Arquitecturas de Redes Integradas Ámbito
advertisement

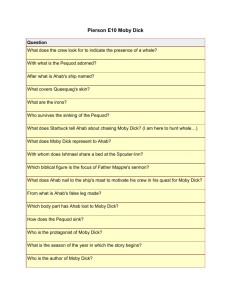
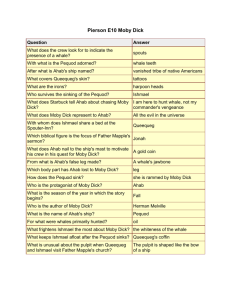
Arquitecturas de Redes Integradas Introducción Ámbito ?Realizar trabajos de investigación novedosos en aspectos relacionados con las tecnologías de red de 4ª Generación, incluyendo aspectos de movilidad, soporte de calidad de servicio, autenticación, autorización, contabilidad, gestión de perfiles de usuarios, así como la transición entre redes 3G y 4G. Introducción 2 1 1. Arquitectura 4G ? ? ? ? Arquitecturas de Red de 4G. Integración de tecnologías de acceso heterogeneas. Red de Acceso Radio basada en IP. Transición e interoperación 3G-4G 2. Movilidad ? ? ? Trabajos de investigación relacionados con el soporte de mecanismos eficientes de movilidad en redes 4G: Movilidad en redes 4G Interoperación con tecnologías de acceso heterogéneas 3. Calidad de Servicio ? ? ? ? Arquitecturas de red de soporte de QoS en 4G. Adaptación de parámetros con tecnologías de acceso heterogéneas. Armonización de mecanismos de QoS entre redes 3G y 4G. Nuevos mecanismos de señalización para proporcionar QoS extremo a extremo. 4. AAAC ? ? ? ? ? Protocolos de transporte de AAAC Interoperabilidad entre elementos de red basados en HLR/VLR y sistemas AAAC Soporte de Modelos de Pago: post-pago, pre-pago Soporte de mecanismos OSA en redes 4G. Análisis de vulnerabilidades y estudio de mecanismos de segurida d. 5. Servicios Introducción 3 Método ? Clases de seguimiento ~ mensuales. ? Presentación trabajo realizado y planificación a futuro. ? Discusión de resultados, método, trabajos relacionados. ? Generación de un artículo ~10 hojas y presentación final. ? Plazo entrega 1 de Julio 2004 ? Presentación semana 5-9 Julio 2004. Introducción 4 2 Planificación ?Presentación: 9/12/03 ?Presentación de trabajos: 9/01/2004 ?Seguimiento: 13/02/2004 ?Seguimiento: ?Seguimiento ?Seguimiento ?Entrega Artículo y Transparencias: 1 de Julio de 2004 ?Presentación Final: 5 de Julio de 2004 Introducción 5 Towards 4G – Facts and Assumptions ? Facts ? Millions of mobile devices/mobile users “walking” around the world – changing IP addresses ? Always on paradigm of the Internet ? Assumptions: ? Roaming Agreements - different operators/technologies ? Each user has one contract ? IP convergence layer ? 4G network will be a commercial one Introducción 6 3 Mobility Evolution 2G 3G Release 5 and beyond IPv6-based network with mobility, QoS and AAA IST Moby Dick IPv6 IPv4 2000 2010 Introducción 7 Moby Dick Problem Space Auditing Authentication AAAC Authorisation Accounting Charging Security QoS Differentiated Services Signalling L3 / L2 mapping Policing Handover (seamless, fast) Mobility Mobile IP Paging Context Transfer Introducción 8 4 Moby Dick Mobility Issues ? Improve handover latency and data loss over standard MIPv6 ? Latency of over 300 ms too high ? Make before break instead of break before make ? Integrate AAA and QoS ? Standard Mobile IP supports nomadic scenarios rather than seamless mobility ? Candidates for implementation discussed within IETF: ? Fast Handover (FMIPv6) ? Hierarchical schemes, e.g. HMIPv6 ? Simulations were done before a decision was taken in the project Introducción 9 Moby Dick QoS Issues ? The provision of end-to-end QoS despite of Mobility and AAA requirements taking care of: ? Scalability ? Performance ? Candidates as discussed in the IETF: ? Integrated Services (IntServ) ? Differentiated Services (DiffServ) Moby Dick: Service oriented approach achieved by adoption of DiffServ in combination with QoS Broker/AAAC Introducción 10 5 Moby Dick AAA Issues ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Authentication – Proof of Users Identity Authorisation – Management of Users permissions Metering – Generation of raw usage data Accounting – Provision/Post Processing of Metering data for Charging Auditing – Proof of service provisioning Charging – Calculating charges based on Accounting Interaction with standard IP security (IPsec) Moby Dick: AAAArch + Diameter enriched with IETF RTFM Meter, Auditing and Charging - supporting seamless Mobility Introducción 11 Moby Dick A PURE-IP 4G Architecture Introducción 12 6 Moby Dick – Key Characteristics ? Use of UMTS-TDD spectrum ? IP directly on top of TD-CDMA ? Adapted Radio-dependent elements: TD-CDMA interface and the radio link protocol ? All other network elements (RNC, HLR, VLR, EIR, MSC, GMSC, SGSN, GGSN, …) are replaced /redistributed by a functional IP-based equivalent (Mobile IPv6, AAA Server, QoS Broker) ? Subset of 3GPP RRC protocol adapted to the Moby Dick IPv6 interface Introducción 13 Moby Dick – Key Characteristics (2) ? IPv6-based solution for IP-Mobility across different technologies ? Heterogeneous access technologies ? TD-CDMA (base technology of UMTS TDD) ? Wireless LAN 802.11b ? Standard Ethernet ? Integration of mobility management including ? Handover and paging ? End-to-end QoS ? Authentication, Authorisation, Accounting, Auditing and Charging Introducción 14 7 Horizontal Integration ? Moby Dick integrates ? AAA ? QoS ? Mobility ? MAQ – Mobility - AAA – QoS ? ? ? ? ? Assign/configure CoA Perform Authentication Enable Authorization Send BU /consume resources according to user profile Accounting Introducción 15 Vertical Integration Mobile Terminal (MT), Access Router (AR), AAA Server, centralized profile ? MT: Handover decision/initiation (Mobility), Registration (AAA) ? AR: Mobility Management, context transfer ? Additionally: • Radio Gateway: IP to TD-CDMA • QoS Broker • AAAC Server: Communication to QoS Broker during registration ? Centralized profile for “light-weight” signalling for probabilistic service provisioning Introducción 16 8 User Mobility in Moby Dick ? Terminal Mobility in IP: user corresponds to IP Address ? Terminal Mobility in 2G: User corresponds to SIM card ? User Mobility in Moby Dick: User corresponds to User having a user profile stored somewhere at the “home network domain” (AAA.h Server) Introducción 17 User Profile AAA.H AAA.F QoS B User profile DB AR User Profile (AAAH) Personal User data, Roaming permissions NVUP User profile subset 2 User Profile Subset 1 (AAAF) Remaining Budget, Service specific permissions NVUP (QoSB) Technical Parameters (Bandwidth…) User Profile Subset 2 (AR) (Metering conf, IPsec) Introducción 18 9 Key Scenarios ? Registration ? MN is switched on ? MN firstly connects to any administrative domain = > Mobility scenario across administrative domains is registration ? Session Setup ? Service Authorization ? Handover ? Intra-domain mobility scenario Introducción 19 Summary ? Moby Dick integrated mobility, QoS, AAA based on existing standards ? Handover performance depends on scenario and additional factors – Fast Handover improves performance for intra-domain scenarios ? Fast handover messages carry context information to allow immediate authorisation ? The project has implemented IP paging ? Seamless integration of TD-CDMA to overall architecture ? Key achievement: IP layer is able to handle seamless mobility, in a quality comparable to 2G, between technologies and supporting multimedia services Introducción 20 10 Moby Dick Impact ? Moby Dick is finishing in December 2003 ? Room to improve ?techniques for QoS Management ?tighter integration of registration scenarios ?proper radio resource management ?Integration of OSS mechanisms in a commercialized mobile Internet ? Areas being explored commercially in the future… ?Operators: new management systems (QoS Brokers) ?Manufacturers: Overall System Concept as reference ?Academics: Daidalos Mobile University Cheaper way for building “towards 4G” systems Introducción 21 11