Ch. 29 Plant Diversity I How Plants Colonized Land
advertisement

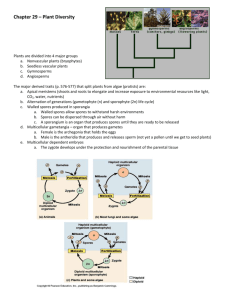
Ch. 29 Plant Diversity I How Plants Colonized Land Jan 24­7:37 PM 1 Essential Question How did plants make the transition from water to land? Jan 24­7:39 PM 2 Plant history ­cyanobacteria (algae) on land 1.2 billion years ago ­500 million years ago ­ plants on land ­currently about 290,000 species locations ­ all except mountain tops, some desert and polar regions ­important for other organisms to survive ­stabilize landscapes, supply oxygen, base of food chain Jan 24­7:42 PM 3 Characteristics that land plants have in common with protists (algae) 1. brown, green , red algae multicellular eukaryotic photoautotrophic 2. green algae, dinoflagellates, brown algae cell walls ­ cellulose 3. green algae, euglenoids, some dinoflagellates chloroplasts ­ chlorophyll a and b Jan 24­7:46 PM 4 Charophyceans closest relative of land plants green algae traits that land plants share with only charophyceans A. Structural/biochemical evidence 1. rosette cellulose­synthesizing complexes ­rose shaped proteins in plasma membrane ­other plants = linear ­higher % of cellulose Jan 24­7:54 PM 5 2. peroxisome enzymes = peroxisomes ­lower loss of organic products by photorespiration 3. Flagellated sperm ­ land plants with sperm and charophyceans is similar 4. Phragmoplast ­cytoskeletal elements that help form cell plate in mitosis http://botit.botany.wisc.edu/images/130/Meiosis/Lilium_microsporogenesis/Phragmoplast_Cell_Plate.html Jan 24­7:59 PM 6 B. Genetic evidence ­nuclear and chloroplast gene comparison between plant and algae closest to charophyceans (Charo and Coleochaete) Jan 24­8:03 PM 7 C. Adaptations for land ­charophyceans live on pond/lake edges ­edges can dry ­form a sporopollenin ­ polymer ­prevent desiccation ­could live on land ­once on land ­ample sunlight, carbon dioxide, soil nutrients, lack of herbivores & pathogens Jan 24­8:08 PM 8 A. Traits of land plants that Charophyceans do not have ­evolved as derived traits 1. Apical meristems ­ regions of cell division tips of shoots and roots ­cells become surface epidermis ­shoot apical meristems ­ generate leaves Jan 24­8:15 PM 9 2. Alternation of Generations ­reproductive cycle ­derived characteristic of land plants (not present in relative of land plants and charophyceans) ­both multicellular haploid and multicellular diploid stages Jan 24­8:26 PM 10 gametophyte­haploid reproduce by mitosis to make eggs and sperm sporophyte ­ diploid produce spores (haploid by meiosis) Jan 29­8:19 AM 11 3. walled spores produced in Sporangia sporangia = produce spores spores made by sporocytes by meiosis wall of spores = sporopollenin fern spore Jan 24­8:45 PM 12 4. Multicellular gametangia gametes have multicellular organs called gametangia female gametangia = archegonia male gametangia = antheridia Antheridium Archegonium Jan 24­8:53 PM 13 5. Multicellular, dependent embryos develop from zygotes in female placental transfer cells in embryo ­ help nutrients get from maternal tissue to embryo Jan 24­8:57 PM 14 other adaptations for land a. adaptations of water conservation 1.cuticle ­ polmers of polyesters and waxes ­ waterproofing to prevent desiccation 2. stomata ­ pores areas of gas exchange, and water evaporation stomata of begonia Cuticle http://employees.csbsju.edu/ssaupe/images/stomata/mettler.jpg Jan 24­9:21 PM 15 b. Adaptations of water transport (vascular tissue*) xylem ­ carry water and minerals up from roots ­made of dead cells phloem ­ carry nutrients (sugars, amino acids, other organic products * absent in bryophytes (mosses) Jan 24­9:30 PM 16 c. secondary compounds ­products of secondary metabolic pathways (branches off primary metabolic pathways) ­alkaloids ­terpenes ­tannins bitter ­ help against herbivores ­phenolics (flavenoids) ­ absorb UV rays, symbiotic relationships with soil microbes Jan 24­9:41 PM 17 Bryophytes ­ "nonvascular plants" liverwort moss moss hornwort Jan 24­9:49 PM 18 life cycle of moss Jan 28­8:33 PM 19 moss life cycle Jan 29­8:32 AM 20 In life cycle ­ gametophyte stage is dominant stage Sperm needs water (dew droplets) to get sperm to eggs Protonemata ­ mass of green, branched, one­ celled thick filaments that absorb water, cell to cell or some have conducting tissue Mar 10­8:33 AM 21 Sphagnum moss (peat moss) peat bog closeup leaf Jan 29­8:33 AM 22 mummy found in peat bog Mar 10­8:22 AM 23 origin of vascular plants carboniferous period ­ vascular plants began to diversify and seed plants not evolved yet 420 million years ago ­no taller than 50 cm. ­branched sporophytes Jan 28­8:37 PM 24 main traits of vascular plants: 1. life cycles­ dominant sporophytes (larger) than gametophyte 2. transport in vascular tissues xylem­ water/minerals ­has tracheids­tube­shaped cells (dead cells) that carry water/minerals up from roots ­ have lignin in cell walls phloem ­ sugar conducting cells (living) ­arranged in tubes ­transport sugar, amino acids Mar 10­8:16 AM 25 3. Evolution of roots ­organs that anchor plants, absorb water and nutrients from soil 4. Evolution of leaves ­organs that increase surface area for collecting solar energy for photosynthesis ­microphylls ­ small spine shaped leaves with single vein 410 million years ago ­megaphylls ­ leaves with highly vascular system; 370 million years ago Jan 28­8:48 PM 26 Hypothesis for evolution of leaves May have originated from sporangia May have evolved from the fusion of branched stems Jan 29­8:36 AM 27 ­evolution of sporophylls (modified leaves with sporangia) homosporous ­ one type of sporophyll with one type of spore heterosporous ­ two types of sporophylls and two kinds of spores megasporophylls ­ produce megaspores ­ make female gametophytes microspores ­ develop into male gametophytes Jan 28­8:59 PM 28 Pteridophytes Club moss Whisk fern fern horsetail Jan 28­8:36 PM 29 Lycophyte Jan 29­8:36 AM 30 Life cycle of a fern Jan 28­9:07 PM 31 fern sorus Jan 29­8:38 AM 32 Fern gametophyte Jan 29­8:39 AM 33 fern sporophytes Jan 29­8:40 AM 34 Artist's conception of carboniferous forest based on fossil evidence Jan 29­8:41 AM 35 ­only plants with vascular tissue can have true roots, stems, and leaves Feb 25­10:10 AM 36 So ­ what adaptations allowed plants to grow on land? Mar 10­9:21 AM 37 Mar 15­10:41 AM 38