COURSE: MACHINE ELEMENTS CALCULATION STUDIES
advertisement

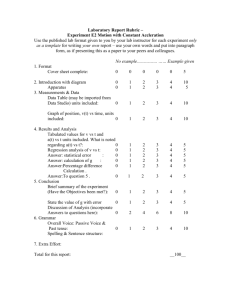
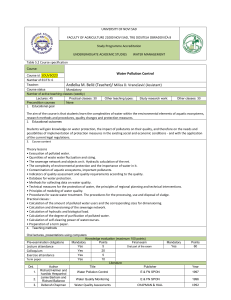
40048 MACHINE ELEMENTS CALCULATION Page 1 of 3 COURSE: MACHINE ELEMENTS CALCULATION STUDIES: INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING (2nd cycle) TYPE: OP YEAR: 4th CREDITS (hours/week): 7,5 (3) ECTS CREDITS: 5 PROFESSOR: Dr. Andrés-Amador García Granada LANGUAGE: Spanish SEMESTER: 2nd PREREQUIREMENTS: Elasticity and materials strength, Technology of materials, Computer Aided Design PREVIOUS KNOWLEDGES: Kinematics and machine dynamics. Materials Strength. CAD. COURSES THAT HAVE TO BE STUDIED SIMULTANEOUSLY: none. COURSE DESCRIPTION: The present course is intended to teach up to date manufacturing processes, precision manufacturing, economics of manufacturing processes and. Also it is expected to teach on the design theory, DFx, the use of mechanical parts standards and the assembly of groups of parts. COURSE OBJECTIVES: Graduates of our program of industrial engineering acquire the knowledges and develop the abilities hereinafter mentioned: a.- Learn to design parts and products, making an emphasis on the need to update those knowledges. b.- Acquire the ability to formulate and solve problems related with the design process in engineering with interdisciplinary focus and working in teams. c.- Understand the need to fulfill rules of quality, work safety, sustainability and environmental safety. CONTENTS: 1. Introduction. 2. Materials for machina elements 3. Movement transmision elements 4. Axels and shafts Couplings, clutches and brakes 5. Bearings 6. Machine elements joining 7. Housings and holders METHODOLOGY: 40048 MACHINE ELEMENTS CALCULATION Page 2 of 3 Teaching is carried out in master classes, practices and classes of problems where real cases are discussed and solved in groups. Practices uses simulation and real machines and are described next: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Calculation software introduction Parts joining calculation. Real machines case study Gearing calculation. Automobiles transmissions inspection Axels, shafts and associated parts calculation. Case studies in real machines Housing study and calculation. Inspection of real parts Students must also search literature, consult periodical publications, look up computerized material and database of techno-scientific information. EVALUATION: A.- Exams D.- Homework F.- Team works J.- Problems classes participation L.- Participation in the laboratory Final qualification of the course consists of the 50 % of the exam result, 30 % of product calculations and development practices and 20 % of the class problems and laboratory practices. CRITERIA FOR RESULTS EVALUATION: Objective 1: Learn to design parts and products, making an emphasis on the need to update those knowledges. [A, D, J]. Objective 2: Acquire the ability to formulate and solve problems related with the design process in engineering with interdisciplinary focus and working in teams [A, D, F, J, L]. Objective 3: Understand the need to fulfill rules of quality, work safety, sustainability and environmental safety [A, J, L]. ORDINARY BIBLIOGRAPHY: 1. Faires, Virgil M “Diseño de elementos de maquinas”, Limusa, S.A. México, 2003. 2. Hamrock, Bernard,J “Elementos de maquinas”, Mc Graw-Hill,Mexico, 2000. 3. Norton, Robert L “Diseño de maquinas”, Prentice Hall, México, 1999. 4. Shigley, J. E. y Mischke, C. R. “Diseño en Ingeniería Mecánica”, 5ª ed. McGraw Hill. 1990 40048 MACHINE ELEMENTS CALCULATION Page 3 of 3 BIBLIOGRAPHY or COMPLEMENTARY MATERIAL : 1. Meadows, J. D. “Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing” Marcel Dekker Inc. 1995. 2. Scheneck D. & Bronzino J. “Biomechanics”. CRC Press. 2002 3. Harnoy A. “Bearing Design in Machinery”. Mercel Dekker, Inc. 2003. 4. Luque, P., Álvares, D., Vera, C. “Ingeniería del Automóvil”. Thomson. 2004., Álvares, D., Vera, C. “Ingeniería del Automóvil”. Thomson, 2004. PREPAIRED BY: Dr. Guillermo Reyes Pozo DATE OF THE LAST REVIEW: April, 2009