Design of Work Systems
advertisement
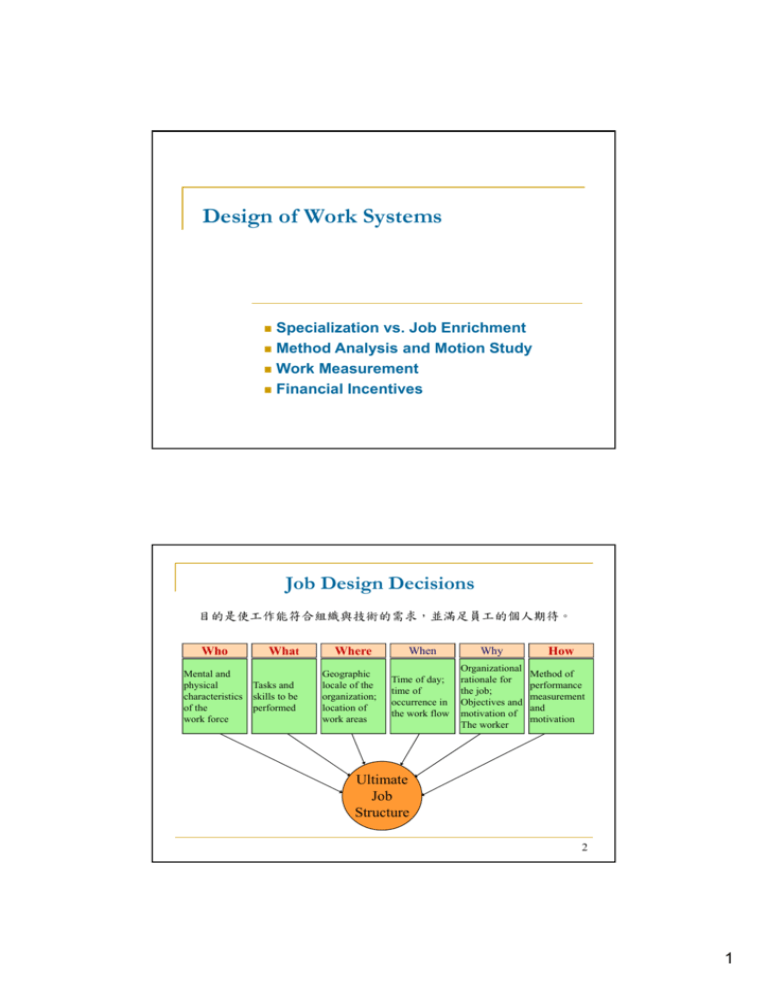
Design of Work Systems Specialization vs. Job Enrichment Method Analysis and Motion Study Work Measurement Financial Incentives Job Design Decisions 目的是使工作能符合組織與技術的需求,並滿足員工的個人期待。 Who Mental and physical characteristics of the work force What Tasks and skills to be performed Where Geographic locale of the organization; location of work areas When Why Time of day; time of occurrence in the work flow Organizational rationale for the job; Objectives and motivation of The worker How Method of performance measurement and motivation Ultimate Job Structure 2 1 Worker’s interaction with equipment: 人與機器的配合 Worker’s interaction with other workers: 團隊合作 Flight turnaround time 3 Labor Specialization To Management Advantages Disadvantages To Labor Simplifies training Low wages High productivity Difficult to motivate quality Worker dissatisfaction resulting absenteeism and high turnover Little skill requirement Minimum responsibility Little mental efforts needed Boring Little control over work Little opportunity to job promotion How much specialization is enough? 4 2 Behavioral Approaches to Job Design Job Enlargement Giving a worker a larger portion of the total task by horizontal loading 訓練員工學習多種技術層次相當的工作 Job Rotation Workers periodically exchange jobs 工作輪調可提升員工知識與技能,人力調派較有彈性 Job Enrichment Increasing responsibility for planning and coordination tasks, by vertical loading 訓練員工學習規劃、設計、執行,讓員工負起更大責任 5 Behavioral Considerations in Job Design 服務業low customer contact的工作,適合以製 造業的方式進行 提高生產力 偏向專業分工以提升效率,讓人去配合流程 It’s about quantity. High customer contact的服務業或是純粹使用腦 力的工作,需要用重質不重量的方式來管理 偏向工作內容多元化,讓人自己發揮 It’s about quality. 6 3 Methods Analysis: analyze how a job is done 何時應該重新分析工作方法: Changes in tools and equipment Changes in product design or new products Changes in materials or procedures Other factors (e.g. accidents, quality problems) 7 Methods Analysis Procedure 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Identify the operation to be studied Get employee input Study and document current method Analyze the job Propose new methods Install new methods Follow-up to ensure improvements have been achieved 8 4 Process Chart Symbols 9 Flow Process Chart Identify delay or storage Reduce travel distance Reduce material handling Rearrange workplace Group similar activities Use improved equipment Ideas for improvement 泡麵 10 5 Motion Study is the systematic study of the human motions used to perform an operation. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Eliminate unnecessary motions Combine activities Reduce fatigue Improve the arrangement of the workplace Improve the design of tools and equipment 11 Physical Considerations in Job Design Work physiology sets work-rest cycles according to the energy expended in various parts of the job. Motion classification 1. Finger 2. Wrist 3. Elbow 4. Shoulder 5. Trunk Laptop and office ergonomics 12 6 Ergonomics: Incorporation of human factors in the design of the workplace Ventilation Noise & Vibration Temperature & Humidity Illumination Color Work Breaks Safety 13 血汗工廠? 14 7 Work Measurement 分析工作方式並設定標準工時 Standard time: The amount of time it should take a qualified worker to complete a specific task, working at a sustainable rate, using given methods, tools and equipment, raw materials, and workplace arrangement. Why use it? Schedule work and allocate capacity Motivate and measure work performance Estimate labor costs Benchmarks for improvement 15 Stopwatch Time Study 1.明確定義工作項目與方法 2.決定重複測量次數 n 3.以碼表重複測量所需時間 n T1 x i 1 n 1i n T2 x i 1 2i n 4. 考慮評比係數(performance rating)與寬放時間 NT T1 PR1 T2 PR2 Standard time=NT (1+Allowance percentage) Example 3 16 8 17 Work Sampling: estimating the proportion of time that a worker spends on various activities and idle time. 護理工作繁重且人員短缺,但是護理師經常花費時間在 非護理相關的工作,造成資源浪費。 Randomly select a nurse and observe whether or not she is performing non-nursing activities. Make such observations at 1000 random times during the week. Suppose 600 of them are nursing activities. Conclude that non-nursing activities account for 403% of time. Hire low cost labor to perform non-nursing activities to avoid a shortage of well-trained nurses. 18 9 Motivation Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs 員工都願意擔負更大的責任?願意盡力提高績效? Self actualization Esteem needs Belongingness and love needs Safe or security needs Physiological needs ? ? 工作滿意度 工作動機或生產力 懲 工作保障 + 獎勵制度 工作績效 19 Financial Incentive Plans Time-based vs. Output-based Hourly Pay, Straight Salary, Piece Rate, Commissions Individual and Small Group Incentive Plans Pay for Knowledge, Pay for Performance 績效獎金 Wei-Yin Chen Organization-wide Plans Profit Sharing, Gain Sharing 年終獎金 20 10 Summary Job design: Work Efficiency versus Job Satisfaction Working conditions are an important aspect of job design. Work measurement is required for capacity planning, cost estimation, and performance evaluation. Job design must be understood and agreed to by both management and employees Show me the money. 21 11