Mitosis and Meiosis Vocabulary These terms relate to the Production
advertisement

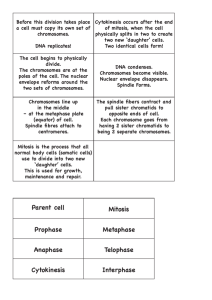
Mitosis and Meiosis Vocabulary These terms relate to the Production of body cells: Mitosis Surface area to volume ratio - the amount of surface covering an object (or a cell) compared to the volume contained within; as surface to volume ratio decreases in cells, division becomes necessary Cell Division - the process of creating two new cells Mitosis - when the nucleus itself divides into two new nuclei Cytokinesis - when the rest of the cell divides to form two new daughter cells Chromatin - when the DNA inside the nucleus appears as disorganized, long strands Chromosomes - when the DNA coils tightly, shortens and thickens prior to mitosis DNA molecule - another name for a chromosome; contains the genes Replication - the process of chromosomes making exact duplicates Sister chromatids - the two sides of the "X" formed by replicated chromosomes Centromere - a central protein bundle that connects sister chromatids Autosomes - all chromosomes except for the sex chromosomes Genes - codes within DNA that specify a particular trait Alleles - two alternate forms of each gene (such as blue eyes or brown eyes) Somatic cells - All of the body cells Gametes - sperm and egg cells, also referred to as sex cells Diploid number - the total number of chromosomes in normal body cells; two matching homologs of each kind Cell cycle - the entire life cycle of the parent cell Interphase- the cell is carrying out its normal everyday cell activities as well as preparing for the Mitotic phase G1 and G2 phases - gap phases; G1 is mostly growth and development G2 occurs after replication of chromosomes and involves replication of additional organelles and membranes in preparation for cell division S phase - synthesis of new DNA; also called replication Prophase -the first phase of mitosis characterized by a disappearance of the nuclear membrane and nucleolus Spindle basket - This structure will assist in pulling apart the doubled chromosomes Metaphase - the second phase of mitosis where all of the doubled chromosomes move to the center of the cell, called the equator Anaphase - the third phase of mitosis where the spindle fiber shorten from the poles, pulling the doubled chromosomes apart from each other, toward the poles of the cell Telophase - the final phase of mitosis characterized by the separated chromosomes reaching the poles of the cell. The nuclear membrane and nucleolus begins to reappear around each set of chromosomes Cell plate - a structure which eventually forms a cell wall that begins to grow out from the center and merely separates the two daughter cells Microtubule - organizing center which performs the job of the centriole in plants These terms refer specifically to meiosis Genetic recombinations - different ways chromosomes can provide variation in the species depending on which chromosomes are inherited and whether or not crossing over occurs Sex chromosomes - in humans, XY designates a male; XX designates a female Crossing over - each chromatid may exchange a part of itself with its homolog as it crosses over the other during late prophase I or early metaphase I of meiosis Homologous pairs - matching chromosomes that each came from either the father or the mother; homologs code for different versions of the same genes Meiosis - the division of a nucleus that results in four nuclei with one half the original number of chromosomes; used to produce gametes Haploid number - one half the total number of chromosomes in a normal body cell; one of each kind of homolog Oogenesis - meiosis that produces eggs (ova) Ovum - an egg resulting from oogenesis Spermatogenesis - meiosis that produces sperm These terms relate to testing of the fetus for any genetic disorder: Nondisjunction Mutations - improper separation of sister chromatids may result in a cell having one too many chromosomes (trisomy) or not having one of a certain chromosome (monosomy) Karyotype - a photograph of an individual's chromosomes Amniocentesis - when a long needle withdraws fluid around fetus; some of the embryo's cells that have sloughed off into the fluid will be collected and examined Chorionic Villi Testing - scraping a few cells from villi of the placenta which connect fetus to mother in the uterus Ultrasound - images formed by sound waves can be converted into pictures of the uterus to determine gross structural abnormalities of the fetus; this is a safe and non-invasive procedure