - concentration is at an equilibrium - related to your cells – fluids and substances are always moving in and out of cells. They are trying to maintain a balance. Homeostasis mechanisms in your body – Body Temperature = 98.6°F (37°C) Problem: Cold – your body temp. drops below 98.6°F Solution: Your body starts to shiver to move muscles. The movement of your muscles produces heat. Your body constricts blood vessels next to skin. This will not allow the warmth in blood to get close to the skin and leave. Problem: Heat – your body temp. rises above 98.6°F Solution: Your body starts to sweat. The sweat moves to the surface of the skin to be evaporated. This evaporation process will cause cooling of the body. Your body makes the blood vessels near the skin get larger. This allows for more heat to be removed from your body. Your heart starts beating faster. This allows for more blood to flow to the skin and release more heat. Blood Pressure – Problem = high blood pressure Solution = the heart beats less often. The contracting of the heart will cause more pressure or force on blood vessels than there already is. Problem = low blood pressure Solution = the heart beats more often. The contracting of the heart will cause more pressure or force on the blood vessels. Levels of Organization Atoms – tiny, visible particles that make up all things Molecules – many atoms bunched together Cells – organelles inside cells make them work Tissues – layers of cells Organs – many layers of tissues Organ Systems – many organs working together Organism – a living thing Organization of the Human Body Body Cavities: Axial Portion – everything but the arms and legs Appendicular Portion – arms & legs I. Axial Cavities A. Dorsal Cavity: 1. Cranial Cavity – skull & Brain 2. Spinal Cavity – spinal cord and vertebrae B. Ventral Cavity: 1. Thoracic Cavity – skin, muscles, bones, (organs = heart and lungs) - thoracic and abdominopelvic cavity are separated by the diaphragm 2. Abdominopelvic cavity – skin, muscles, bones 1. Upper Abdominopelvic cavity – organs: stomach, liver, spleen, gall bladder, small and large intestines. 2. Lower Pelvic Cavity – organs: end of large intestine, urinary bladder, reproductive organs. 3. Other Cavities: 1. Oral Cavity – teeth and tongue 2. Nasal Cavity – nostrils, sinuses 3. Orbital Cavity – eyes 4. Middle Ear Cavity – middle ear bones Thoracic and Abdominopelvic Membranes - a parietal membrane is on the outside with a cavity of fluid in between the visceral membrane, which is always on top of the organ. I. Thoracic Membranes A. Pleural Membranes – membranes that surround the lungs 1. Parietal pleura – membrane that is attached to the wall of the thoracic cavity and forms a lining. 2. Visceral Pleura – membrane that covers the organ. There are two sections in the thoracic cavity. One section includes the lungs. The second includes the heart, esophagus, trachea, and thymus gland. A region called the mediastinum separates them. The largest portion of the mediastinum contains the heart. B. Pericardial Membranes – membranes that surround the heart. 1. Parietal Pericardium – outer most lining around the heart. 2. Visceral Pericardium – inner most lining around the heart (lining on the organ) II. Abdominopelvic Membrane A. Peritoneal Membranes – membranes that surrounds organs in the abdomen. 1. Parietal Peritoneum – outer most lining around organs. 2. Visceral Peritoneum – inner most lining around the organs (lining on the organ) Organ Systems (11 Systems) Integumentary System – body covering Includes: skin, hair, nails, sweat glands, sebaceous glands. - aides in regulating body temperature and in sensory. Skeletal System – support Includes: muscles and bones Nervous System – adjust body for homeostasis Includes: brain, spinal cord, nerves, sense organs - detects changes in body or that occur around body Endocrine System – adjust body for homeostasis Includes: pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas, thymus, ovary, testes, pineal - glands that produce hormones Hormones – produced by glands to effect a target tissue. Hormones will alter the metabolism of the target tissue. Will occur for a relatively long period. Digestive System – processing and transporting nutrients, oxygen, and wastes. Includes: mouth, tongue, teeth, salivary glands, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, liver, gall bladder, pancreas, small and large intestine. - breaks down food into smaller molecules to get energy. Respiratory System – processing and transporting intake and output of air for exchange of gases between blood and air Includes: nasal cavity, pharynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs Circulatory System – processing and transporting blood Includes: heart, arteries, veins, capillaries, blood - blood carries gases, nutrients, hormones, and wastes Lymphatic System – processing and transporting Includes: lymphatic vessels, lymphatic fluids, lymph nodes, thymus gland, spleen - transports tissue fluid from tissue back to blood stream and carries fatty substances away from digestive organs. - also aids in defending your body against infections. Urinary System – processing and transporting Includes: kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra - maintains body’s water, electrolytes, and acid/base balance Reproductive System – reproduction Includes: male = scrotum, testes, epididymides, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, bulbourethral glands, penis, urethra. female = ovaries, uterine tube, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, clitoris, vulva Anatomical Terminology Anatomical Position – standing up right, face forward, arms at side, palms forward. Positions: Superior – above a body part or close to head Inferior – below a body part or close to feet Anterior – front (ventral) Posterior – back (dorsal) Medial – imaginary midline that divides the body into right and left halves Lateral – sides Proximal – a body part that is closer to a point of attachment or closer to the trunk of the body than another part. Distal – a body part that is farther to a point of attachment or farther from the trunk of the body than another part. Superficial – near the surface Peripheral – also means outward or near the surface Deep – describes where the internal organs are Body Sections: Sagittal – dividing the body into a right and left portion Transverse – dividing the body into a top and bottom portion (horizontal) Frontal – dividing the body into a front and back portion (coronal) Body Regions: Epigastric Region – upper region where stomach is Umbilical Region – middle portion; intestines behind belly button Hypogastric Region – lower region of intestine