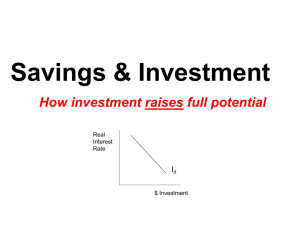
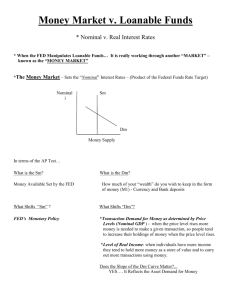
Study Guide 3 S2014.tst
advertisement

ECON102 Spring 2014 Study Guide 3 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) An increase in the demand for loanable funds will occur if there is A) an increase in the real interest rate. B) an increase in the nominal interest rate accompanied by an equal increase in inflation. C) an increase in expected profits from firm investment projects. D) a decrease in the real interest rate. 2) In a closed economy, private saving is equal to which of the following? (Y = GDP, C = Consumption, G = Government purchases, T = Taxes, and TR = Transfers) A) Y +TR - C - T B) Y - G - T C) Y - G - T +TR D) Y - C - T 3) The quantity of goods and services that can be produced by one worker or by one hour of work is referred to as A) human capital. B) technology. C) real GDP. D) labor productivity. 4) If government saving is negative, then A) T - TR < G. B) Y +TR < C - T. C) T > TR. D) G > T. 5) If government purchases are $400 million, taxes are $700 million, and transfers are $200 million, which of the following is true? A) Public saving is $500 million. B) The budget deficit is $500 million. C) Public saving is $100 million. D) The budget deficit is $100 million. 6) The demand for loanable funds is downward sloping because the ________ the interest rate, the ________ the number of profitable investment projects a firm can undertake, and the ________ the quantity demanded of loanable funds. A) greater; greater; greater B) greater; smaller; greater C) lower; greater; greater D) lower; smaller; greater 7) According to the "Rule of 70", how many years will it take for real GDP per capita to double when the growth rate of real GDP per capita is 5%? A) less than 1 year B) 5 years C) 14 years D) 35 years 8) Potential GDP refers to A) the difference between the highest level of real GDP per quarter and the lowest level of real GDP per quarter within any given year. B) the level of GDP attained when all firms are producing at capacity. C) the level of GDP attained by the country with the highest growth in real GDP in a given year. D) the extent to which real GDP is above or below nominal GDP. 9) Financial securities that represent promises to repay a fixed amount of funds are known as A) stocks. B) bonds. C) pension funds. D) insurance premiums. 1 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 10) Explain and show graphically how an increase in household saving affects the equilibrium interest rate and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds. 11) What factors increase potential GDP? Include a definition of potential GDP in your answer. 12) Consider the following data for a closed economy: a. Y = $12 trillion b. C = $8 trillion c. I= $3 trillion d. TR = $2 trillion e. T = $3 trillion Use the data provided to calculate the level of private saving and the level of public saving and demonstrate their relationship to investment. 13) Explain and show graphically how an increase in government spending affects the equilibrium interest rate in the market for loanable funds. 2 Answer Key Testname: STUDY GUIDE 3 S2014 1) C 2) A 3) D 4) A 5) C 6) C 7) C 8) B 9) B 10) An increase in household saving increases the supply of loanable funds, shifting the supply curve for loanable funds to the right, as shown below. The increase in the supply of loanable funds results in a decrease in the equilibrium interest rate and an increase in the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds. 11) Potential GDP is the level of GDP attained when all firms are producing at capacity. Growth in potential GDP is determined by growth in the labor force and the capital stock and by technological change. Capital investments accompany growth in the labor force, encouraging technological progress and increasing potential GDP. 12) Private saving is equal to Y +TR - C - T, and public saving is equal to T - G - TR. Plugging in the appropriate numbers for private saving, private saving = Y +TR - C - T = $12t + $2t - $8t - $3t = $3 trillion. Using the identity for output in a closed economy, G = Y - C - I = $12t - $8t - $3t = $1t, so public saving = $3t - $1t - $2t = $0. Adding together private saving of $3 trillion and public saving of $0 yields saving of $3 trillion, which is exactly equal to investment of $3 trillion. 13) When government spending increases, government saving (T - G - TR) falls. This decrease in government saving shifts the supply curve for loanable funds to the left, increasing the equilibrium interest rate as shown below. 3