Word Roots
advertisement

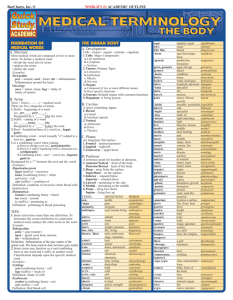
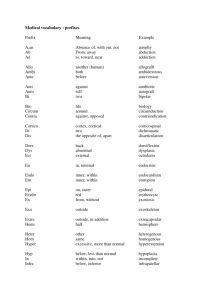
lecture 3 Medical Terminology Word Parts and Word Building Rules Word Roots TIPS: 1.Some terms have more than one definition. To determine the correct definition in a particular medical word, analyze the other terms in the word. Example: Poliomyelitis polio = gray (matter) myel = spinal cord, bone marrow itis = inflammation Definition: Inflammation of the gray matter of the spinal cord. The bone marrow does not have gray matter. 2.Some terms may function as a root/combining form in one word and a suffix in another word. Classification depends upon the specific medical word. Examples: Cytology cyto (combining form) = cell logy (suffix) = study of Definition: Study of cells Erythrocyte erythro (combining form) = red cyte (suffix) = cell Definition: Red blood cell A word root is the foundation of a medical term and contains its primary meaning. All medical terms have at least one word root. Most word roots are derived from Greek or Latin language. Thus, two different roots may have the same meaning. For example, the Greek word dermatos and the Latin word cutane both refer to the skin. As a general rule, Greek roots are used to build words that describe a disease, condition, treatment, or diagnosis. Latin roots are used to build words that describe anatomical structures. Consequently, the Greek root dermat is used primarily in terms that describe a disease, condition, treatment, or diagnosis of the skin; the Latin root cutane is used primarily to describe an anatomical structure. (See Table 1-1.) Table 1-1 Examples of Word Roots This table lists examples of word roots as well as their phonetic pronunciations. Begin learning the pronunciations as you review the information below. English Term Greek or Latin Term* Word Root Word Analysis skin dermatos (Gr) dermat dermat/itis (dĕr-mă-T Ī-tı̆s): inflammation of the skin A term that describes a skin disease cutis (L) cutane cutane/ous (sŭb-kū-TĀ-nē-ŭs): pertaining to the skin A term that describes an anatomical structure kidney nephros (Gr) nephr nephr/oma (nĕ-FRŌ-mă): tumor of the kidney A term that describes a kidney disease renes (L) ren ren/al (RĒ-năl): pertains to the kidney A term that describes an anatomical structure mouth stomatos (Gr) stomat stomat/itis (stō-mă-T Ī-tı̆s): inflammation of the mouth A term that describes any inflammatory condition of the mouth oris (L) or or/al (OR-ăl): pertaining to the mouth A term that describes an anatomical structure *It is not important to know the origin of a medical word.This information is provided here to help avoid confusion and illustrate that there may be two different word roots for a single term. 1 Word Parts and Word Building Rules Combining Form A combining form is created when a word root is combined with a vowel. This vowel, known as a combining vowel, is usually an o, but occasionally it is an i. The combining vowel is used to join the word parts appropriately when creating words. It also helps in pronunciation by allowing the word to flow as opposed to being choppy without the aid of the vowel. Rule: Generally, when using more than one word root (as in a compound word) a combining vowel is needed to separate the different word roots regardless of whether the second or third word root begins with a vowel. (There are exceptions to the rule!) Example 1: In the word cardiomyopathy, which means “any disease that affects the structure and function of the heart (i.e., the heart muscle),” there are two word roots: cardi (meaning “heart”) and my (meaning “muscle”). These are followed by the suffix -pathy, which means “disease.” The best way to determine the number of word roots in a compound word is to look for the combining vowels and divide, or separate, the word into elements. Let’s divide the word cardiomyopathy to illustrate. cardi / o / my / o / -pathy ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ root ⫹ vowel ⫹ root ⫹ vowel ⫹ suffix Example 2: In the word myoelectric, which means “pertaining to the electrical properties of the muscle,” there are two word roots: my (meaning “muscle”) and electr (meaning “electric”). These are followed by the suffix -ic, which means “pertaining to.” The combining vowel is used even though the word root electr begins with a vowel. my / o / electr ↑ ↑ ↑ root ⫹ vowel ⫹ root / -ic ↑ ⫹ suffix Example 3: Now comes an exception to the rule. In the word lymphadenopathy, which literally means “any disease of the lymph nodes” (but refers to enlargement of the lymph nodes, by dictionary definition), there are two roots: lymph (meaning “lymph”) and aden (meaning “gland”). These are followed by the suffix -pathy, which means “disease.” The combining vowel is not used in this word to separate the two roots, as it is in the others. There is not always a clear-cut explanation as to why the vowel is used in combining some roots and not in others, but the rule of using the vowel to separate the word roots in compound words applies more often than not. One might speculate that it is easier to pronounce lymphadenopathy without using the o than it would be if using the o to separate the two roots in this compound word. lymph / ↑ root 2 aden / ↑ ⫹ root ⫹ o ↑ / -pathy ↑ vowel ⫹ suffix Medical Terminology Word Parts Examples Medical Terms prefix + word root anti- (prefix meaning against) + thyroid (root word for thyroid gland) antithyroid • literal definition: against the thyroid • actual usage: (agent) suppressing thyroid activity word root + suffix gastr (word root for stomach) + -ic (suffix meaning pertaining to) gastric • definition: pertaining to the stomach combining form (word root + combining vowel) + suffix cardi (root word for heart) + /o (a combining vowel) + -logy (suffix meaning study of ) cardiology • definition: study of the heart prefix + suffix an- (prefix meaning no, without) + -emia (suffix meaning blood) anemia • literal definition: without (or no) blood • actual usage: decreased number of red blood cells or decreased hemoglobin in the cells prefix + root word + suffix epi- (prefix meaning above, over) + gastr (root word for stomach) + -algia (suffix meaning pain) epigastralgia • literal definition: pain above the stomach • actual usage: pain in the upper region of the abdomen compound word* + suffix ot/o (root word for ear) + rhin/o (root word for nose) + laryng/o (root word for throat or larynx) + -logy (suffix meaning study of ) otorhinolaryngology • definition: the branch of medicine dealing with diseases of the ear, nose, and throat * Two or more root words connected with a combining vowel. 4.1 Root words for body parts #1 Body element Greek root Latin root Examples abdomen lapar(o)- abodomin- Laparoscopy artery arteri(o)- — Arteriosclerosis blood hemat-, haemat- sangui-, sanguine- Hemorrhage (haem-, hem-) spleen Splen(o)- Lien(o)- Splenomegaly,lienorenal bone osteo- — Osteoarthritis brain encephal(o)- cerebr(o)- Encephalitis breast mast(o)- mamm(o)- Mastectomy chest steth(o)- thorac(i)-, thorac(o)- Thoracotomy ear ot(o)- aur- Otisis eye ophthalm(o)- ocul(o)- Ophthalmoscopy heart cardi(o)- cordi- Cardiograph intestine enter(o)- — Enterotoxins 3 Word Parts and Word Building Rules 4.2 Root words for body parts #2 Body element Greek root Latin root Examples kidney nephr(o)- ren- Nephrology, renal liver hepat- (hepatic-) — Hepatitis lungs pneumon- pulmon(i)- (pulmo-) Pneumonia mind psych- — Psychology neck trachel(o)- cervic- Tracheotomy, nerve; the nervous system neur(o)- nerv- Neurology nose rhin(o)- nas- Rhinitis, nasal skin dermat- (derm-) cut-, cuticul- Dermatitis skull crani(o)- — Cranium stomach gastr(o)- ventr(o)- Gastritis 4.3 Root words for body parts #3 Body element throat Greek root Latin root Examples pharyng(o)- — Pharyngitis laryng(o)- — Laryngitis tooth odont(o)- dent- Dentist tongue gloss-, glott- lingu(a)- Glossitis Gum Gingiva- — Gingivitis urine, urinary System ur(o)- urin(o)- Urologist, urinalysis vein, the veins phleb(o)- ven- Phlebitis, venous (upper throat cavity) throat (lower throat cavity/voice box]) 4.4 Colors Body element 4 Greek root Latin root Examples black melano- — Melanoma blue cyano- — Cyanosis gray, grey polio- — Poliomyelitis green chlor- — Chlorine red erythr(o)-, rhod(o)- rub-, rubr- Erythrocyte, ruby red-yellow cirrh(o)- — Cirrhosis white leuc-, leuk- alb- Leukemia, albino yellow xanth(o)- — Xanthoma Medical Terminology Table 2-2 Word Roots and Combining Forms for Body Parts Word Part Definition Word Example Pronunciation Definition abdomin/o abdomen abdominocystic ab-dom´-i-no-sis-tic pertaining to the abdomen and gallbladder aden/o gland adenitis ad´-e-ni-tis inflammation of a gland an/o anus anoplasty an´-oh-plas-te plastic repair of the anus andr/o men android an-droid resembling a man angi/o vessel angiectomy an´-je´-ek-to-me excision of part of a blood vessel or lymph vessel appendage attached to or outgrowth appendectomy ah-pen-dek´-to-me excision of the vermiform appendix appendic/o appendix appendicolysis ah-pen-di-kol´-i-sis surgical separation of adhesions binding the appendix arteri/o artery arteriogram ar-te-re-o-gram´ an x-ray picture of an artery arthr/o joint arthrocele ar-thro-sel a joint swelling cardi/o heart cardiology kar-de-ol´-ogy study of the heart cephal/o head cephalic se´-phăl-ic pertaining to the head cerebr/o cerebrum (part of the brain) cerebral ser´-e-bral pertaining to the brain cyst/o bladder cystocele sis-toh-seel hernia of the bladder into the vagina cyt/o cell cytology si´-toh-lōgy study of the body cells encephal/o brain encephaloma en-sef´-ah-lo-mah a swelling or tumor of the brain (continues) 5 ch02.indd 9 7/18/2013 6:23:33 PM Word Parts and Word Building Rules Table 2-2 Word Roots and Combining Forms for Body Parts (continued ) Word Part Definition Word Example Pronunciation Definition enter/o intestines enteritis en-ter-i´-tis inflammation of the intestine (usually small intestine) esophag/o esophagus esophagism e-sof-ah-jism spasm of the esophagus gastro/o stomach gastropathy gas-trop-ah-the any disease of the stomach gloss/o tongue glossodynia glos´-o-din-e-ah pain in the tongue gyne woman gynephobia jin´-e-fo-be-ah morbid aversion to women hem/o blood hematoma he-ma-toh´-mah blood clot in an organ or under the skin hepat/o liver hepatocele hep-ah-to-sel hernia of the liver hyster/o uterus hysterolith his-ter-o-lith´ a uterine calculus (stone) ile/o ileum (small intestine) Ileus il-e-us intestinal obstruction irid/o iris (eye) iridomalacia ir´-i-do-mah-la-sheah softening of the iris kerat/o cornea of eye; horny substance keratorrhexis ker´-ah-to-rek-sis rupture of the cornea lamina, lamin/o thin, flat part of vertebra laminotomy lam´-i-not-o-me transection of a vertebral lamina lapar/o abdominal wall laparorrhaphy lap´-ah-ror-ah-fe suture of the abdominal wall lingua tongue nigralingua ni-gra-ling-gwah black tongue lob/o lobe, as of lung or brain lobotomy lo-bot-o-me cutting of nerve fibers connecting a lobe of the brain with the thalamus mamm/o breast mammogram mam-o-gram x-ray recording of breast tissue mast/o breast mastitis mas-ti-tis inflammation of the breast my/o muscle myocarditis mi´-o-kar-di-tis inflammation of the heart muscle myel/o bone marrow; spinal cord myelocyte mi-e-lo-sit´ immature cell of bone marrow myring/o eardrum myringoplasty mi-ring-o-plas´-te surgical reconstruction of the eardrum nephr/o kidney nephritis ne-fri-tis inflammation of the kidney neur/o nerve neuralgia nu-ral-je-ah pain in a nerve oophor/o ovary oophorocystosis o-of´-o-ro-sis-to-sis formation of an ovarian cyst ophthalm/o eye ophthalmorrhagia of-thal´-mo-ra-je-ah hemorrhage from the eye orchi/o testicle orchiopathy or´-ke-op-ah-the any disease of the testes 6 ch02.indd 10 7/18/2013 6:23:34 PM Medical Terminology Table 2-2 Word Roots and Combining Forms for Body Parts (continued ) Word Part Definition Word Example Pronunciation Definition orchid/o testicle orchidorrhaphy or´-ki-dor-ah-fe surgical fixation of an undescended testis into the scrotum by suturing oste/o bone osteoporosis os´-te-o-po-ro-sis abnormal thinning of the skeleton ot/o ear otitis o-ti-tis inflammation of the ear pancreat/o pancreas pancreatogenous pan´-kre-ah-toje-nus arising in the pancreas pharyng/o pharynx pharyngismus far´-in-jis-mus muscular spasm of the pharynx phleb/o vein phlebotomy fle-bot-o-me incision of a vein pneum/o lungs (air or gas) pneumonectomy nu´-mo-nek-to-me excision of lung tissue proct/o rectum proctodynia prok´-to-din-e-ah pain in the rectum prostat/o prostate gland prostatitis pros´-tah-ti-tis inflammation of the prostate pyel/o pelvis of kidney pyelectasis pi´-e-lek-tah-sis dilation of the renal pelvis rect/o rectum and/or anus rectocele rek-to-sel hernial protrusion of part of the rectum into the vagina ren/i renal (kidney) reniform ren-i-form kidney-shaped rhin/o nose rhinitis ri-ni-tis inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose sacr/o sacrum sacrolumbar sa´-kro-lum-bar pertaining to the sacrum and loins salping/o fallopian tube salpingocyesis sal-ping´-go-ci-e-sis development of an embryo in the uterine tube; a tubal pregnancy splen/o spleen splenoptosis sple-nop-to-sis downward displacement of the spleen spondyl/o vertebra spondylodymus spon´-di-lod-i-mus twin fetuses united by the vertebrae steth/o chest stethospasm steth-o-spasm spasm of the chest muscles stomat/o mouth stomatomalacia sto-mah-to-ma-lashe-ah softening of the structures of the mouth ten/o tendon tendolysis ten-dol-i-sis the freeing of tendon adhesions thorac/a thorax (chest) thoracentesis tho´-rah-sen-te-sis surgical puncture and drainage of the thoracic cavity thyr/o thyroid gland thyroxine thi-rok-sin a hormone of the thyroid gland that contains iodine trache/o trachea tracheoscopy tra´-ke-os-ko-pe inspection of the interior of the trachea (continues) 7 ch02.indd 11 7/18/2013 6:23:35 PM Word Parts and Word Building Rules Table 2-2 Word Roots and Combining Forms for Body Parts (continued ) Word Part Definition Word Example Pronunciation Definition tympan/o eardrum tympanum tim-pah-num part of the cavity of the middle ear, in the temporal bone ureter/o ureter ureteropathy u-re´-ter-op-ah-the any disease of the ureter vas/o vessel vascular vas-ku-lar pertaining to blood vessels ven/i vein venipuncture ven´-i-punk-chur surgical puncture of a vein ch02.indd 12 7/18/2013 6:23:35 PM