Method C305 - Kerosene - Department of Transport and Main Roads
advertisement

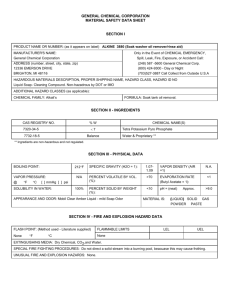
Laboratory Chemical Handling Manual Safe Handling & Storage of Kerosene METHOD C305 Intent Intent Description Description Use Storage Spill Disposal Hazard First aid Technical 1.Intent This laboratory technique describes the processes for the use, storage, spill resolution and disposal for kerosene. The technique also provides information on fire, explosion and hazards as well as first aid treatment. 2. Product description Kerosene is a Class 3: Flammable Liquid and has damaging properties as follows: Kerosene toxicity information Inhalation May cause respiratory tract irritation. Ingestion Aspiration hazard if swallowed – can enter lungs and cause damage. Aspiration of this product into the lungs may cause chemical pneumonia and can be fatal. Aspiration into the lungs can occur while vomiting after ingestion of this product. Do not siphon by mouth. Skin Likely to cause skin irritation. Personal hygiene measures taken to prevent skin irritation are expected to be adequate to prevent risk of skin cancer. Occasional skin contact with this product is not expected to have serious effects, but good personal hygiene should be practiced and repeated skin contact avoided. There may be a potential risk of skin cancer from prolonged or repeated skin contact with this product in the absence of good personal hygiene. Eye Unlikely to cause more than transient stinging or redness if accidental eye contact occurs. Carcinogenic Effects No component of this product at levels greater than or equal to 0.1% is identified as a carcinogen. Acute Toxicity Information May cause irritation to eyes, nose and throat due to exposure to vapour, mists or fumes. E LL U Issue date: November 2011 D RO T N PY O O NC C page 1 of 14 Laboratory Chemical Handling Manual Safe Handling & Storage of Kerosene METHOD C305 Intent Description Use Storage Spill Disposal Hazard First aid Technical 3. Use of kerosene 3.1 Mandatory PPE When handling kerosene, ensure you utilise the following mandatory PPE: • Long-sleeved 100% cotton shirt and full-length 100% cotton trousers. For additional protection, a knee-length 100% cotton laboratory coat (with long sleeves which clip at the wrist) can also be worn. • Nitrile or super nitrile gloves. • Eye protection: either safety glasses, spectacles, goggles or face shield (complying with AS 1337). • Enclosed safety shoes (complying with AS 2210). Figure 1: Person wearing appropriate PPE E LL U Issue date: November 2011 D RO T N PY O O NC C page 2 of 14 3.2Precautions When handling kerosene: • It is advisable to apply a barrier cream to the hands prior to use. • Always have at least one other person present in the laboratory. • Keep containers closed and in an upright position when not in use. • Avoid breathing vapours or spray mists. • Keep containers away from sources of heat (including hot plates, Bunsen burners, ovens and sunlight) except when heating for testing purposes. • Maintain a high level of personal hygiene when using kerosene, by always washing hands before eating, drinking, smoking or using toilet facilities. • It is advisable to apply a moisturiser after washing hands. 3.3Decanting When decanting kerosene, the following must be observed: • Decanting of kerosene must be carried out in a fume cupboard (do not inhale vapours). • Decanted aliquots can be stored in small safety drums, wash bottles or reagent bottles. Never return decanted aliquots to the supply container. • Dispose of unused aliquots in an appropriate manner (see Section 6: Disposal). • Before decanting from one metal container to another metal container, connect an earthing strap between the containers or have one or both of the containers connected to an earthing rod. E LL Video 1: Decanting U Issue date: November 2011 D RO T N PY O O NC C page 3 of 14 3.4Labelling Containers must be appropriately labelled. Containers with capacity larger than 500 mL: Figure 2: Labelling on containers >500 mL Labels on containers require the following information: • Product and chemical name. • Dangerous goods class (e.g. Class 3: Flammable Liquid). • United Nations (UN 1223) Number. • Ingredients and formulation details where relevant. • Risk phrases. • Safety phrases. • First aid procedures. • Emergency procedures. • Details of manufacturer or importer. • Reference to MSDS. Wash bottles with capacity smaller than 500 mL: Labels on containers require the product and chemical name. E LL U Issue date: November 2011 D RO T N PY O O NC C page 4 of 14 Figure 3: Labelling on wash bottle <500 mL 3.5 Carrying kerosene Kerosene containers are to be transferred as follows: • Wash bottles may be transferred by hand. • Small (<2.5 L) containers must be transferred using a laboratory carrier. • Medium (2.5 L) containers must be transferred using a laboratory carrier. • Containers with a mass of 20 kg or larger must be transferred using a trolley. E LL U Issue date: November 2011 D RO T N PY O O NC C page 5 of 14 Laboratory Chemical Handling Manual Safe Handling & Storage of Kerosene METHOD C305 Intent Description Use Storage Storage Spill Disposal Hazard First aid Technical 4. Storage of kerosene To prevent injury to personnel, damage to equipment and to meet legislative storage requirements, kerosene is to be stored as follows: 4.1 Storage general Kerosene, being a flammable liquid is to be stored as follows: • Monitor containers for deficiencies such as damage or leaks on a monthly basis. • Store in an approved container with appropriate labelling. • Store in a cool, well-ventilated area. • Keep containers tightly closed when not in use and protected against physical damage. • Avoid all possible sources of ignition (spark or flame). • Never store with food, beverages or food packaging. Kerosene cannot be stored with any of the following substances: Class Definition Chemicals included in this class 1 Explosives – 2.1 Flammable Gases Liquid Petroleum gas, Dymark Spray and Mark Aerosol (paint), Hydrogen (compressed). 2.3 Toxic Gases – 4.2 Spontaneously Combustible Substances Activated Charcoal. 5.1 Oxidising Agents Ammonium Nitrate, Hydrogen Peroxide, Perchloric acid, Silver Nitrate, Potassium Permanganate, Chromic acid. 5.2 Organic Peroxides – 6 Toxic Substances (where toxic substances are cyanides and corrosives are acids) Ammonium Oxalate, Mercuric Iodide, Phenol crystals and solution, Barium Chloride (6.1), ED Chloroform (6.1), Methyl Orange (6.1), Potassium LL Chromate (6.1), Trichloroethylene (6.1). RO U Issue date: November 2011 N T PY O O NC C page 6 of 14 Class Definition Chemicals included in this class 7 Radioactive Substances Americium/Berylium, Cesium. 9 Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods Lead (metal plate), Magnesium (tooling plate/slab). 4.2 Laboratory storage • For quantities of 20 litres or less, store in a bunded, vented, flammable liquid storage cabinet (complying with AS 1940). • Storage cabinets must be located away from sources of heat such as hot plates, Bunsen burners, ovens and sunlight. • Have appropriate fire extinguishers near any storage area. Suitable extinguishers include water fog, carbon dioxide, dry chemical or alcohol foam. 4.3 Bulk storage • For bulk storage, e.g. 200 litre drums, store in a secure, well ventilated, bunded storage area. • Have appropriate fire extinguishers in and near any bulk storage area. Suitable extinguishers include water fog, carbon dioxide, dry chemical or alcohol foam. E LL U Issue date: November 2011 D RO T N PY O O NC C page 7 of 14 Laboratory Chemical Handling Manual Safe Handling & Storage of Kerosene METHOD C305 Intent Description Use Storage Spill Spill Disposal Hazard First aid Technical 5. Spill resolution Spills or leaks of kerosene must be cleaned up immediately. 5.1 Mandatory PPE • Long-sleeved 100% cotton shirt and full-length 100% cotton trousers. For additional protection, a knee-length 100% cotton laboratory coat (with long sleeves which clip at the wrist) can also be worn. • Respiratory Equipment, eg, Half-Face Filter Respirator Class A1P2 (complying with AS/ NZS 1715) for spills in excess of 2 Litres. • Nitrile or super nitrile gloves. • Eye protection: either safety glasses, spectacles, goggles or face shield (complying with AS 1337). • Enclosed safety shoes (complying with AS 2210). 5.2 Immediate action • Stop any leak if safe to do so. • Evacuate all unnecessary personnel. • Turn off all sources of heat. • Keep combustible materials away from the immediate area of the spill. • Turn off air-conditioning (if possible). • Open windows and doors to increase ventilation (if possible). • Inform the local water authority or EPA if contamination of sewers or waterways occurs. E LL U Issue date: November 2011 D RO T N PY O O NC C page 8 of 14 Video 2: Spill procedures 5.3 Clean up • Cover the spill with absorbent material such as Chemsorb, Bentonite or Vermiculite or another suitable proprietary product. • Place the contaminated absorbent material in a closed fume cupboard free from any heat source and allow the solvent to evaporate using the air from the exhaust system. • Once the contaminated absorbent material is dry, place it into a plastic bag and seal with a cable tie for subsequent disposal (see Section 6: Disposal). • Ventilate the spill site to evaporate any remaining liquid and dispel vapours. E LL U Issue date: November 2011 D RO T N PY O O NC C page 9 of 14 Laboratory Chemical Handling Manual Safe Handling & Storage of Kerosene METHOD C305 Intent Description Use Storage Spill Disposal Disposal Hazard First aid Technical 6.Disposal 6.1Pre-Treatment • Empty kerosene containers (including 200 litre drums) should be thoroughly washed out with water. The washings are to be absorbed by an inert absorbent such as Chemsorb, Bentonite or Vermiculite. • Labels on empty supply containers must be removed or fully obliterated. 6.2 Disposal method The containers and absorbent material can be disposed of as follows: • Absorbent material contaminated by washings is placed in a closed fume cupboard free from any heat source and the solvent is allowed to evaporate using the air from the exhaust system, until the absorbent material is dry. • Washed out supply drums or containers can be recycled. • Supply containers and degraded wash bottles must be placed in general waste. • Contaminated dry absorbent material (in a sealed plastic bag) can be disposed of in general waste. E LL U Issue date: November 2011 D RO T N PY O O NC C page 10 of 14 Laboratory Chemical Handling Manual Safe Handling & Storage of Kerosene METHOD C305 Intent Description Use Storage Spill Disposal Hazard First aid Technical 7. Fire and explosion hazard information In case of fire with kerosene present: • Suitable Extinguishing Media: In case of fire, use foam, dry chemical or carbon dioxide extinguisher or spray. Do not use water jet. • Hazards from Combustion Products: Carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. • Fire/Explosion Hazards: Flammable liquid and vapour, vapour may cause flash fire, vapours may accumulate in low or confined areas, travel a considerable distance to a source of ignition and flashback. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. • Special Fire-Fighting Procedures: DO NOT FIGHT FIRE WHEN IT REACHES MATERIAL, withdraw from fire and let it burn, promptly isolate the scene by removing all persons from the vicinity of the incident. If there is a fire, first move people out of line-of-sight of the scene and away from windows. E LL U Issue date: November 2011 D RO T N PY O O NC C page 11 of 14 Laboratory Chemical Handling Manual Safe Handling & Storage of Kerosene METHOD C305 Intent Description Use Storage Spill Disposal Hazard First First aid aid Technical 8. First aid procedures In case of exposure with kerosene: • Inhalation: If inhaled, remove to fresh air. SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION if symptoms appear. • Ingestion: If swallowed, do NOT induce vomiting. Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Aspiration hazard if swallowed – can enter lungs and cause damage. SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION. • Skin: Immediately wash exposed skin with soap and water. Remove contaminated clothing and shoes. Wash clothing before reuse. Clean shoes thoroughly before reuse. SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION IMMEDIATELY. In extreme situations of saturation with this product, drench with water, remove clothing as soon as possible and wash skin with soap and water. SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE if skin becomes red, swollen or painful. • Eye: If in contact with the eye(s), hold eyelids apart and flush the eye continuously with running water. Take care not to rinse contaminated water into the non-affected eye. Continue flushing for at least 15 minutes or until advised to stop by the Poisons Information Centre or a doctor. SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION IMMEDIATLEY. • First Aid Facilities Required: Eye wash station, safety shower and normal washroom facilities. • Advice to Doctor: Treat symptomatically. For advice call the Poisons Information Centre below. Emergency contacts • Poisons Information Centre: 131 126 • Australian Emergency Services: 000 E LL U Issue date: November 2011 D RO T N PY O O NC C page 12 of 14 Laboratory Chemical Handling Manual Safe Handling & Storage of Kerosene METHOD C305 Intent Description Use Storage Spill Disposal Hazard Technical Technical First aid 9. Technical information Kerosene chemical and physical information Molecular Formula - Appearance Colourless, blue or tinted liquid. Melting Point N/A Boiling Point 150 °C to 280 °C Solubility in Water Very slightly soluble in water. Specific Gravity 0.78 - 0.82 Flash Point >38 °C Stability Stable under recommended storage conditions. Incompatible Materials Avoid all possible sources of ignition (spark or flame). Avoid excessive heat. Hazardous Decomposition Products Carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. Hazardous Polymerisation Will not occur. Hazardous Reactions Oxidising Agents. E LL U Issue date: November 2011 D RO T N PY O O NC C page 13 of 14 The following controls are used by TMR to minimise risks when handling kerosene: Current Transport and Main Roads controls Engineering Controls / Ventilation Fume Cupboard complying with AS 1807 and AS 2243. Safe Work Procedures As per this technique/MSDS. First Aid Facilities Eyewash station, safety shower, and normal washroom facilities. Spill Procedures Refer to Sections 5.2 and 5.3. Waste Disposal Procedures Refer to Section 6.2. Fire/Explosion Hazard Refer to Section 7. Administrative Controls Nil PPE Refer to Section 5.1. Emergency Procedures Phone 1800 638 556 Training Provided Assessed element of competency. Previous Monitoring Results Nil Storage & Handling Requirements Flammable Liquid Cabinet complying with AS 1940 and bulk store complying with this technique. Monitoring Required No Health Surveillance Required No E LL U Issue date: November 2011 D RO T N PY O O NC C page 14 of 14