Articles of Confederation - The Federalist Papers Test Review
advertisement

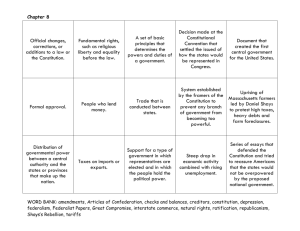
Articles of Confederation - The Federalist Papers Test Review Timeline • Know: What were/are the Articles of Confederation? Know: 3 components of the Articles of Confederation that still exists in our government today • Articles of Confederation-Powers of Congress – • Make war/peace, send/receive ambassadors, make treaties, borrow money, build navy, raise Army by asking States, uniform standards of weights and measures, settle disputes among States Articles of Confederation-State Obligations – Obey Articles and acts of Congress, funds and troops provided, treat citizens of other States fair, full faith and credit, surrender fugitives, submit disputes to Congress, open travel and trade Know 3 weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation and Shay’s Rebellion • • Articles of ConfederationWeaknesses (49) Shay’s Rebellion Constitutional Convention • Know: the purpose of the Philadelphia Convention and the final outcome • Know: Who were the writers of the Constitution? What are 2 things you know about the Framers? Creating the Constitution • Know: James Madison’s Notes “Father of the Constitution” Know 3 components of The Virginia Plan that still exist in our government today and who supported the plan(large state support) • • Plan for strong national government James Madison/Edmund Randolph • • Three (3) Branches (66) Bicameral Congress – – – – – Representation based on State population or money Lower House (H of R) chosen by popular election Upper House chosen by H of R Congress powers same as A of C + others Choose “National Executive and Judiciary” –Veto power –Execute laws –1 or more supreme tribunals + inferior tribunals – States support Union – Guaranteed representative democracy – Admit new States into union Know 2 components of The New Jersey Plan that still exist in our government today and which states supported plan (small state support) • Plan for strong national government • • William Patterson Unicameral Congress – – – Equal representation/State Tax and trade regulation power limited “Federal Executive” and “Federal Judiciary” Know the Compromises • • • Connecticut Compromise 3/5 Compromise Commerce and Slave Trade Compromise Know the difference between the Federalists and Anti-Federalists • Federalists – – – Favored ratification A of C weak New gov’t w/Constitution needed • Anti-Federalists – – – – – – Opposed ratification Critique ratification process No mention of God States could not print $ Central gov’t increased power Lack of bill of rights Anti-Federalist Papers • Written anonymously in New York Press under pseudonym Cato & Brutus -Opposed ratification of Constitution 1) Written in secret 2) Extralegal 3) Constitution took important powers from states 4) Lacked a Bill of Rights • Counterarguments • Promise Federalist Papers • The Federalist: 85 essays in support of Constitution ratification -Alexander Hamilton (NY), James Madison (VA), John Jay (NY) wrote under the pseudonym Publius -Without a republic there will be anarchy Federalist Papers • #10 (written by Madison) -most important -called for federal republic -defense of federalism -safeguard against factions Federalist Papers • #51: (Madison) -Independent branches of government -Checks & Balances • #70: (Hamilton) -defense of one man executive Federalist Papers • #78: (Hamilton) -Judicial Branch -Judicial Review • #84: (Hamilton) No need for Bill of Rights Ratification • 9 of 13 states need to ratify for it to be in effect • Delaware 1st Dec 7, 1787 -Signed September 17, 1787 Constitution Day • New Hampshire 9th June 21, 1788 • New York July 26, 1787 -G Washington (Pres); J Adams (VP) -59 in House of Rep/22 Senate; meet March 4, 1789 in Federal Hall -April 30, 1788 G Washington takes Oath of Office • Rhode Island last to ratify May 29, 1790 • James Madison proposes 12 amendments; 10 ratified in 1791 = Bill of Rights