Marketing Functions
advertisement

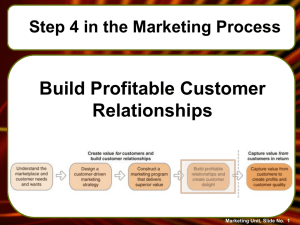
Lesson – 3 In last Lesson we had a detailed view of Marketing process and core marketing concepts. For today the focus of discussion is on the increasingly powerful role of customers in the marketing process and the need for marketers to provide value that exceeds customer expectations. Along with the concept of relationship marketing major functions performed by the marketing are also presented so today we will be discussing the following topics: A. MARKETING FUNCTIONS B. CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT Marketing Functions There are eight Universal functions that are performed in marketing these are as shown in fig these are Buying, selling, transporting, storing, standardizing and grading, financing and finally risk taking now lets discuss these one by one: • • • Information Buying Buying: (Raw material to produce goods and services and Selling to purchase finished goods or Risk Taking services as retailer or whole Universal Marketing Marketing seller to sell them again for final Functions Functions customers and consumers). It is Transporting a function that ensures that Financing product offerings are available in sufficient quantities to meet Standardizing Storing and Grading customer demands Selling: The function to be performed to sell the products/services/idea to satisfy customer needs or wants. Using advertising, personal selling, and sales promotion to match goods and services to customer needs Transporting: Function related to create the availability of product or services. It is used for moving products from their points of production to location convenient for purchases • Storing: Warehouses are used to store the products for further distribution. • Standardizing and grading: To provide more quality products and services without variation in the quality. Ensuring that product offerings meet established and grading quality and quantity control standards of size, weight, and other product variables • Financing: Providing the financial resources to carry out different function e.g. promotion of product and providing credit for channel members (wholesalers retailers) or consumers • Risk taking: Marketer takes a risk specifically when any new product is introduced in a market because there are equal chances of success and failure. Dealing with uncertainty about consumer purchases resulting from creation and marketing of goods and services that consumers may purchase in the future Securing Marketing Information: Collecting information about consumers, competitors, information and channel members (wholesalers, and retailers) for use in making marketing decisions Almost all marketing functions are based on information acquired from external environment and information distributed out of organization. Marketer seeks information to find out customer needs and wants which are to be satisfied than after producing goods and services awareness about the availability is required so that consumer can purchase the available goods and services. • Marketing Management: Marketing management is “the art and science of choosing target markets and building profitable relationships with them.” Creating, delivering and communicating superior customer value is key. Marketing management is the conscious effort to achieve desired exchange outcomes with target markets. The marketer’s basic skill lies in influencing the level, timing, and composition of demand for a product, service, organization, place, person, idea, or some form of information. Marketing Management is defined as the analysis, planning, implementation, and control of programs designed to create, build, and maintain beneficial exchanges with target buyers for the purpose of achieving organisational objectives. Which are: Demand Management - marketing management is concerned with increasing demand, as well as changing or even reducing demand. Marketing management is concerned not only with finding and increasing demand, but also with changing or even reducing it. 1). Demarketing: Marketing to reduce demand temporarily or permanently; the aim is not to destroy demand but only to reduce or shift it. Demarketing’s aim is to reduce demand temporarily or permanently (move traffic away from a popular tourist attraction during peak demand times). 2). In reality, marketing management is really demand management. Building Profitable Customer Relationships - Beyond designing strategies to attract new customers, marketing organizations also go all out to retain current customers and build lasting customer relationships. (This is our second topic to be discussed today). Customer Relationship Management Before going in the detail of customer relationship marketing first we should know that what is relationship marketing? It is basically Establishing a long-term continuous relationship with the customer, initiated and managed by the firm. This relationship must provide value to both parties. If a customer is lost, not only is that particular transaction lost, but perhaps all future transactions throughout the life of that customer. As discussed earlier that marketing is the organizational function charged with defining customer targets and the best way to satisfy needs and wants competitively and profitably. Since consumers and business buyers face an abundance of suppliers seeking to satisfy their every need, companies and nonprofit organizations cannot survive today by simply doing a good job. They must do an excellent job if they are to remain in the increasingly competitive global marketplace. Many studies have demonstrated that the key to profitable performance is to know and satisfy target customers with competitively superior offers. This process takes place today in an increasingly global, technical, and competitive environment. When marketing helps everyone in a firm really meet the needs of a customer both before and after a purchase, the firm doesn’t just get a single sale. Rather, it has a sale and an ongoing relationship with the customer. That’s why we emphasize that marketing concerns a flow of need-satisfying goods and services to the customer. Often, that flow is not just for a single transaction but rather is part of building a long-lasting relationship that is beneficial to both the firm and the customer. Customer Relationship Management 1. CRM Customer relationship management “CRM is the overall process of building and maintaining profitable customer relationships by delivering superior customer value and satisfaction.” CRM Customer relationship management can be defined: as strategies focused on increasing customer satisfaction, loyalty, and profitability by leveraging superior customer knowledge acquired, stored, and acted upon with the aid of information technology. 2. The basic goals of the CRM are: Customer relationship marketing provides the key to retaining customers and involves providing financial and social benefits as well as structural ties to the customers. Companies must decide how much relationship marketing to invest in different market segments and individual customers, from such levels as basic, reactive, accountable, proactive, and full partnership. Much depends on estimating customer lifetime value against the cost stream required to attract and retain these customers. Total quality marketing is seen today as a major approach to providing customer satisfaction and company profitability. Companies must understand how their customers perceive quality and how much quality they expect. Companies must then strive to offer relatively higher quality than their competitors. This involves total management and employee commitment as well as measurement and reward systems. Marketers play an especially critical role in their company’s drive toward higher quality. The basic goals of CRM are: • • • • • • • • • • • • The idea of CRM is that it helps businesses use technology to gain insight into the behavior of customers and the value of those customers. If it works as hoped, a business can: Provide better customer service Make call centers more efficient Help sales staff close deals faster Simplify marketing and sales processes Discover new customers Enable companies to provide excellent real-time customer service by developing a relationship with each valued customer through the effective use of individual account information Based on customer attributes, companies can customize market offerings, services, programs, messages, and media Reduces the rate of customer defection Increases the longevity of the customer relationship Enhances the growth potential of each customer through “share of wallet,” crossselling, and up-selling Makes low-profit customers more profitable or terminates them Focuses disproportionate effort on high value customers CRM is mainly based upon the customer loyalty that is of great importance for the marketer because firms have realized the value of customer retention. Winning a new customer is usually 5- 10 times more costly than retaining an existing customer Customers are usually more profitable the longer you keep them. The value of loyalty goes beyond single customer for the reason that loyal customers provide more and more credible referrals but the angry gossip of disloyal customers can devastate a firm. 3. Building Profitable Customer Relationships Managing demand means managing customers because: 1. A demand comes from new customers and repeat customers. 2. Today, besides making efforts to attract new customers, marketers are going all out to retain and build relationships with existing customers. It costs five times as much to attract a new customer as it does to keep a current customer satisfied. 3. Because of changing demographics, a slow-growth economy, more sophisticated competitors, and overcapacity in many industries, many markets and market shares are shrinking. The key to successful customer retention is superior customer value and satisfaction.