REACH Product Information Sheet
advertisement

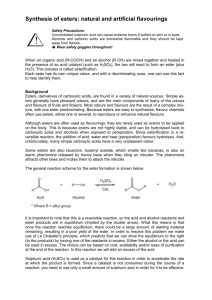
FOOD & NUTRITION EUROPE EMULSIFIERS EMULSIFIERS The multiple functionalities of emulsifiers EMULSIONS AND EMULSIFIERS An emulsion is a blend of two immiscible liquids, with droplets of one phase (dispersed phase) distributed in the other phase (continuous phase). In general these are unstable systems in which the dispersed phase droplets tend to agglomerate or coalescence and separate out. The boundary between the two phases is called the interface. continuous phase oil phase dispersed phase water phase interface Emulsifiers contain both hydrophilic and lipophilic parts. The hydrophilic head is easy to hydrate (water soluble) and the lipophilic tail is impossible or very difficult to hydrate (oil soluble). Emulsifiers concentrate at the interface between oil and water and reduce the surface or interfacial tension, thereby making the emulsion more stable. In many industries emulsifiers are referred to as “surfactants”, which is an abbreviation of surface active agents. hydrophilic head lipophilic tail In commercial food emulsifiers the hydrophilic part can consist of glycerol, sorbitol, sucrose, propylene glycol or polyglycerol. The lipophilic part is formed by fatty acids derived from fats and oils such as soybean oil, rapeseed oil, coconut oil and palm kernel oils. oil-in-water (O/W) emulsion water-in-oil (W/O) emulsion Page 2 of 13 Brenntag Food & Nutrition Europe, Stinnes Platz 1, 45472 Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany, Phone: +49 (0)208 7828 7015, Fax: +49 (0)208 7828 149, email: food-europe@brenntag.eu, www.brenntag-specialties-europe.com EMULSIFIERS The stability of an emulsion depends on: Droplet size: a smaller droplet size facilitates emulsion stability. The droplet size can be influenced by homogenization. Viscosity of continuous phase: a higher viscosity facilitates emulsion stability. The viscosity of the water phase can be influenced by the addition of hydrocolloids or thickening agents. Specific density of the two phases: if the difference in density between the two phases is small, the emulsion will be more stable. For essential oils in beverages weighting agents can be used to increase the density of the essential oil. Quality of the interfacial film: the film can consist of emulsifiers and / or proteins. EMULSIFIERS PRODUCT RANGE Following emulsifiers are generally used in the food processing industry: E number Short name Long name E 322 Lecithins Lecithins E 432 – 436 Polysorbates Polyoxyethylene sorbitan esters E 471 MDG / Monoglycerides Mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids E 472 a ACETEM Acetic acid esters of MDG E 472 b LACTEM Lactic acid esters of MDG E 472 c CITREM Citric acid esters of MDG E 472 e DATEM Mono- and diacetyl tartaric acid esters of MDG E 473 Sucrose esters Sucrose esters of fatty acids E 475 Polyglycerol esters Polyglycerol esters of fatty acids E 476 PGPR Polyglycerol polyricinoleate E 477 Propylene glycol esters Propane-1,2-diol esters of fatty acids E 481 SSL Sodium stearoyl-2-lactylate E 482 CSL Calcium stearoyl-2-lactylate E 491 – 495 Sorbitan fatty acid esters Source and Manufacturing Below information on raw material source and manufacturing of food emulsifiers provides some insight in the molecular structure of emulsifiers. Lecithin (E322) is a mixture of phospholipids, it consists of a glycerol backbone with phosphatidyl groups. The phosphatidyl groups are phosphate esters of diglyceride. Lecithin is a natural emulsifier, obtained mainly from vegetable oilseeds. Monoglycerides are the most commonly used food emulsifiers. Monoglycerides are produced from glycerol and oils or fats (triglycerides). Fats, Oils, Fatty Acids + Glycerol Monoglycerides (E471) Monoglycerides can be further processed by esterification with organic acids: Monoglycerides + Acetic acid anhydride ACETEM (E472a) Page 3 of 13 Brenntag Food & Nutrition Europe, Stinnes Platz 1, 45472 Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany, Phone: +49 (0)208 7828 7015, Fax: +49 (0)208 7828 149, email: food-europe@brenntag.eu, www.brenntag-specialties-europe.com EMULSIFIERS Monoglycerides + Lactic acid LACTEM (E472 b) Monoglycerides + Citric acid CITREM (E472 c) Monoglycerides + Tartaric acid Acetic acid anhydride DATEM (E472e) Instead of glycerol other hydrophilic alcohols can be used for the manufacturing of food emulsifiers: Sorbitol Sorbitan fatty acid esters (E491 – 495) Sorbitan fatty acid esters (E491 – 495) can be further processed into: Polysorbates (E432 – 436) Fats, Oils, Fatty Acids + Polyglycerol Polyglycerol esters (E475, E476) Fats, Oils, Fatty Acids + Propylene glycol Propylene glycol esters (E477) Fats, Oils, Fatty Acids + Sugar Sucrose esters (E473) Fats, Oils, Fatty Acids + Lactic acid Fats, Oils, Fatty Acids + further processed to: SSL (E481) & CSL (E 482) Product characteristics Some issues which are important to notice while working with food emulsifiers are the following: Emulsifiers are mixtures During the esterification process the fatty acids are distributed at random, so a mixture of mono- and diglyceride (esters) are formed. Each molecule has slightly different functionalities. As an example a simplified picture of theoretical possible structures for a MDG ester are given. Commercial emulsifiers are characterised by the major component, but minor amounts of related molecules will also be present. fatty acid organic acid glycerol fatty acid fatty acid glycerol organic acid fatty acid glycerol glycerol fatty acid OH H HJ organic acid Page 4 of 13 Brenntag Food & Nutrition Europe, Stinnes Platz 1, 45472 Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany, Phone: +49 (0)208 7828 7015, Fax: +49 (0)208 7828 149, email: food-europe@brenntag.eu, www.brenntag-specialties-europe.com EMULSIFIERS fatty acid organic acid glycerol organic acid glycerol glycerol fatty acid fatty acid organic acid organic acid organic acid OH Monoglycerides are characterised by their mono-content, e.g. 90% or 60%. Fatty acid composition The type of fatty acid (the type of fat or oil used) influences the characteristics of the emulsifier. Therefore some understanding of fat technology helps understanding emulsifier behaviour. The fatty acid composition influences the melting point of fats and oils, and in the same way influences the melting point of emulsifiers. Fatty acids with a longer chain length and which are more saturated, will result in higher melting points. Monoglycerides are also characterised by the fatty acid composition: saturated or unsaturated fatty acids. Crystal form. Fats and oils can form different crystals which affect the texture and physical properties of the fat. The three major crystalline forms are referred to as alpha-, beta prime- and beta-crystals. The alpha crystal has the lowest melting point and forms fine and flexible agglomerates. Some emulsifiers are referred to as alpha tending emulsifiers; these are most stable in the alpha crystalline form. The alpha crystalline formation is very effective for whipping properties. HLB: Hydrophilic Lipophilic Balance Emulsifiers can be characterized by the Hydrophilic Lipophilic Balance. The balance is measured on molecular weight and is an indication of the solubility of the emulsifier. The HLB scale varies between 0 and 20. An emulsifier with a low HLB value is more soluble in oil and promotes water-in-oil emulsions. An emulsifier with a high HLB value is more soluble in water and promotes oil-in-water emulsions. The HLB value is a somewhat theoretical value, it only considers water and oil, and food systems are more complicated. But the HLB value of an emulsifier can be used as an indication about its possible use. An indication of performance based on HLB value is given below. Mixing of oils W/O emulsions Wetting properties O/W emulsions Micro-emulsions HLB value: 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 Page 5 of 13 Brenntag Food & Nutrition Europe, Stinnes Platz 1, 45472 Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany, Phone: +49 (0)208 7828 7015, Fax: +49 (0)208 7828 149, email: food-europe@brenntag.eu, www.brenntag-specialties-europe.com EMULSIFIERS In a similar way also the average HLB value of emulsifiers can be given. Lecithins Polysorbates MDG ACETEM, LACTEM DATEM Sucrose esters Polyglycerol esters Propylene glcyol esters PGPR Sorbitan esters HLB value: 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 A very broad HLB range refers to different emulsifiers within one group. For example sucrose esters can be manufactured with a very high mono-content resulting in a high HLB value and with a very low mono content resulting in low HLB value, and therefore sucrose esters are covering almost the complete HLB scale. FUNCTIONALITY OF EMULSIFIERS Multi-Phase Systems As explained above emulsifiers concentrate to the surface between the oil and water phase, two liquid phases. But in fact emulsifiers will concentrate to any surface of two immiscible phases, so also to: the interface of gas and liquid / solid as air bubbles in a whipped cream or cake batter. the interface of solids and liquids as ice crystals in icecream or sugar crystals in chocolate. Emulsifiers influence the consistency, the viscosity and the texture of many multi-phase food systems. Interaction with other ingredients Emulsifiers interact with many other components in food systems resulting in different functionalities. Interaction with starch Emulsifiers with a long fatty acid chain form complexes with starch; the fatty acid chain penetrates the amylose helix and prevents starch retrogradation. Retrogradation is the mechanism responsible for staling of bread, so the use of emulsifiers can extend the shelf life. Another attribute of the use of emulsifiers in starch based products is the reduction of stickiness in reconstituted products such as pasta and instant mashed potatoes. Page 6 of 13 Brenntag Food & Nutrition Europe, Stinnes Platz 1, 45472 Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany, Phone: +49 (0)208 7828 7015, Fax: +49 (0)208 7828 149, email: food-europe@brenntag.eu, www.brenntag-specialties-europe.com EMULSIFIERS Interaction with protein Emulsifiers with an ionic structure can interact with proteins, particularly wheat gluten. This interaction strengthens the gluten network in yeast raised dough, making it more stable against mechanical stress, resulting in increased volume and improved crumb structure. Interaction with fat Emulsifiers are fat-like substances and they influence fat in several ways. Emulsifiers can promote or inhibit crystallization, influence the crystal shape of the fat, and improve the dispersion of fat crystals inside the food product. Other functionalities Emulsifiers can also act as: lubricant and release agent, lubrication of extruded products but also lubrication of food processing equipment. release or anti-sticking agent, for demolding purposes during food processing or anti-sticking to confectionary packaging. The table below summarizes the functionalities of different emulsifiers: Emulsion stability Aeration properties Starch interaction Protein interaction Fat modification Lecithin (fluid) + _ + + ++++ Polysorbates + +++ +++ +++ + + E number Short name E 322 E 432 - 436 E 471 MDG +++ +++ ++++ _ E 472 a ACETEM n.a. ++++ n.a. n.a. n.a. E 472 b LACTEM n.a. ++++ n.a. n.a. n.a. E 472 e DATEM n.a. n.a. n.a. ++++ n.a. E 473 Sucrose esters ++++ ++++ n.a. n.a. n.a. E 475 Polyglycerol esters +++ ++++ + + +++ E 476 PGPR ++++ n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. ++++ + +++ +++ _ SSL, CSL ++++ +++ +++ ++++ _ Sorbitan esters +++ + _ _ ++++ E 477 Propylene glycol esters E 481- 482 E 491 - 495 ++++ excellent performance +++ good performance + some performance n.a. no references in literature This table is only a guideline. In most food products a combination of emulsifiers is used to achieve maximum functionality. PROCESSING REQUIREMENTS Optimal emulsifier functionality is determined by the correct food processing conditions. The most important factors are temperature and amount of energy applied in mixing or shearing. Emulsifiers need to be heated above their melting temperature to become functional. High speed mixing or homogenisation is needed to decrease droplet or air bubble size and get the emulsifiers distributed on the surface of the interface. Mixing is also needed to hydrate the emulsifier. Most food processing conditions will allow sufficient temperatures. But if the processing conditions are at too low temperatures or full hydration can not be ensured, then the emulsifiers need to be in a functional state before they are incorporated in the system. For these conditions the industry has developed emulsified shortenings, hydrated emulsifiers in paste and solid form and dry (whipping) concentrates, which can be used as an ingredient, and which are produced in such a way that the emulsifiers are in the optimal formation to be completely functional. Page 7 of 13 Brenntag Food & Nutrition Europe, Stinnes Platz 1, 45472 Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany, Phone: +49 (0)208 7828 7015, Fax: +49 (0)208 7828 149, email: food-europe@brenntag.eu, www.brenntag-specialties-europe.com EMULSIFIERS APPLICATIONS Below sections give short information about emulsifiers and their functionality in specific applications. It should be noted that in many cases combinations of emulsifiers are used to achieve the optimal performance. BAKERY Application Emulsifier Benefits Cake, Bread MDG Reacts with starch to delay retrogradation resulting in an improved softness of the crumb and extended shelf life. Bread DATEM Lecithin Strengthens the gluten, resulting in improved dough stability and improved gas retention. The final product shows a higher volume and a good crumb structure. Cake, Bread CSL SSL Provide starch as well as gluten interaction. Cake LACTEM ACETEM Polyglycerol esters Polypropylene glycol esters Sucrose esters Facilitate whipping of the batter and enhance volume as well as texture. The final choice of (combination of) emulsifier depends on the type of cake and the preparation method. Cake Aeration or whipping concentrates Powders or pastes with emulsifier combinations on carrier of dairy or vegetable proteins and carbohydrates. The emulsifiers within the concentrates are in the functional state so can be used in all-in method (all ingredients mixed at the same time) of cake preparation. Fillings LACTEM ACETEM Polyglycerol esters Polypropylene glycol esters Sucrose esters No fat, low fat and fat fillings, aerated or not aerated fillings use emulsifiers to achieve the right texture and stability. Depending on the type of filling and the required functionality, the optimal (combination of) emuslifer needs to be selected. Icings, fondants, fillings Sucrose esters Controlled sugar crystallisation resulting in small sugar crystals with a long shelf life and a whiter appearance. CONFECTIONARY Page 8 of 13 Brenntag Food & Nutrition Europe, Stinnes Platz 1, 45472 Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany, Phone: +49 (0)208 7828 7015, Fax: +49 (0)208 7828 149, email: food-europe@brenntag.eu, www.brenntag-specialties-europe.com EMULSIFIERS Application Emulsifier Benefits Soft candy Chewy candy Sucrose esters Controlled sugar crystallisation resulting in small sugar crystals with a long shelf life and an improved texture. Chocolate Lecithins PGPR Viscosity reduction and control in chocolate and reduction of fat bloom. The combination of PGPR and lecithin makes cocoabutter reduction possible while maintaining optimal viscosity and fluidity. Chewing gum Lecithins ACETEM Softening of the gum base, improved chew-ability and anti-sticking. CONVENIENCE FOOD Application Emulsifier Benefits Emulsified cooking sauces Several Stabilise the O/W emulsion, see functionality tables to select possible options. Salad dressings Mayonaise Several Stabilise the O/W emulsion, see functionality tables to select possible options. Emulsifier Benefits MDG Icecream is a multiphase system. MDG acts on each interface providing stabilisation, improved extrusion, improved heat shock and controlled overrun. MDG is the main used emulsifier in icecream, the MDG is often combined with other emulsifiers as used in the other whipped products. DAIRY Application Icecream Page 9 of 13 Brenntag Food & Nutrition Europe, Stinnes Platz 1, 45472 Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany, Phone: +49 (0)208 7828 7015, Fax: +49 (0)208 7828 149, email: food-europe@brenntag.eu, www.brenntag-specialties-europe.com EMULSIFIERS Application Emulsifier Benefits (Whipped) toppings and cream LACTEM ACETEM Polyglycerol esters Polypropylene glycol esters Sucrose esters Emulsion stabilisation, controlled overrun and volume, influence texture. Whipped dairy desserts LACTEM ACETEM Polyglycerol esters Polypropylene glycol esters Sucrose esters Emulsion stabilisation, controlled overrun and volume, improved texture and mouthfeel. LACTEM is preferred in RTE dessert, ACETEM is preferred in instant products. Aereated products Aeration or whipping concentrates Powders consisting of emulsifier combinations, vegetable oils and proteins on carbohydrate carrier. The emulsifiers within the concentrates are in the functional state so will be fully effective in any preparation method. Coffeewhiteners MDG Sorbitanesters Polysorbates Sucrose esters Different emulsifiers are used to stabilise the emulsion and prevent oil out. Sucrose esters protect proteins in acid products such as coffee, thus prevent feathering of coffee whiteners and creamers. UHT products Sucrose esters Sucrose esters interact with dairy proteins resulting in less sensitivity for heat and prevention of fouling of UHT equipment. Application Emulsifier Benefits Margarine and spreads MDG Emulsification and crystal modification in all types of margarines and spreads. In general MDG is the main emulsifier used and will be combined with other emulsifiers for additional functionalities. Cooking margarine CITREM Lecithin Anti-spatttering in cooking margarines. Reduced fat margarine and spreads PGPR Supports emulsification especially in low fat (40%) and very low fat (<30%) spreads. Industrial margarine Polyglycerol esters Improve plasticity in industrial margarine. Helps to create a dry surface in puff pastry margarine. Industrial margarine Polyglycerol esters PGPR Providing aeration by control of crystallisation in industrial margarines for cake preparation. FATS & OILS MEAT PROCESSING Page 10 of 13 Brenntag Food & Nutrition Europe, Stinnes Platz 1, 45472 Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany, Phone: +49 (0)208 7828 7015, Fax: +49 (0)208 7828 149, email: food-europe@brenntag.eu, www.brenntag-specialties-europe.com EMULSIFIERS Application Emulsifier Benefits Emulsified meat products CITREM Emulsification in emulsified sausages and pates, resulting in a better fat distribution and reduced fat separation. Meat Casing ACETEM Film forming properties which can be applied in meat casings. OTHER APPLICATIONS Application Emulsifier Benefits Release or demolding agents ACETEM Lecithin PGPR Release agent in demolding agents and lubricant for food processing equipment Dry powders Lecithin Excellent wetting agent to improve dispersability of powders Beverage base Polysorbates Stabilisation of flavour emulsions Extruded products several Lubrication in extruded starch based products such as pasta and noodles Canned coffee Sucrose esters Anti microbial properties, preventing spores development in canned coffee drinks. REGULATORY Emulsifiers are food additives. Their use is subject to EC Regulation 1333/2008 on Food Additives. Directive 95/2/EC on food additives other than colours and sweeteners will be replaced by Regulation 1333/2008, but will remain in force during the transition period to allow time to prepare Annexes. Food Additives which are permitted for use in foods as per Directive 95/2, shall be entered in the Annex of 1333/2008 after review. Annex 1 of Regulation 1333/2008 describes the functional classes of food additives: “Emulsifiers are substances which make it possible to form or maintain a homogenous mixture of two or more immiscible phases such as oil and water in a foodstuff.” The annexes listing the approved additives are not published yet. Therefore we refer to the annexes as in Directive 95/2. Annex I lists the food additives generally permitted for us in foodstuffs. These may be added following quantum satis principle. Following emulsifiers are listed in Annex 1: E 322 Lecithins Lecithins E 471 MDG / monoglycerides Mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids E 472 a ACETEM Acetic acid esters of MDG E 472 b LACTEM Lactic acid esters of MDG E 472 c CITREM Citric acid esters of MDG E 472 e DATEM Mono- and diacetyl tartaric acid esters of MDG Annex IV lists the “other permitted additieves”, for which the allowed applications as well as the maximum use levels are specified. Following emulsifiers are listed in Annex IV: E 432 – 436 Polysorbates Polyoxyethylene sorbitan esters E 473 Sucrose esters Sucrose esters of fatty acids Page 11 of 13 Brenntag Food & Nutrition Europe, Stinnes Platz 1, 45472 Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany, Phone: +49 (0)208 7828 7015, Fax: +49 (0)208 7828 149, email: food-europe@brenntag.eu, www.brenntag-specialties-europe.com EMULSIFIERS E 475 Polyglycerol esters Polyglycerol esters of fatty acids E 476 PGPR Polyglycerol polyricinoleate E 477 Propyleneglycol esters Propane-1,2-diol esters of fatty acids E 481 SSL Sodium stearoyl-2-lactylate E 482 CSL Calcium stearoyl-2-lactylate E 491 – 495 Sorbitan fatty acid esters For access to the complete text of the Regulations and Directives: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/nl/index.htm CONTACT US Brenntag Europe is delighted to offer its customers a wide portfolio of emulsifiers. If you would like to discuss with one of our food dedicated specialists, which particular products would best meet your requirements, then please write a short email to food-europe@brenntag.eu and your local Brenntag office will provide you with the requested information and samples. Information Sources: Report “Maximising the use of food emulsifiers”, Steven R. Baker, University of Illinois, 1997 Index of food emulsifiers, published by EFEMA, European Emulsifier Manufacturer´s Association (www.emulsifiers.org) “Emulsifiers for the Food Industry”, Clyde E. Stauffer, Chapter 8 from “Bailey’s Industrial Oil and Fat Products, 2005 Brochures and websites of our suppliers The data contained within this publication is intended for information purposes only and is correct to the best of our knowledge. Any recommendations or suggestions are made without warranty or guarantee. It is the sole responsibility of the user of the products to evaluate for each individual product, their suitability for a particular purpose and their legal and regulatory compliance. In addition, nothing contained within this publication should be construed as a recommendation to use any product in conflict with existing patents. Page 12 of 13 Brenntag Food & Nutrition Europe, Stinnes Platz 1, 45472 Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany, Phone: +49 (0)208 7828 7015, Fax: +49 (0)208 7828 149, email: food-europe@brenntag.eu, www.brenntag-specialties-europe.com YOUR RIGHT INGREDIENT – TODAY AND TOMORROW Brenntag Food & Nutrition Europe is committed to encouraging creativity and innovation that enables our partners to make the most out of trends and developments Please visit www.brenntag-specialties-europe.com FOOD&NUTRITION EUROPE Brenntag Food & Nutrition Europe Stinnes Platz 1 45472 Mülheim an der Ruhr Germany Phone: +49 (0) 208 7828 7015 Fax: +49 (0) 208 7828 149 email: food-europe@brenntag.eu www.brenntag-specialties-europe.com