ANALOG ELECTRONICS 204 – FORMULA SHEET
advertisement

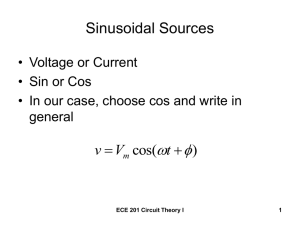
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS 104 – FORMULA SHEET 1. DC CIRCUITS (Resistive) (i) Ohm’s Law: V = R.I or I = G.V (ii) Delta to Y Transformations (Ra, Rb, Rc) to (R1, R2, R3): R1 = (iii) (iv) 3. Rb Rc R1 R2 + R2 R3 + R3 R1 ….. Ra = Ra + Rb + Rc R1 Power: P = V .I = V G = I Operational Amplifier Model: 2 2 SWITCHED CIRCUITS (First and Second Order Transient Responses) (i) First Order DE: (ii) Solution: (iii) R (iv) Overdamped Solution: (v) Critically Damped: (vi) Underdamped : (ii) A→∞ (iii) (iv) AC CIRCUITS (Phasors and Impedances) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) Complex Number: a + jb = a 2 + b 2 ∠ tan −1 A cosθ + B sin θ = sin θ = cos(θ − π2 ) A + B cos(θ − tan 2 2 b a −1 B A (v) ) v(t ) = Vm cos(ω .t + φ ) ⇒ V = Vm ∠φ = Vm cos φ + jVm sin φ Z = R + jX , Y = G + jB , Z L = jω .L , Z c = − j ω1.C Mutual Inductance: v1 = L di1 1 dt ±M di2 dt and k = M / L1 L2 ⇒ V1 = ( jω .L1 ) I 1 ± ( jω .M ) I 2 (vii) 2 2 Pav = Vrms I rms cos φ = I rms R = Vrms G where Vrms = Vm / 2 * S = V .I = Vrms I rms cos φ + jVrms I rms sin φ (viii) Complex Power: (ix) Energy stored: capacitor, y + 2α where A & B from boundary conditions d dt y + ω o2 y = f (t ) where Wc = 12 CV 2 ; inductor, WL = 12 LI 2 . y (t ) = ( A.e −σ 1t + B.e −σ 2t ) + forced Response y (t ) = ( A.e −α .t + B.t.e −α .t ) + forced Response s = α ± jω d = α 2 + ω d2 ∠ tan −1 ±ω d α = K∠ ± φ y (t ) = A.e −α .t cos(ω d .t ) + B.e −σ .t sin(ω d .t ) + forced R APPLICATIONS (frequency response, filters, 2-port networks) (i) 2. d2 dt 2 − Tt ω o = 1 / LC (natural freq) and α is the damping factor 4. Ro → 0 y + T1 y = f (t ) where T = RC or T = L/R y (t ) = A + B.e Second Order DE: Solution : where Ri → ∞ d dt V out = H ( jω ) ∠H ( jω ) V in The Magnitude Response can be expressed in dB = 20 log H ( jω ) Transfer Function: H ( jω ) = The half-power bandwidth is defined between 2 frequencies at which the response drops down by -3dB (i.e. 0.707 of Maximum value). Band-pass Filters are characterised by the centre frequency (ωο) and the halfpower bandwidth ( ∆ω ) . Quality factor, Q = ω o / ∆ω . (viii) (ix) z-parameters are defined as: V1 = z11 I1 + z12 I2 and V2 = z21 I1 + z22 I2 Transmission parameters are defined as: V1 = a11 V2 - a12 I2 and I1 = a21 V2 - a22 I2 Hybrid parameters are defined as: V1 = h11 I1 + h12 V2 and I2 = h21 I1 + h22 V2 Conditions for Reciprocity: z12 = z21, (a11.a22 - a12.a21) = 1, h12 = -h21. Additional Conditions for Symmetry: z11 = z22, a11 = a22, (h11.h22 - h12.h21) = 1 (x) Converting [Z] to [A]: a11 (vi) (vii) (xi) z z ∆ 1 = 11 , a12 = z , a 21 = , a 22 = 22 z 21 z 21 z 21 z 21 z z ∆ 1 Converting [Z] to [H]: h11 = z , h12 = 12 , h21 = − 21 , h22 = z 22 z 22 z 22 z 22