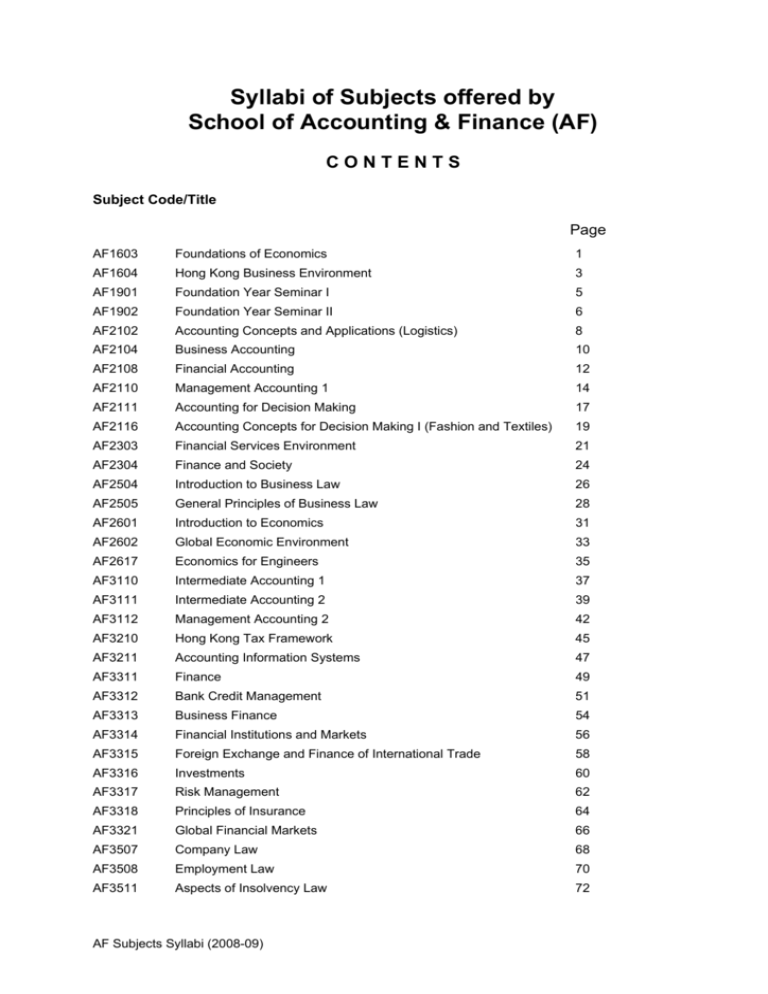
Syllabi of Subjects offered by
School of Accounting & Finance (AF)
CONTENTS
Subject Code/Title
Page
AF1603
Foundations of Economics
1
AF1604
Hong Kong Business Environment
3
AF1901
Foundation Year Seminar I
5
AF1902
Foundation Year Seminar II
6
AF2102
Accounting Concepts and Applications (Logistics)
8
AF2104
Business Accounting
10
AF2108
Financial Accounting
12
AF2110
Management Accounting 1
14
AF2111
Accounting for Decision Making
17
AF2116
Accounting Concepts for Decision Making I (Fashion and Textiles)
19
AF2303
Financial Services Environment
21
AF2304
Finance and Society
24
AF2504
Introduction to Business Law
26
AF2505
General Principles of Business Law
28
AF2601
Introduction to Economics
31
AF2602
Global Economic Environment
33
AF2617
Economics for Engineers
35
AF3110
Intermediate Accounting 1
37
AF3111
Intermediate Accounting 2
39
AF3112
Management Accounting 2
42
AF3210
Hong Kong Tax Framework
45
AF3211
Accounting Information Systems
47
AF3311
Finance
49
AF3312
Bank Credit Management
51
AF3313
Business Finance
54
AF3314
Financial Institutions and Markets
56
AF3315
Foreign Exchange and Finance of International Trade
58
AF3316
Investments
60
AF3317
Risk Management
62
AF3318
Principles of Insurance
64
AF3321
Global Financial Markets
66
AF3507
Company Law
68
AF3508
Employment Law
70
AF3511
Aspects of Insolvency Law
72
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
AF3601
Managerial Economics
75
AF3604
Monetary and Financial Systems
77
AF3901
Economics for Engineers
79
AF4106
Advanced Financial Accounting
81
AF4107
Financial Statement Analysis (Elective subject)
83
AF4108
Issues in Management Accounting
85
AF4109
International Accounting
88
AF4212
International Tax Planning and Management
90
AF4215
Information Systems Audit and Control
92
AF4216
Auditing and Assurance 1
94
AF4217
Auditing and Assurance 2
96
AF4218
Financial Reporting Framework in China
99
AF4220
Forensic Accounting
101
AF4221
Strategic Tax Planning and Management
104
AF4222
China Tax Framework
106
AF4223
Analysis and Design of Accounting Information Systems
109
AF4224
Information Systems Audit and Control
110
AF4300
Introduction to Derivative Securities
113
AF4306
International Finance
115
AF4314
Company Valuation and Analysis
117
AF4317
Derivative Securities
119
AF4318
Financial System in China
121
AF4320
Corporate Finance
123
AF4321
Case Study in Finance
125
AF4322
Management of Financial Institutions
127
AF4323
International Finance
129
AF4324
Financial Planning
132
AF4325
Wealth Management
133
AF4326
Fixed Income Securities
136
AF4328
Mergers and Acquisitions
138
AF4331
Business Valuation
141
AF4332
Corporate Risk Management
143
AF4510
Law and Practice of Banking
145
AF4511
E-Business Law
148
AF4512
Corporate Governance and Compliance
151
AF4513
Corporate Social Responsibility
154
AF4605
Hong Kong – China Business
157
AF4606
Economic Development of Asia-Pacific Countries
159
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
Subject Code
:
AF1603
Subject Title
:
Foundations of Economics
Level
:
1
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Tutorials
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
None
Co-requisites
:
None
Exclusion
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
D
Final Examination
D
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Outcomes by enabling students to
apply fundamental economic concepts to analysis of real world economic activities, and
communicate effectively. It also requires students to work effectively with and through
others.
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
explain the fundamental economic concepts.
use appropriate tools to apply the fundamental economic concepts to analysis real
world situations.
evaluate basic economic data.
Indicative Teaching/ Learning Approach
Lectures will introduce the fundamental economic concepts, with specific reference to the
analysis on common economic activities.
Tutorials provide students with the opportunity to deepen their understanding of the concepts
taught in lectures. The activities in tutorials include student presentations and discussions of
problems sets.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
The ability to explain fundamental economic concepts and use appropriate tools to apply
them in real world situations will be assessed in a quiz and a final examination. Evaluation
of basic economic data, effective communication and the ability to work with others are
assessed in the Group presentation and the discussion of problem sets.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
1
Indicative Content/ Outline Syllabus
What is economics?
Scarcity and opportunity cost, The role of the market, Positive and normative, Relation with
other subject disciplines.
Demand and supply analysis
Determinants of the demand curve, Determinants of the supply curve, Market equilibrium.
Perfect competition
The quest of profits and the equilibrium in a competitive market.
The income and output of nations
National income accounting, output determination, Economic growth, fiscal policy and
aggregate demand, monetary policy and aggregate demand.
Inflation and Unemployment
The causes and costs of inflation, the causes and costs of unemployment
International Trade
Exchange rates and the balance of payments, Foreign trade and output determination
Indicative Reading
Stanley L. Brue and Campbell R. Mcconnell (2007), Essentials of Economics, 1st Edition,
McGraw-Hill, U.S.A.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
2
Subject Code
:
AF1604
Subject Title
:
Hong Kong Business Environment
Level
:
1
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Tutorials
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
Foundations of Economics (AF1603)
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
Building on the foundation study in the working of Hong Kong being a modern city economy,
this subject aims to introduce the essentials of the economy of Hong Kong which are basic
to the study of the system and the territory’s business environment. This subject contributes
to the achievement of the BBA Outcomes by enabling students to analyze business
situations and problems by applying concepts from economics and finance (Outcome 7), to
identify and analyze various business issues of the domestic environment (Outcome 12),
and communicate effectively (Outcomes 1 and 2).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students are expected to be able to:
•
•
•
Analyze the social and business structures of Hong Kong;
Synthesize Hong Kong’s business, financial and economic environment; and
Evaluate the major policies implemented by the Hong Kong Government.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
Concepts and business issues of the Hong Kong environment will be introduced through
lectures, which students will be required to apply in their seminar activities.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Classwork, including learning-to-learn exercises, will help students to apply concepts, and to
identify and analyze various business issues (Outcomes 7 and 12). Effective
communications will be assessed through group presentation and class discussion. Other
coursework assessment tools include a presentation, a report and a mid-term test
(Outcomes 1 and 2).
Indicative Content / Outline Syllabus
Economic Setting
Growth and industrialization, business and industrial structures
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
3
Social Structure
Community, prosperity and stability, income and inequality
Market Environment
Competition and competition policy, business restructuring
Trade and Financial Sector
External trade, international financial centre, security markets, retail and logistic
businesses.
Labour and Employment
Employment, labour resources and Hong Kong’s competitiveness.
Government and Politics
Government and administration, executive council, legislative council
Hong Kong – China Mainland Integration
Economic integration and synergy effects, trade and investment, factor mobility
Indicative Reading
Essential Reading
Ng, S. K. and D. Lethbridge (eds.), The Business Environment in Hong Kong, Oxford
University Press, most recent edition.
Reference List
Li Kui-wai, The Hong Kong Economy: From Recovery to Restructure, McGraw Hill, most
recent edition.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
4
Subject Code
:
AF1901 / LGT1201 / MM1001
Subject Title
:
Foundation Year Seminar I
Level
:
1
Credits
:
1
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
14 hours
100%
OBJECTIVES
To enable students to have a foretaste of studying Business and to provide opportunities for
more interaction with the faculty members, through which students would also be helped to
cultivate a sense of belonging to their parent departments and to build up their own identity.
LEARNING OUTCOMES
On successful completion of this subject, students are expected to be able to :
•
•
•
Apply creative thinking to their university studies
Identify and resolve ethical issues which arise in respect of university life
Appreciate the requirement of their respective professions of study acquire skills for
studying in University
KEYWORD SYLLABUS
All-rounded Education at PolyU
How to Excel in University and Business Studies
Introduction to the Faculty of Business
Introduction to Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) Programmes
Introduction to Accounting and Finance
Introduction to Logistics
Introduction to Management and Marketing
TEACHING AND LEARNING APPROACH
Students are required to participate in sharing and discussion in order to shape the subject
for themselves. Students will be required to submit a reflective essay at the end of the
semester.
SUBJECT CO-ORDINATOR
DAVIES Howard
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
5
Subject Code
:
AF1902
Subject Title
:
Foundation Year Seminar II
Level
:
1
Credits
:
1
Mode of Study
:
Seminars 14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
None
Co-requisites
:
None
Exclusion
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
100%
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Coursework
D
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Outcomes by enabling students to
have a foretaste of studying accounting and finance, to learn to identify and analyze those
aspects of the domestic and global business environment that set the ‘parameters of choice’
within which business organizations set objectives and take actions (Outcome 12) , to learn
from faculty members and industry practitioners on how to identify and resolve ethical issues
as they arise generally and in specific business settings (Outcome 5), to carry out and act
upon self-appraisal and reflective thinking, in the areas of creativity, teamwork, leadership
and career selection and learning to learn (Outcome 8), and to communicate verbally in
English (Outcome 1) as well as to communicate in writing in English (Outcome 2). The
seminars provide opportunities for more interaction with the faculty members and industry
practitioners, through which students would also be helped to cultivate a sense of belonging
to the School of Accounting and Finance and to build up their own identity.
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
Gain exposure to the professions of accounting and finance
•
Demonstrate a basic knowledge of the contemporary issues, threats and opportunities in
the accounting and finance profession
•
Acquire skills for studying in accounting and finance
•
Demonstrate an ability to carry out reflective thinking in the areas of career development
and career selection and an ability to communicate in writing in English at a level
appropriate for their level of study.
Indicative Teaching/ Learning Approach
During seminars, students are required to participate in sharing and discussion. Guest
speakers in the related industries and sectors will be invited to talk about the career
prospects and expected attributes of potential employees. Firm visits may be arranged.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
6
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Students will be required to submit a reflective essay, written in English (Outcome 2), at the
end of the semester. They are required to reflect on what important lessons they have
learned from the seminars (Outcome 5, Outcome 8, and Outcome 12), identify major issues
in their study and future career development, and assess their own preparedness for
studying and subsequently working in the accounting and finance professions (Outcome 8).
Indicative Content / Outline Syllabus
Accounting and Finance Professions and Market Economy
Generic skills for a professional in Accounting and Finance
Professionalism. Ethics. Behavioural Characteristics.
Knowledge Base for a Professional in Accounting and Finance
Core Competence. Interdisciplinary Knowledge – Accounting, Finance, Tax, Law and
Economics.
Professional Accountants in Practice
Non-practising Professional Accountants
Financial Accountants. Management Accountants. Tax Advisers and Assessors. Internal
Auditors. Academics and Accountants Working in Non-Profit Organisations / Government /
NGOs.
Professionals in Finance and Financial Services
Financial Analysts. Brokers. Investment Advisers. Commercial Banks. Merchant Banks.
Investment Banks.
Professionals in other disciplines
Business Consultancy. Insolvency / Liquidation. Economists and Commercial Law.
Indicative Reading
Position Paper on Proposals to Strengthen the Regulatory Framework of the Accountancy
Profession and Amendments to the Professional Accountants Ordinance and By-Laws
(http://www.hkicpa.org.hk/publications/other/position_paper.pdf)
A Plus magazine (http://www.hkicpa.org.hk/APLUS.php)
Information Paper "Setting Hong Kong Financial Reporting Standards"
(http://www.hkicpa.org.hk/professionaltechnical/accounting/dueprocess/Info_paper_FRS.pdf)
Internal Control and Risk Management - A Basic Framework
(http://www.hkicpa.org.hk/publications/corporategovernanceguides/Guide_Eng_August.pdf)
HKSFA E-newsLetter, The Hong Kong Society of Financial Analysts Ltd.
(http://www.hksfa.org/about_HKSFA/publication.html)
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
7
Subject Code
:
AF2102
Subject Title
:
Accounting Concepts and Applications (Logistics)
Level
:
2
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Tutorials
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject enables students
•
to identify and evaluate the basic concepts in accounting and
•
to apply the accounting knowledge for making business decisions.
It also requires students to
•
Work effectively in groups and as individuals with an awareness of multidisciplinary
influences and challenges and to
•
apply problem solving and investigative skills.
Learning Outcomes
On successful completion of this subject, students should be able to:
•
apply and use the building blocks of the accounting system.
•
prepare simple financial statements.
•
use accounting tools to examine financial statement numbers in a systematic way.
•
apply various costing concepts in decision analysis
•
apply the accounting knowledge and skills in solving business problems.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
Students are initiated to the key concepts in lectures while the tutorial would provide an
avenue for interactive discussion between the instructor and students and among students.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
8
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Use accounting building blocks to build up the information system. Prepare simple financial
statements. Use accounting tools to examine the financial statements of selected firms.
Apply various costing concepts in case studies. Apply the accounting knowledge and skills in
solving case problems.
Indicative Content
Introduction to Accounting Information
Accounting as an information system
Accrual Accounting Concepts
Merchandising Operations as a case study
Reporting and Analysing Receivables and Long-Lived Assets
Preparation of Financial Statements
Income Statement
Retained Earnings Statement
Balance Sheet
Statement of Cash flows
Introduction to Financial Statement Analysis
Objectives of financial statement analysis
Horizontal analysis and vertical analysis
Analysis of profitability, liquidity and capital structure
Costing Principles and Operations Management issues
Manufacturing costs, product costs and period costs.
Enterprise Resources Planning and other developments in operations management.
Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis
Variable and fixed costs, contribution margin & breakeven analysis
Incremental Analysis and Capital Budgeting
Incremental analysis in make/ buy or stop/ process further and various decisions.
concept of present value and capital expenditure decision making
The
Indicative Reading
Kimmel, Weygandt and Kieso, 2nd Edition, Accounting, Tools for Business Decision
Making, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2008
Dyson, J.R., Accounting for Non-Accounting Students, 7th Edition, Financial Times PrenticeHall, 2007.
Williams, Haka, Bettner and Meigs, Financial and Managerial Accounting: The Basis for
Business Decisions, 14th Edition, Mc-Graw Hill, 2008.
Glautier and Underdown, Accounting Theory and Practice, 7th Edition, Pitman, 2001.
Horngren, C. and G. Foster, Cost Accounting – A Managerial Emphasis, 13th Edition,
Prentice-Hall, 2009.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
9
Subject Code
:
AF2104
Subject Title
:
Business Accounting
Level
:
2
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Tutorials
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
40%
Final Examination
60%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject enables students to record and analyze accounting information and to apply it in
a business context. It also enables students to identify and evaluate the accounting
information required for different types of decision making.
Learning Outcomes
On successful completion of this subject, students will be able to:
1. identify the financial accounting concepts and evaluate the way the concepts are applied
in the preparation of financial statements.
2. prepare and interpret a basic set of financial statements.
3. identify the uses and limitations of accounting information in decision-making
4. apply basic cost concepts and techniques for decision-making, planning and control
5. identify and evaluate the information for capital investment decision-making.
INDICATIVE TEACHING/LEARNING APPROACH
A two hour lecture will be conducted each week to initiate students into the ideas, concepts
and techniques of the topics in the syllabus, which is then reinforced by a one hour tutorial
designed to consolidate and develop students’ knowledge through discussion and practical
problem solving.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
The students will be assessed on how accounting information are formulated and to apply it
to business context in the tutorial discussion, the group/individual assignments and the midterm test. The application of accounting information and financial report analysis will be
assessed in the mid-term test and the final examination.
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Overview of Financial Statements and Reporting Process
Accounting as an information system, users of accounting information. Forms of business
organizations. Overview of business activities. Accounting guidelines. Principal financial
statements. Other items in published annual reports.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
10
Preparation of the Basic Financial Statements
An overview of the balance sheet and its underlying concepts. The accounting process.
Income statement measurement and its principles. An overview of statement of cash flow.
Preparation of final accounts for limited companies.
Accounting for Inventory and Fixed Assets
Choice of different valuation bases and their implications on financial statement reporting.
Introduction to Financial Statement Analysis
Objectives of financial statement analysis. Use of ratio analysis. Usefulness of ratios.
Analysis of profitability. Liquidity and risk. Capital structure. Interpretation of the analysis.
Limitations of financial statement analysis.
Introduction to Management Accounting
Introduction and relationship of management accounting with financial accounting. Cost
accounting. Planning and control: budgeting.
Short-term and Long-term Decisions Making
Basic cost concept and cost behavior and the application of cost-volume-profit analysis.
Capital investment appraisal using the payback method, profitability index, accounting rate of
return, net present value and internal rate of return.
Indicative Reading
Recommended Textbook
Marshall, D. H., at el Accounting What the Numbers Mean, 8th edition (International edition),
McGraw-Hill
Recommended References
Horngren, Harrison and Bamber, Accounting, 6th edition, Prentical Hall.
Weygandt, J.J., Keiso, D.E. and Kimmel, P.D., Accounting: Tools for Business Decision
Making
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
11
Subject Code
:
AF2108
Subject Title
:
Financial Accounting
Level
:
2
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Tutorials
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(Grade D)
Final Examination
(Grade D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of BBA Outcomes by enabling students to
analyse financial reports (Outcome 9), apply accounting conceptual framework in the
business problems analysis (Outcome 7) and process a foundation of financial accounting
skills and knowledge, on which to base the process of continuous professional development
(Outcome 13). It also contributes to the development of information technology skill
(Outcome 6) and ethical reasoning (Outcome 5).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
Explain the role and importance of accounting information in assisting decision-making
in a business context.
•
Apply the financial accounting conceptual framework in the recording, processing,
summarizing and reporting phases of the accounting cycle.
•
Evaluate the assumptions, principles and conventions underlying financial accounting
processes.
•
Identify and resolve accounting related ethical issues as they arise.
•
Apply appropriate analytical tools for the interpretation of financial statements.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
A two hour lecture will be conducted each week to initiate students into the ideas, concepts
and techniques of the topics in the syllabus, which is then reinforced by a one hour tutorial
designed to consolidate and develop students’ knowledge through discussion and practical
problem solving. Students will be assigned and assessed with a group project which
simulates the maintenance of a set of accounting records for a company.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
12
Indicative Assessment Tasks
The application of financial accounting framework (Outcome 7) and fundamental financial
accounting skills and knowledge (Outcome 13) will be assessed in the pop quiz, mid-term
test, the project assignment and the final examination. The knowledge in the use of current
information technology (Outcome 6) is assessed in the mid-term test. The students will also
be required to analyse financial statements (Outcome 9), identify and resolve accounting
related ethical dilemmas (Outcome 5) in mini case studies in the final examination.
Indicative Content/ Outline Syllabus
The Business and Accounting Environment
Different types of businesses, their common objectives and basic features. The need for
accounting as a basis for decision making. Ethical considerations in financial reporting.
The Financial Accounting Framework
Accounting equation and double entry bookkeeping system. Differences between cash and
accrual bases of accounting. Preparation of journals, ledger accounts, trial balance and
basic financial statements. Prepayments and accruals. Valuation of debtors, stock and fixed
assets. Quality of earnings and earnings management. Control of cash through bank
reconciliation statement.
Accounting Principles and Concepts
Fundamental accounting concepts and other accounting principles that underlie the
preparation of financial statements.
Company Accounting
Features of the corporate form of business ownership. Rights and obligations of interested
parties. Issues relating to company accounts. Preparation of financial statements of a
company. Corporate governance issues in financial reporting.
Analysis and Interpretation of Financial Statement
Need for analysis and interpretation of financial statements. Interpretation techniques
including ratio analysis and cash flow statement. Calculation and interpretation of basic
financial ratios. Limitations of ratio analysis.
Indicative Reading
Recommended Textbook
Weygandt, J.J., D.E. Kieso and P.D. Kimmel, Financial Accounting, Latest Edition, Wiley.
Recommended References
Horngren, Harrison and Bamber, Accounting, Latest Edition, Prentice Hall.
Ferrell, Fraedrich and Ferrell, Business Ethics – Ethical Decision Making and Cases, 6th
edition, 2005, Houghton Mifflin Company.
Stice, Stice and Skousen, Intermediate Accounting, Latest Edition, Thomson, South-Western.
Williams, J.R., S.F. Haka, M.S. Bettner and J.V. Carcello, Financial Accounting, the Latest
Edition, McGraw-Hill.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
13
Subject Code
:
AF2110
Subject Title
:
Management Accounting 1
Level
:
2
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Tutorials
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA (Hons) Programme Outcomes by
enabling students to anaylse business situations and problems by applying conceptual
frameworks drawn from accounting, finance, economics, behavioural science and
quantitative methods (Outcome 7). It will prepare students for identifying, analyzing the
means by which value is created in goods and services and delivered to end users
(Outcome 10). The subject will also enable students to develop critical thinking and
analytical skills (Outcome 4), and ethical awareness (Outcome 5) in the management
accounting context. In addition, the subject will provide students with sufficient
professionally-specific skills and knowledge in management accounting to make an
immediate contribution to the organization in which they are first employed (Outcome 13).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
Understand and critically apply the appropriate concepts and techniques to generate
cost information to help management in organizational planning and control (Outcomes 7
& 13).
•
Identify and analyse the means to create value in goods and services and deliver to end
users, using appropriate costing methods and management accounting techniques
(Outcomes 10 & 13).
•
Suggest alternative solutions to various management decision-making problems, based
on their understanding of relevant cost information and other management accounting
tools, in achieving business and corporate strategic objectives (Outcomes 4 & 13).
•
Evaluate ethical issues from a management accounting perspective and suggest
appropriate responses to aid management decision-making processes (Outcomes 5 &
13).
Indicative Teaching/Teaching Approach
The two-hour weekly lecture will be structured to guide and promote students’ understanding
of relevant concepts and management accounting practices. In addition, there will be one
tutorial of one hour per week. The tutorials will adopt a student-centered approach, including
case analysis, electronic assignments, newspaper and professional articles for discussion
and team-presentation.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
14
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Assessment components include group-based case analysis with report and presentation;
mid-term examination; participation; and final examination. The assessment tasks require
students to demonstrate their understanding and critical application of the appropriate
concepts and professional skills to generate cost information to help management in
organizational planning, control and decision-making processes (Outcomes 4, 7 and 13);
ability to identify and analyse the means to create value in goods and services and deliver to
end users, (Outcomes 10 & 13); and ability to evaluate ethical issues from a management
accounting perspective and suggest appropriate responses (Outcomes 5 & 13).
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Managerial Accounting and the Business Environment
Comparison of financial and managerial accounting. Expanding role of managerial
accounting. The role of a management accountant in enhancing corporate governance.
Code of professional ethics.
Cost Concepts, Cost Classification, Cost Estimation and Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
Cost and management accounting terms. Cost objectives. Management process and its
implication for the management accountant. Different methods in cost estimation.
Assumptions behind the cost-volume-profit analysis. Break-even point. Relationship between
CVP and cost planning. Margin of safety. Operating Leverage.
Absorption and Marginal Costing
Differences between absorption and marginal costing. Effect of changes in production and
sales level on profit. Use of information for external reporting and internal decision making.
Job Costing
Cost System Design. Approach to job costing. Cost accumulation system and cost
objectives. Pre-determined overhead recovery rate. Service and operation departments cost
allocation.
Budgeting
Master budget and its usefulness to organizations. Zero-based budgeting. Incremental
budgeting. Fundamental budgetary behaviour.
Relevant Costs for Decision Making and Pricing
The decision making process. Cost concepts for decision making. Applications of relevant
costs in different settings including constrained resources. Pricing policies for products and
services.
Performance Measurement
Decentralisation and responsibility centers. Segment Reporting. Financial and non-Financial
measures of performance and outcomes. The Balanced Scorecard. Performance measures
and compensation.
An Overview of Contemporary Issues in Management Accounting
Contemporary management accounting practices. Quality cost management. Role of
management accounting in business sustainability and corporate social responsibility.
Indicative Reading
Prescribed Textbooks
Garrison, R.H., E.W. Noreen and P.C. Brewer, Managerial Accounting, 12th Edition,
McGraw-Hill, 2007.
Managerial Accounting (Customised Edition), McGraw-Hill, 2007*.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
15
References
Hilton, R.W., Maher, M.W. and F.H. Selto, Cost Management: Strategies for Business
Decisions, 3rd Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2006.
Blocher, E.J., K.H. Chen and T.W. Lin, Cost Management: A Strategic Emphasis, 3rd
Edition, McGraw Hill, latest edition.
Selected readings from professional journals and current news reports will be provided to
students during the course.
* Only required for students who are going to take both Management Accounting 1 & 2
(AF2110 & AF3112).
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
16
Subject Code
:
AF2111
Subject Title
:
Accounting for Decision Making
Level
:
2
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Tutorials
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
None
Exclusions
:
Financial Accounting (AF2108)
Management Accounting 1 (AF2110)
Assessment
Minimum Pass Grade
:
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to equip students with sufficient professional skills and knowledge
and enabling them to analyze business situations and problems in the investment context. It
also enabling students to effectively communicate verbally and in writing in English , and
identify ethical issues as they arise.
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
Describe the role and importance of management and financial accounting information in
assisting decision-making in a business environment.
•
Identify assumptions, principles and conventions underlying financial reports.
•
Interpret and analyze financial reports
•
Apply cost and accounting information to aid managerial decision-making.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
A two hour mass lecture will be conducted each week to initiate students into the ideas,
concepts and techniques of the topics in the syllabus, which is then reinforced by a one hour
tutorial designed to consolidate and develop students’ knowledge through discussion and
practical problem solving.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Individual project assignment will enable students to apply professional skills and
knowledge, to analyze business situations and problems, to think critically and creatively and
to communicate effectively in English. Written test and examination will test students’
professional skill and knowledge of the subject and to communicate effectively in English.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
17
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Framework of Financial Reporting
Need for information in capital markets, basic financial statements, accounting cycle:
capturing economics events; accruals and deferrals; reporting financial results, role of the
auditor.
Elements of Financial Statements
Merchandising activities, financial assets, inventories and cost of goods sold, plant and
intangible assets, liabilities, equities, income and changes in retained earnings, cash flow
statement.
Analysis and Interpretation of Financial Statements
Financial ratios, financial statement analysis, measuring business performance, globalization
and foreign currency transactions.
Managerial Accounting Information
Accounting systems for measuring costs: overhead allocations and absorption costing
Planning, Control and Analysis
Standard costing and budget, inventory planning and control, cost-volume-profit analysis,
incremental analysis.
Indicative Reading
Williams, J., S. Haka and M.S. Bettner, Financial and Managerial Accounting: The Basis for
Business Decisions 2008, McGraw Hill.
Horngren, C.T., W.T. Harrison and L.S. Bamber, Accounting, 2007 Prentice Hall.
Horngren, C.T., G.L. Sundem and W.O. Stratton, Introduction to Management Accounting
2008, Prentice Hall.
Jones, M., Accounting 2006, Wiley.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
18
Subject Code
:
AF2116
Subject Title
:
Accounting Concepts for Decision Making I
(Fashion and Textiles)
Level
:
2
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Tutorials
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
None
Co-requisites
:
None
Exclusion
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
40 %
Final Examination
60 %
Coursework
D
Final Examination
D
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to enable students to effectively communicate verbally and in writing
in English , and identify ethical issues as they arise. It also equips students with sufficient
professional skills and knowledge and enabling them to analyze business situations and
problems.
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
Interpret financial accounting information
•
Design and record accounting information in main manufacturing and trading
activities
•
Conduct accounting and costing information analyses for different types of
operational decisions
•
Measure profit performance by comparing accounting budgets with actual accounting
records
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
Lectures aim to introduce the key issues of each topic to students and tutorials provide a
forum for discussing assigned exercises and queries arising from lectures and readings.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Individual project assignment will enable students to apply professional skills and
knowledge, to analyze business situations and problems, to think critically and creatively and
to communicate effectively in English. Written test and examination will test students’
professional skill and knowledge of the subject and to communicate effectively in English.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
19
Indicative Content
Introduction to Accounting Information
Forms of business organizations. Accounting as an information system. Importance of
controls. Users of accounting information. The accounting cycle. The accounting equation.
Basic accounting rules and concepts. Double-entry systems and book keeping for assets.
Liabilities and equity.
Understanding Financial Statements
Principal financial statements and their information contents. Concepts underlying the
preparation of these financial statements. Preparation of basic financial statements e.g. trial
balance, profit and loss account, balance sheet and cash flow statement. Understanding of
manufacturing accounts.
Introduction to Financial Statement Analysis
Objectives of financial statement analysis. Horizontal analysis versus longitudinal analysis.
Analysis of profitability. Liquidity and capital structure. Key concepts of working capital
management. Limitations of financial statement analysis.
Introduction to Costing Principles
Cost classification and accumulation. Typical costing methods and their applications.
Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis
CVP analysis as a decision making technique. The concepts of contribution. Break-even
point and margin of safety. Limitations of CVP analysis.
Introduction to Budgetary Control
Budgetary control and the budgeting process.
Indicative Reading
Dyson, J.R., Accounting for Non-Accounting Students, 7th Edition, Financial Times PrenticeHall.
Jones, Michael, Accounting, 2nd edition, John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Glautier and Underdown, Accounting Theory and Practice. 6th Edition, Pitman.
Horngren, C. and G. Foster, Cost Accounting – A Managerial Emphasis, 12th Edition,
Prentice-Hall.
Williams, Haka, Bettner and Meigs, Financial and Managerial Accounting: The Basis for
Business Decisions, 13th Edition, Mc-Graw Hill.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
20
Subject Code
:
AF2303
Subject Title
:
Financial Services Environment
Level
:
2
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Tutorials
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA in Financial Services Programme
Outcomes by enabling students to enhance their global outlook (Outcome 3) through the
studies on the domestic and international financial markets regulatory framework. This
subject also provides foundation knowledge for other financial services subjects and
develops the student’s understanding of the environment in which Hong Kong financial
institutions operate (Outcome 9), and how the environment impacts upon the industry and
vice versa (Outcome 12).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students should be able to:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Describe the different types of financial markets and institutions operating in Hong Kong,
their structure and activities;
Describe the financial markets and their features;
Explain the role of various financial markets in the delivery of financial services;
Examine the major financial services and products to personal and business clients;
Outline the main characteristics of the domestic and international regulatory framework
in which financial institutions and markets operate and discuss the implications for
customers and service providers;
Examine the key strategic issues facing the industry; and
Assess the impact of the changing financial environment, both domestic and
international, upon the operations and business strategy of financial institutions in Hong
Kong.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
Teaching will include lectures and seminars. Lectures will be used to introduce the
underlying concepts. Seminars will be used to discuss some current issues affecting the
local and international financial markets and institutions. Students may be required to
undertake a group project and present a report on a topic within the subject area.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
21
Indicative Assessment Tasks
The individual project will help students to apply concepts, and think critically and creatively
(Outcome 4&7). The group project and class presentation will enhance students’
communication skills (Outcome 1&2). The ability to work with others will be assessed via a
form of Evaluation of Group Performance (Outcome 8).
The final examination will assess the level of understanding of students in this subject.
These include the understanding on the domestic and international financial markets
regulatory framework (Outcome 3), the knowledge of the environment in which Hong Kong
financial institutions operate (Outcome 9), how the environment affects the industry and vice
versa (Outcome 12).
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Financial Services and the Economy
Economic sectors, financial markets. Current situation and importance of financial services
industry in Hong Kong. Functions of financial intermediaries.
Financial Markets and Financial Institutions
Overview of major financial markets in Hong Kong, their development, structure and
competitiveness. Features of authorized institutions, insurance companies, pension funds,
investment funds, stockbrokers, personal financial planning institutions in Hong Kong.
Financial Services and Products in Hong Kong
Characteristics of the mainstream services and products provided by authorized institutions,
insurance companies, pension funds, investment funds, stockbrokers, and personal financial
planning institutions.
Regulation of the Financial Services Industry
Rationale for government regulation of financial services industry. Regulatory framework of
the financial sector in Hong Kong. Regulatory authorities including SFC, HKEx, HKFI,
HKMA, and MPFSA. Investor protection. Depositor Protection. Overview of major financial
services legislation in Hong Kong.
Trends in Financial Services Industry in Hong Kong
Developments and trends of international and regional regulation of financial services
industry. Impact of technology, QFII, QDII and CEPA on the industry.
Indicative Reading
Hong Kong Government. Hong Kong Yearbook, Latest Edition.
Brighouse, David, The Financial Services Environment, Latest Edition, Financial World
Publishing.
Dietrich, J. Kimball, Financial Services and Financial Institutions, Value Creation in Theory
and Practice, Latest Edition, Prentice Hall International Editions.
Hong Kong Securities and Futures Commission, Quarterly Bulletin and Annual Report,
Latest Edition.
Hong Kong Monetary Authority, Quarterly Bulletin and Annual Report, Latest Edition.
Hong Kong Monetary Authority, Guide to Hong Kong Monetary and Banking Terms
http://www.info.gov.hk/hkma/eng/public/ghkmbt/ghkmbt_b.htm
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
22
Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Company Limited, Investor Education, Frequently
Asked Questions, Chapter 4, Securities Products
http://www.hkex.com.hk/invedu/faq/faqsehk.htm
Relevant Material from the Following Internet Sources:
The Hong Kong Monetary Authority: http://www.info.gov.hk/hkma
Office of the Commissioner of Insurance: http://www.oci.gov.hk
The Securities and Futures Commission: http://www.hksfc.org/hk
Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Company Limited: http://www.hkex.com.hk
Hong Kong Investment Funds Association: http://www.hkifa.org
The Mandatory Provident Fund Schemes Authority: http://www.mpfahk.org/
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
23
Subject Code
:
AF2304
Subject Title
:
Finance and Society
Level
:
2
Credits
:
2
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
Pre-requisites
:
None
Exclusions
:
Financial Services Environment (AF2301), Business
Finance (AF3302), Introduction to Finance (AF3308),
Finance (AF3311)
Assessment
:
Continuous Assessments
28 hours
50%
(include projects, assignments and group presentation)
Final Examination
50%
Minimum Pass Grade
:
This subject is graded by Pass or Fail only. Students are
required to pass in both the continuous assessments and the final examination in order to
obtain an overall pass in this subject.
ROLE AND PURPOSE
This subject will address the many ways in which finance affects our life and our society.
With daily examples and issues commonly shown in the newspapers, this subject will help
students of different disciplines to appreciate the relevance and importance of finance to
their daily lives. The subject will also provide students with a broad and intellectual view on
how finance affects the economy.
LEARNING OUTCOMES
On completing this subject, students will:
•
•
•
Appreciate the relevance of finance and how finance affects their daily lives.
Have a general understanding on how finance affects the economy and the society.
Gain a critical perspective on corporate world and the finance industry
INDICATIVE CONTENT
Finance and the Financial System
What is finance? What is the financial system? What are the functions of the financial
system to the economy?
Personal Financial Decision-making
The time value of money. Credit-card interest and payment. Education as investment. Buy or
rent decision on property. Life-cycle financial planning.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
24
The Corporate World
Human behaviour and profit-making firms. Corporate investments, R&D, capital markets,
and economic development. Corporate failure, corporate restructuring.
Financial Market, Risks, and Bubbles
Market efficiency and behavioral finance, financial innovations and risk management, fads,
bubbles, and financial market collapse.
Finance and Society
Finance and the sources of economic growth, bubbles and economic downturn, corporate
misconduct, corporate governance, and corporate ethics, the Hong Kong situation
TEACHING/LEARNING APPROACH
In the lectures the general principles of the syllabus topic will be presented and developed,
together with guidance on further reading and activities. Lectures may also be used for the
presentation and discussion of leading cases.
INDICATIVE READING
References
Madura, J., Personal Finance, 2nd Edition, Pearson Addison Wesley, 2004.
Ross, S., R.W. Westerfield and B.D. Jordan, Fundamentals of Corporate Finance, 6th
Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2003.
Partnoy, Frank, Infectious Greed: How Deceit and Risk Corrupted the Financial
Markets, Times, 2003.
Bodie, Zvi and Robert C. Merton, Finance, Prentice-Hall, 2000.
Kindleberger, Charles P., Manias, Panics, and Crashes: A History of Financial Crisis,
4th Edition, John Wiley & Sons, 2000.
SUBJECT CO-ORDINATOR
NG Anthony
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
25
Subject Code
:
AF 2504
Subject Title
:
Introduction to Business Law
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures and Tutorials 42 hours
Pre-requisites
:
None
Co-requisites
:
None
Exclusion
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50 %
Final Examination
50 %
Coursework
D
Final Examination
D
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Outcomes by enabling students to
analyze business problems by applying conceptual frameworks drawn from case law and
legislation (Outcome 7), demonstrate critical and creative thinking in the business setting
(Outcome 4), identify and resolve ethical issues arising in the business (Outcome 5) and
communicate effectively (Outcomes 1 and 2)
Learning Outcomes:
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
Identify, examine and resolve business-related legal problems by analyzing case law
and legislation
•
Identify and evaluate the practical actions required for resolving legal issues in business
•
Follow future legal developments in commercial law
Indicative Teaching/ Learning Approach
Lectures will introduce legal principles, legislation, and case law, which students will be
required to apply during their tutorials and in their final examination.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
A legal problem based essay will help students to demonstrate critical and creative thinking
(Outcome 4), apply appropriate legislation and common law principles (Outcome 7) and
communicate effectively (Outcome 2), as will the role-play. Rubrics will be used for
assessing learning outcomes for both assessment tasks. The examination will enable
students to demonstrate their written English skills (Outcome 2), legal knowledge, legal
reasoning and critical thinking skills by analyzing business problems and applying the law to
resolve the problem (Outcome 7).
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
26
Indicative Content / Outline Syllabus
Legal Framework
The Hong Kong legal framework: the Executive Council the Legislative Council and the
judiciary; dispute resolution.
The Law of Contract
Essentials of a valid contract; reasons for invalid or unenforceable contracts; terms of
contract.; discharge of contract and remedies; electronic contracts; contracts for the supply
of service.
Sale and Supply of Goods
The nature of goods; implied terms; transfer of property and risk; retention of title clauses;
sale by non-owner; rights and remedies of the seller and buyer.
Law of Commercial Associations
Agency relationships; the nature of corporate personality and the comparison between
partnerships and incorporated associations.
Employment Law
Employment contracts and terms; employees and independent contractors; common law
duties of the employer and employee; constructive and unfair dismissal; bringing an action in
the Labour Tribunal.
Tort
Negligence; professional liability for careless misstatements; ethical responsibility for words
and conduct.
Indicative Reading
Textbooks
Anjunan, K. & Majid, A. (2002), Business Law in Hong Kong, Lexis Nexus.
Stott, V. (2001), An Introduction to Business Law in Hong Kong, 3rd Edition, Longman Asia.
Legislation
The Laws of Hong Kong
Halsbury’s Annotated Ordinances
http://www.justice.gov.hk
Law Reports
Hong Kong Law Reports
Hong Kong Law Reports and Digest
Hong Kong Cases
Final Court of Appeal Cases
All England Law Reports (UK)
HK Electronic Citations (Westlaw)
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
27
Subject Code
:
AF2505
Subject title
:
General Principles of Business Law
Level
:
2
Credits
:
3
Mode of study
:
Seminars
Prerequisites
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
42 hours
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the Higher Diploma in International Transport
Logistics Outcomes by enabling students to investigate and analyze business problems by
themselves and in groups (Outcome 2) applying conceptual frameworks drawn from case
law and legislation (Outcomes 4 and 6), demonstrate critical and creative thinking in the
business setting (Outcome 6), identify and resolve ethical and legal issues arising in the
business (Outcome 6) and communicate effectively by presenting their findings and
conclusions in concise, readable and organized prose (Outcome 1).
Learning Outcomes:
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
Identify, examine and resolve business-related legal problems by analyzing case law
and legislation
Identify and evaluate the practical actions required for resolving legal issues in the field
Follow and appreciate future legal developments in commercial law
Indicative Teaching/ Learning Approach
Instruction will be delivered by way of lectures and seminars.
The lectures will explain and emphasise key concepts and will assist students in the
assimilation of basic legal theory, together with its practical application to the business
environment. Lectures will provide further analysis of the topics contained in the syllabus
with particular emphasis on practical examples, and discussions of how the law effects
business decisions. Lectures will be conducted in an interactive manner requiring prior
preparation, and class participation by students.
Seminars will be problem based and promote student participation in the learning process,
through discussion and application of law to facts. Students may also be expected to
prepare relevant legal documents likely to be encountered in business. The emphasis
throughout seminars will be on the practical application of legal theory. Seminars will
reinforce topics, which have been dealt with more generally in the lecture.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
28
Indicative Assessment Tasks
The individual assignment will require students to identify the applicable concepts (Outcome
2), to think critically and creatively (Outcome 6), apply the law to the given fact situations
(Outcomes 4 and 6) and discuss legal issues in prose that is organized grammatical and
readable (Outcome 1). The examination will call for the same skills and outcomes. Effective
communication will also be involved in class presentations
Indicative Content / Outline Syllabus
Sources of Law and the Hong Kong Legal System
Legal framework including the nature of law and custom. The Basic Law, common law
equity and judicial precedent. The importance of legislation in the business environment and
statutory interpretation. The role and jurisdiction of the Hong Kong civil and criminal courts.
Tribunals and alternative methods of dispute resolution.
The Law of Contract
Essentials of a valid contract. Reasons for invalid or unenforceable contracts. Privity of
contract. Terms of contract. Exclusion clauses with special reference to contracts for the
sales of goods. Discharge of contract and remedies. Electronic contract law.
Sale and Supply of Goods
The nature of goods. Implied terms. Transfer of property and risk. Retention of title clauses.
Sale by non-owner. Rights and remedies of seller and buyer. Definition and application of
contracts for the supply of services. Implied terms. Exclusion clauses.
Law of Commercial Associations
Agency relationships. Nature of corporate personality. Comparison between partnerships
and incorporated associations.
Carriage of goods
CIF, FOB contracts.
Tort
Negligence. Professional liability for careless misstatements. Duty of care. Breach of duty of
care. Neighbour principle. Consequential damage and remoteness. Calculus of risk and
remedies. Ethical responsibility for words and conduct.
Indicative Reading
Arjunan, Krishnan and Abdul Majid, Business Law in Hong Kong, Hong Kong, LexisNexis,
2002
Further Reading
Fisher, M. Contract Law in Hong Kong: Cases and Commentary, Hong Kong Sweet &
Maxwell, 1996
Shum, C. General Principles of Hong Kong Law, 3rd Edition, Hong Kong Longman, 1998
Wesley, Smith P. Introduction to the Hong Kong Legal System, 2nd Edition, Hong Kong
University Press, 1998.
Wickens, R. Professional Liability, Hong Kong University Press, 3rd Edition, 1996
Wright, C, W. Mcauliffe and A. Gamros, Internet Law in Hong Kong, Sweet & Maxwell Asia,
Hong Kong 2003.
http://www.justice.gov.hk
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
29
Law Reports
Hong Kong Law Reports
Hong Kong Law Reports and Digest
Hong Kong Cases
All England Law Reports
Weekly Law Reports
Appeal Cases
Final Court of Appeal Cases
Hong Kong Electronic Citations
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
30
Subject Code
:
AF2601
Subject Title
:
Introduction to Economics
Level
:
2
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lecture
28 hours
Tutorials
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
None
Co-requisites
:
None
Exclusion
:
Assessment
:
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Coursework
50 %
Final Examination
50 %
Coursework
D
Final Examination
D
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Outcomes by enabling students to
analyze business situations and problems (Outcome 7) by applying conceptual frameworks
drawn from Economics, and identify and analyze the means (Outcome 10) by which value is
created in goods and services and delivered to users. It also identifies and analyzes
(Outcome 12) those aspects of the domestic and global business environment that set the
‘parameter of choice’ within which business organizations set objectives and take actions.
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to
•
•
•
•
Appraise the issues involved in the allocation of scarce resources for individual
economic agents and the economy as a whole.
Conduct economic analysis of the behaviour of firms and markets.
Evaluate the issues relating to the macroeconomy and analyze the effectiveness of
government economic policy.
Apply relevant economic knowledge to enhance their understanding of other business
subjects.
Indicative Teaching/ Learning Approach
Lectures focus on the introduction and explanation of key economic concepts, with specific
reference to current economic issues wherever appropriate.
Tutorials provide students with the opportunity to deepen their understanding of the concepts
taught in lectures and to apply the theories to the analysis of real-life economic issues. The
activities in tutorials include student presentations and discussions of problem sets and case
studies.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
31
Indicative Assessment Tasks
During tutorials, students will be required to present and discuss problem set questions to
test their ability to analyze business situations and problems (Outcome 7), and to identify
and analyze the means (Outcome 10) by which value is created in goods and services.
Discussion of economic analysis conducted by prominent economists will help students to
analyze (Outcome 12) the business environment.
Mid term test and final examination are used to test students’ ability in understanding and
applying the concepts learnt from the subject.
Indicative Content/ Outline Syllabus
The Scope of Economic Analysis
Concept of scarcity and opportunity cost. Nature of economic science. Relation with other
subject disciplines. Cost and benefit analysis.
Demand, Supply and the Price Mechanism
The law of demand. Elasticity of demand. The law of supply. Production and cost. Price
control.
Market Structure
Perfect competition. Monopoly. Oligopoly and game theory. Cases of market failure.
National Income Accounting and Determination
Major macroeconomic issues. Concepts and approaches to national income accounting.
Aggregate expenditure and national income determination.
Fiscal Policy and Monetary Policy
Roles of government spending and taxation. Demand for money. Banking system and the
money creation process. Determination of interest rate. Central banking and monetary
policy. Inflation and unemployment.
The International Economy
International exchange and gains from trade. The foreign exchange market and alternative
exchange rate systems.
Indicative Reading
Recommended Textbook
Frank, Robert H. and Ben S. Bernanke, Principles of Economics, 3rd edition, McGraw Hill,
2007.
References
Parkin, Michael, Economics, 8th edition, Pearson Addison Wesley, 2008.
Mankiw, N. Gregory, Principles of Economics, 4th edition, Thomson South-Western, 2007.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
32
Subject Code
:
AF2602
Subject Title
:
Global Economic Environment
Level
:
2
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Seminars
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Role and Purpose
This subject aims to provide students with an overview of global business environment
(Outcome 1) and to develop students’ ability to analyze the impact of globalization on
international business, trade and investment (Outcome 2). The subject provides a foundation
for related higher level subjects (Outcome 3) in economics/finance, marketing/international
business and China business studies. Leading-edge theories of international
economics/business and current issues in globalization are covered in the subject to
strengthen students’ knowledge (Outcome 4) on the development of the global economic
environment. Assessment tools of the subject help students to enhance their oral and written
skills and to communicate and work effectively with others. (Outcome 5)
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
recognize the increasing integration of the world economy.
develop the ability to assess international economic, financial and ethical issues.
notify that there is an ethical dimension to many business decisions.
evaluate the effect of political and cultural differences on international business.
analyze the current trends of trade and investment in the global economy.
apply the principles of foreign exchange in international trade.
assess the strategies and behaviors of multinational companies.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
Lectures are designed to provide outlines of key concepts and to provide guidance on further
readings and applications. Videos are used occasionally to facilitate teaching.
Seminars are designed to provide the environment for discussions and critical analysis of the
subject materials. Group presentations of assigned exercises are held in the seminars.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
A variety of assessment tools will be used, including case studies, in-class exercises, group
projects and presentations, debates, quizzes and term tests. The case studies and in-class
exercises will help students to understand the trend of globalization (Outcome 1), to develop
students’ critical thinking and analytical skills (Outcome 2) and to provide a foundation for
related higher level subjects (Outcome 3). Group projects and presentations help to
strengthen students’ knowledge (Outcome 4) on specific topics and enhance teamwork, and
oral and written communication skills (Outcome 5).
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
33
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Globalization
Main forces and drivers of globalization. Concerns of globalization. The changing nature of
international business in response to the changing global economy.
Country Differences
The nature of economic, political and legal systems for different countries. The determinants
of economic growth and development. The nature of economic transformation and social
culture. Ethical issues in international business.
Cross-Border Trade
International trade and national competitive advantage. Instruments of trade policy.
Government intervention. Evolution of the world trading framework.
Cross-Border Investment and Regional Economic Integration
Foreign direct investment in the world economy. Economic and political debate surrounding
regional economic integration. Free trade agreements in different regions.
Global Money System
Functions and nature of foreign exchange market. Workings of the international monetary
system. Financial crises and crisis management by the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
Competing in a Global Marketplace
The organization of international business. Principles of international business strategy.
Global expansion, competitive pressures and strategic choices.
Indicative Reading
Recommended Textbook and References
Hill, Charles W.L., Global Business Today, 6th Edition, New York: McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2009.
Stiglitz, Joseph, Globalization and Its Discontent, London: Penguin Books, 2002.
Wild, J.J., K.L. Wild and J.C.Y. Han, International Business, 4th Edition, N.J.: Prentice Hall,
2008.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
34
Subject Code
:
AF2617
Subject Title
:
Economics for Engineers
Level
:
2
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Tutorials
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
None
Exclusion
:
AF3901
Role and Purpose
This
subject
aims
to
provide
students
with
fundamental
concepts
of
economics/mathematics/engineering and to develop students’ ability to analyze the
economic situations or solve problems by application of these concepts. It also aims to
explain how these concepts can be applied to affect the functioning of an engineering
company and contribute to decision making in engineering operations. It provides a
foundation for related higher level subjects in economics/engineering. Assessment tools of
the subject help students to enhance their oral and written skills and to communicate and
work effectively with others.
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
understand the fundamental concepts of economics/mathematics/engineering.
understand the concepts of costs and revenues in global business operation.
develop the ability to understand economic and engineering issues in reality.
identify, formulate and solve scientific and engineering problems in suitable
mathematical or computable forms.
build up the skills to think innovatively, critically and creatively.
develop the problem-solving skills to deal with economic and engineering problems in
reality.
understand the ethical dimension and responsibility of business and engineering
decisions and the social consequences of any decisions made.
communicate effectively via graphic, numeric, verbal and written media.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
There will be a lecture of two hours per week that will be structured to help students to
understand engineering economics concepts. Besides, there will be an one-hour tutorial per
week, for which students are required to present answers from tutorial questions and discuss
relevant cases and examples relating to the subject.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
A variety of assessment tools will be used, including in-class exercises, group projects and
presentations and mid-term test. The in-class exercises will help students to understand the
fundamental concepts of economics/mathematics/engineering, to develop students’ critical
thinking and analytical skills and to provide a foundation for related higher level subjects in
economics/mathematics/engineering and decision making in reality. Group projects and
presentations help to strengthen students’ knowledge and application and enhance
teamwork, and oral and written communication skills.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
35
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Introduction to Microeconomics
Scarcity, Choice and Opportunity Cost; Demand, Supply and Price; Profit-maximizing
Objective of a Firm; Cost and Output of a Firm; Depreciation and Cost.
Engineering Economic Decisions
Engineering Projects: Strategic Engineering Economic Decisions; Short-term Operational
Economic Decisions.
Time Value of Money and Project Evaluation
Economic Equivalence and Interest Formulas; Evaluation of Engineering Projects using
Methods of Present Value, Annual Worth, and Internal Rate of Return.
Capital Budgeting Decision
Methods of Financing Cost of Capital, and Evaluation of Investment Alternatives.
Indicative Readings
Textbooks
Chan, Park, Contemporary Engineering Economics, 4th Edition, Prentice Hall.
Parkin, Michael, Economics, 8th Edition, Addison Wesley.
Reference Books
William, Sullivan, Wicks Elin and Luxhoj James, Engineering Economy, 13th Edition,
Prentice Hall.
Mankiw, Gregory, Principles of Economics, 4th Edition, Harcourt.
Stiglitz, Joseph and Carl Walsh, Principles of Microeconomics, 4th Edition, W.W. Norton and
Company Inc.
Landsburg, Steven, Armchair Economist: Economics and Everyday Experience, Free Press.
Other Readings
The Economist.
Far Eastern Economic Review.
Hong Kong Economic Journal.
Various newspaper articles.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
36
Subject Code
:
AF3110
Subject Title
:
Intermediate Accounting 1
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
Financial Accounting (AF2108) OR equivalent
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
42 hours
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA outcomes by enabling students to
identify and resolve (outcome 5) ethical issues as they arise generally and in the specific
business setting for which they are being prepared, and apply (outcome 9) basic financial
theories, analyze financial reports and understand the operation of financial markets.
Learning Outcomes
On successful completion of this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
•
Demonstrate a thorough understanding of the conceptual framework of financial
reporting, concepts and techniques of accounting.
Evaluate current accounting practice in light of the accounting principles and standards.
Apply generally accepted accounting principles to situations.
Extend and refine the conceptual understanding and practical application skills in
corporate financial accounting.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
In the seminars, the general principles of the syllabus topic will be presented and developed,
together with guidance on further reading and activities. Furthermore, students will develop
and apply the general principles of the topic in student-centred activities, including student
presentations and discussions.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Class work will help students apply concepts learnt to situations involving ethical dilemma
(outcome 5), and to financial reporting in various situations (outcome 9).
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Foundations of Financial Accounting
The conceptual framework of accounting. The financial reporting process. The regulatory
format and content. The balance sheet, the statement of income and other comprehensive
income, and the statement of changes in equity.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
37
Operating Activities of a Business
Complexities of revenue recognition. Earnings management. Construction contracts. Cost of
goods sold and inventory valuation. Discontinued operations.
Investing Activities of a Business
Investments in non-current operating assets. Investments in debt and equity securities.
Investments in intangible assets. Impairment of assets.
Indicative Reading
Recommended Textbook
Chow, L., S. Kan, D. W. Taylor and C. Tsui, Advanced Financial Accounting in Hong Kong,
5th Edition, Longman, 2006.
References
Kieso, D.E., J.J. Weygandt and T.D. Warfield, Fundamentals of Intermediate Accounting,
Wiley, 2006.
Alfredson, K., K. Leo, R. Picker, P. Pacter and J. Radford, Applying International Accounting
Standards, Wiley, 2005.
Deegan, C., Australian Financial Accounting, 5th Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2007.
Hui, W.F. and P.H. Ng, Accounting in Hong Kong: Regulatory Framework and Advanced
Accounting Practice, SCOPE, City University of Hong Kong, 2008.
Stice, E.K., J.D. Stice and F. Skousen, Intermediate Accounting, 16th Edition, Thomson
Learning, 2007.
Taylor, S. and N. Hall, Hong Kong GAAP: A Practical Guide to Generally Accepted
Accounting Practice, 3rd Edition, Sweet & Maxwell, 2004.
Hong Kong Institute of Certified Accountants (HKICPA), Hong Kong Financial Reporting
Standards and Hong Kong Accounting Standards.
(Available at the HKICPA website: http://www.hkicpa.org.hk/index.php)
Subject Co-ordinator
LAI Kam Wah
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
38
Subject Code
:
AF3111
Subject Title
:
Intermediate Accounting 2
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
Intermediate Accounting 1
Co-requisites
:
None
Exclusion
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50 %
Final Examination
50 %
Coursework
D
Final Examination
D
Minimum Pass Grade
:
42 hours
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Outcomes by enabling students to
demonstrate a global outlook in the context of business (Outcome 3), identify and resolve
ethical issues as they arise (Outcome 5), obtain sufficient financial accounting skills and
knowledge to make an immediate contribution to their employers (Outcome 13) and analyze
financial reports (Outcome 9) prepared according to Hong Kong Accounting Standards and
International Financial Reporting Standards.
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
z
z
z
apply and evaluate the accounting standards generally accepted in Hong Kong for
major items on the liabilities and equity side of the statement of financial position.
compare the conceptual understanding and practical application skills in corporate
financial reporting in a global context.
apply analytical skills and critical thinking on key accounting issues related to liability
and equity.
Indicative Teaching/ Learning Approach
The subject uses a mix mode of teaching with a weekly two-hour lecture and one-hour
seminar. The one-hour seminar will be conducted to initiate students into ideas, concepts
and techniques of the topics, which is then reinforced by their participation in Class
Discussion, Multiple-choice Questions, Individual Case-study based Essay, and Written
Examination. These are designed to consolidate and develop students’ understanding and
analytical ability through problem solving and working on relevant questions.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
39
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Classwork, including the use of tutorial questions and the Individual Case-study based
Essay, will help students to apply concepts, to demonstrate analytical skills (Outcome 9), to
think critically and to identify ethical issues (Outcome 5) and possess sufficient financial
accounting skills and knowledge (Outcome 13) suitable for future career. Examine the
different accounting treatment in liability and equity locally and internationally through
classwork will enable student to demonstrate a global outlook (Outcome 3) in the context of
accounting.
Indicative Content/ Outline Syllabus
Financial Liabilities
Financial instrument; Classification of financial liability; Initial recognition and subsequent
measurement of financial liability; Distinction of financial liability from equity instrument;
Financial liability with characteristic of equity; Split accounting for compound instrument.
Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets
Provision before HKAS 37; Distinction between accruals, provisions and contingent
liabilities; Definition, recognition and measurement of provision, contingent liabilities and
contingent assets; Change in provisions; Restructuring provision; Provision for onerous
contracts.
Leases
Classification of lease; Accounting for lessee and lessor on both finance and operating
leases; Sales and lease back arrangements; Distinguish investment property from property,
plant and equipment; Leasehold property; Operating lease investment property alternative
for leasehold property.
Shareholders’ Equity
Background of Companies Ordinance; Bonus and rights issue of shares; Legal concept of
capital maintenance related to redemption of shares; Redemption of shares at a premium;
Redemption or purchase of own shares out of capital; Maximum distribution of profits.
Ethical Responsibilities of Accountants in Business
Fundamental principles; Threats to compliances and the safeguards
Income Taxes
Introduction to profit tax calculation; Permanent and timing difference; Over- and underprovisions; Conceptual basis for recognition of temporary difference and tax base;
Determination of deferred tax asset and deferred tax liability; Recognition criteria for deferred
tax asset and deferred tax liability; Deferred tax on revaluation of non-current asset and
available-for-sale investment.
Employee Benefits
Short-term and post-retirement benefits; Defined contribution and benefit scheme; Actuarial
assumptions; Projected unit credit method; Components of net defined benefit plan liability
and asset; Actuarial gains or losses and amortization; Past service costs.
Share-based Payments
Problem before HKFRS 2; Equity-settled share-based payments; Performance condition
affecting equity-settled share-based payments; Effect on change in performance vesting
condition; Cash-settled share-based payments.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
40
Earnings per Share
Importance and reason for standardization in earnings per share (EPS) calculation; Basic
EPS with change in capital; Diluted EPS with convertible instruments; Order of dilutive
factors.
Indicative Reading
Required Textbook
Lam and Lau, Intermediate Financial Reporting – An IFRS Perspective, 1st Edition, 2009,
McGraw-Hill Education (Asia).
Reference Textbooks
Chow, Kan, Taylor and Tsui, Advanced Financial Accounting in Hong Kong, 5th Edition,
2006, Longman.
Alfredson, Leo, Picker, Pacter, Radford and Wise, Applying International Financial Reporting
Standards, Enhanced Edition, 2007, John Wiley & Sons Australia Ltd.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
41
Subject Code
:
AF3112
Subject Title
:
Management Accounting 2
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Tutorials
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
Management Accounting 1 (AF2110)
Assessment
:
Coursework
50 %
Final Examination
50 %
Coursework
D
Final Examination
D
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA (Hons) Programme Outcomes by
enabling students to analyze business situations and problems by applying conceptual
frameworks drawn from accounting, finance, economics, and quantitative methods
(Outcome 7). It will enable students to develop critical thinking and analytical skills (Outcome
4), and ethical awareness (Outcome 5) in the management accounting context. This subject
will also prepare students to communicate verbally and in writing in English at a level of
effectiveness sufficient for a business presentation (Outcome 1 and 2). This subject will
contribute to build students’ professionally-specific skills and knowledge to 1) enable them to
make an immediate contribution to the organization they are first employed and 2) base the
process of continuous professional development (Outcome 13).
Learning Outcomes:
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
Apply and critically compare the cost classification, accumulation, and allocation
approaches and techniques.
•
Evaluate the considerations and issues in cost and management accounting system
design.
•
Identify and prepare cost information for accounting purposes.
•
Develop critical thinking, analytical skills and ethical awareness in the management
accounting context.
Indicative Teaching/ Learning Approach
A two-hour mass lecture will be conducted each week to initiate students into the ideas,
concepts and techniques of the topics in the syllabus. In addition, there will be one tutorial of
one hour per week. The tutorials will adopt a student-centered approach, including problem
solving and case analysis for discussion and team-presentation.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
42
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Assessment components include group-based case analysis with report and presentation;
mid-term examination; participation; and final examination. The assessment tasks require
students to demonstrate their understanding and critical application of the appropriate
concepts and techniques to generate cost information to help management in organizational
planning, control and decision-making processes (Outcome 7 and 4); ability to evaluate
ethical issues from a management accounting perspective and suggest appropriate
responses (Outcome 5); and ability to communicate in both written and verbal English at a
level of effectiveness sufficient for a business presentation (Outcome 1&2); and ability to
build professionally-specific skills and knowledge (Outcome 13).
Indicative Content/ Outline Syllabus
Process Costing
Process costing systems – FIFO and Weighted Average Costing Approaches. Treatment of
Transferred-In Goods. Operation Costing.
Spoilage, Rework and Scrap
Accounting for spoilage, rework and scrap under Job costing and process costing
Joint-Product Costs and By-Product Costing
General characteristics. Accounting for joint-product costs. Accounting for by-product.
Effects of joint-product costs on cost control, decision making, and product strategy. Joint
provision of services.
Service Department Cost Allocation
Reasons for service department cost allocation. Allocation bases. Methods of allocating
service department costs.
Activity Based Costing
Understanding cost drivers. Distinctive features of activity based costing. Costing of a
product under a refined costing system. Service department costing: an activity approach.
Standard Costing and Variance Analysis
Standard Costs – Management by Exception. Setting standard costs. Flexible budgets.
Variance analysis. Variable overhead variances. Fixed overhead variances. Variance
investigation and evaluation of controls based on standard costs.
Transfer Pricing
Impact on performance measures. The transfer pricing problems. Optimal transfer pricing.
Alternative transfer-pricing methods. Cost and benefits of transfer pricing.
Capital Budgeting Decisions
Capital budgeting – planning investments. Discounted cash-flows. Net-present-value
method. Required rate of return. Payback method. Preference decisions- ranking of
investment projects. Other approaches to capital budgeting decisions. Tax implication on
capital budgeting. Post-audit of investment projects. What if and sensitivity analysis.
Innovative Inventory and Production Management Techniques
Buying or producing and carrying inventory. Economic ordering quantity. Understanding and
managing production activities and costs: just-in-time systems, flexible manufacturing
systems and computer integrated manufacturing. Theory of constraints.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
43
Indicative Reading
Textbook(s)
Garrison, R.H., E.W. Noreen and P.C. Brewer, Managerial Accounting, 12th Edition
(International), McGraw-Hill, 2007.
Managerial Accounting (Customized Edition), McGraw-Hill, 2008.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
44
Subject Code
:
AF3210
Subject Title
:
Hong Kong Tax Framework
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lecture and tutorial
Pre-requisites
:
Financial Accounting (AF2108) or equivalent
Co-requisites
:
None
Exclusion
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50 %
Final Examination
50 %
Coursework
(Grade D)
Final Examination
(Grade D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
(42 hours)
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA (Hons) Outcomes by enabling
students to analyze business situations and problems by applying tax law principles to
determine the tax liabilities for individuals and business in Hong Kong (Outcome 7), to
identify and resolve ethical issues as they arise in the capacity of a tax professional
(Outcome 5), to work effectively with other students as a team (Outcome 8), and to
communicate in English effectively (Outcomes 1 and 2).
Learning Outcomes:
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
•
•
apply tax principles to determine the tax liabilities for individuals, partnerships and
corporations in Hong Kong;
effectively interpret tax statutes, analyse practical tax problems and apply tax rules;
evaluate legal arguments in tax cases and present one’s own arguments in a reasoned
manner;
formulate and advise on basic tax mitigation arrangements; and
recognise the social responsibility of a tax professional.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
Lectures will impart students with a fundamental understanding of the principles of taxation
and of the current law and practice relating to taxation of individuals, partnerships and
corporations in Hong Kong. Tutorials reinforce students’ understanding and application of
law and principles to practical situations.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
45
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Assessment components include solving of tax problems/cases in presentation, term test
and final examination. These assessment components require students to demonstrate their
ability to analyse and solve problems by applying tax law and principles (Outcome 7) and to
communicate in English effectively (Outcomes 1 and 2). Students are required to deliver the
presentation in small group and their ability to work as a team will be indirectly assessed in
the presentation component (Outcome 8). Their ability to identify ethical issues in business
settings (Outcome 5) will be assessed through their explanation given in presentation, term
test and/or final examination.
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Tax System and Administration in Hong Kong
Introduction to Hong Kong tax system and administration.
Taxation on Property
Scope of charge and computation of property tax in Hong Kong.
Taxation on Employment and Office Income
Scope of charge and computation of salaries tax in Hong Kong for individuals and married
persons.
Taxation of Business Income
Scope of charge and computation of profits tax in Hong Kong for individuals, partnerships
and corporations, including basic source principles and concepts, assessment and deduction
rules, depreciation allowance, and loss relief.
Taxation on Total Income for Individuals
Personal assessment and computation of tax liabilities.
Tax Management
Introduction to anti-avoidance legislation and tax planning opportunities. Social responsibility
of a tax professional.
Indicative Reading
Inland Revenue Ordinance (Chapter 112) and Inland Revenue Rules, updated edition and
amendments, Hong Kong SAR Government.
Smith, D.G. and A. Macpherson, Hong Kong Taxation: Law and Practice, latest edition, the
Chinese University Press.
Lee, D, Advanced Taxation in Hong Kong, latest edition, Longman Asia Ltd.
CCH, Hong Kong Master Tax Guide, latest edition, CCH Asia Pte Limited.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
46
Subject Code
:
AF3211
Subject Title
:
Accounting Information Systems
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminar/Laboratory
Pre-requisites
:
Information Technology for Business (MM2421)
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
42 hours
ROLE AND PURPOSE
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Programme Outcomes by enabling
students to use and evaluate information technology effectively (Outcome 6) and to analyze
business situations and problems by applying conceptual frameworks drawn from the
subject (Outcome 7). In addition, students studying the subject should acquire sufficient
professionally-specific skills and knowledge, on which to base the process of continuous
professional development and to make an immediate contribution to the organization in
which they are first employed (Outcome 13).
LEARNING OUTCOMES
On successfully completing this subject, students should be able to:
•
•
•
•
Document the AIS so as to understand and evaluate them.
Design and implement AIS using data modeling technique, database application
software and accounting software.
Apply the internal control frameworks to AIS control.
Explain the systems development life cycle related to AIS development.
INDICATIVE TEACHING/LEARNING APPROACH
This course will use an integrative approach that combines lectures, exercises, and
computer laboratory work within a three-hour session. Students will have opportunity to gain
hands on experience in using certain database and accounting software applications.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Assessment components include AIS projects, class exercises, midterm test and final
examination. These assessment components require students to demonstrate their ability to
use and evaluate information technology effectively (Outcome 6), to analyze business
situations and problems by applying conceptual frameworks drawn from the subject
(Outcome 7), and to acquire professionally-specific skills and knowledge (Outcome 13).
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
47
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Foundation
Overview of AIS and its subsystems. The role of the AIS in the company value chain.
Overview of the five major transaction cycles. Transaction processing: the data processing
cycle within AIS. Ledgers, chart of accounts, journals. Batch and on-line processing.
Information Systems Documentation Techniques
Documentation techniques used to understand, evaluate, and design information systems.
Preparation and interpretation of data flow diagrams. Interpretation of document flowcharts
relating to internal control. Differences between data flow diagrams and document
flowcharts.
Data Management
Fundamental of database systems. Database design using E-R diagram and REA data
model. Implementing E-R diagram and REA data model using relational database. REA
approach to business process modeling.
Business Processes
Core business processes within the revenue and expenditure cycles. The general ledger
and reporting system. Extensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL).
Controlling Accounting Information System
Overview of control concepts. COSO’s internal control framework and Enterprise Risk
Management Model. Threats and controls in the revenue and expenditure transactions
cycles, as well as in the general ledger and reporting system activities.
Systems Development
Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC). The role of accountants in SDLC. Behavioral
aspects of change. Development strategies for AIS software. End-user computing. Benefits
and risks of IT outsourcing. Business process reengineering. Systems implementation and
conversion.
INDICATIVE READING
-
Romney, M.B. and P.J. Steinbart, Accounting Information Systems, Latest Edition,
Prentice Hall.
-
Li, D.C., Computerized Accounting Using MYOB, McGraw-Hill Education (Asia), 2004.
-
Perry, J.T. and G.P. Schneider, Building Accounting Systems Using Access 2003,
South-Western College Publishing, 2004.
-
Arens, A.A., Systems understanding aid, 5th Edition, Armond Dalton, 2001.
-
Gelinas, U.J. Jr., S.G. Sutton and J. Hunton, Accounting Information Systems, Latest
Edition, South-Western Publishing.
-
MYOB Premier user guide, Latest Version, MYOB Hong Kong.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
48
Subject Code
:
AF3311
Subject Title
:
Finance
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Tutorials
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject aims to introduce to students a range of basic concepts and ideas in modern
finance. After completing this subject, the participants should know the principles involved in
making investment and financing decisions, understand the functions of financial markets
and financial managers, and acquire a basic knowledge of option pricing and financial
planning. This foundation prepares students for more in-depth studies at a later stage
Learning Outcomes:
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
•
•
Understand the role of financial managers and the functions of the financial market;
Understand the concept of present value and its applications in investment appraisal;
Understand the risk-return relation and the determination of cost of capital;
Acquire a broad knowledge of financing decision-making under uncertainty and under
conditions of market imperfection;
Apply basic finance theory to solve practical problems.
Indicative Teaching/ Learning Approach
This class can be seen as an introductory finance class to students with applied
mathematics background. Beside application of mathematics and numerical methods to
finance, students are also required to understand how financial decisions are to be made.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
1. Students are required to actively participate in tutorial sessions. Participation scores are
based on attendance rate and class-room performance. Students who do not prepare for
tutorial will be treated as absence.
2. Midterm Examination would be consisted of thirty multiple choice questions and two long
questions. Questions in the midterm examination are mainly testing students’
understanding of the basic ideas in finance.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
49
3. Final Examination would be consisted of both multiple choice and long questions. In the
final exam, questions are mainly calculation based and some basic application of applied
mathematics for financial decision making. Students are also required to explain results
of their calculation in essay forms.
Indicative Content/ Outline Syllabus
Fundamental Concepts
Goals of management, functions of the financial system, financial statement analysis and
financial planning, asymmetric information, agency problem.
Value
Opportunity cost, discounted cash flow analysis, nominal and real interest rates, future
value, present value, net present value, principles of valuation.
Risk and Return
Portfolio theory, systematic and unsystematic risks, asset pricing, risk/return trade-off,
capital budgeting under uncertainty.
Market Efficiency
Competition, sources of information, weak form efficient market hypothesis, semi-strong
form efficient market hypothesis, strong form efficient market hypothesis, evidence of market
efficiency, implications of market efficiency for financial decision-making.
Dividend Policy and Capital Structure
Dividend policy, leverage, capital structure, weighted average cost of capital.
Options
Option-pricing theory, spotting and valuing options, real options.
Indicative Reading
TEXTBOOK
Main Text:
•
Ross,S.A., R.W. Westerfield and B.D Jordan, Corporate Finance Fundamentals, 7th
Edition. McGraw-Hill, 2007
Optional text:
•
Ross, S.A., R.W. Westerfield and J. Jaffe, Corporate Finance, 7th Edition, McGrawHill, 2005.
•
Bodie, Z. and R.C. Merton, Finance, Prentice-Hall, 2000.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
50
Subject Code
:
AF3312
Subject Title
:
Bank Credit Management
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Seminars
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
Business Finance (AF3313)
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
Final Examination
(D)
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
Building on the foundation studies in Accounting and Finance the subject contributes to the
achievement of the BBA Outcomes by equipping the students with an understanding of the
techniques of effective credit assessment, credit risk management, the customer’s ability to
repay, lending administration, the legal framework within which lending operate, credit
control and recovery. (Outcomes 7, 9 and 13).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
•
Understand the nature of bank lending activities and credit risk;
Apply the principles of good lending in assessing credit propositions from bank
customers;
Conduct credit analysis the purpose of bank lending; and
Assess, modify and justify loan proposals from borrowers.
Students will be able to formulate lending propositions taking into account borrowers’
specific financial needs, legal regulation on bank credit and social responsibility of the
lending institutions.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
A combination of lectures and seminars will be used. Problem based case studies will be
part of teaching and relevant software will be used such as balance sheet analysis and
Excel. Student assignments will emphasize on investigation and solution of problems in a
holistic inter-disciplinary approach.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Individual assignments will be used to test knowledge and understanding of credit analysis
to explore the issues and methodologies to be adopted in assessing a lending proposition.
Group presentations will evaluate the various loan proposals for business customers,
personal customers and professionals and recommend appropriate solutions. The written
examination will require students to apply both practical knowledge and their ability to draw
upon the theoretical principles relevant to the issues concerned. (Outcomes 7, 9 and 13).
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
51
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
An Introduction to the Nature of Bank Lending
The nature of bank lending and credit risk. Purposes and principles of credit analysis.
Sources of information available for bank credit analysis. Steps taken by banks in dealing
with lending propositions.
Types of Bank Credit Facilities and their Features
Credit lines and their fit with customer need. Current account overdraft and revolving line of
credit. Term facilities and their fit with customer need. Fully drawn loan. Mortgage.
Bridging loans. International bank lending. Loan syndication. Project finance. Differences
between personal and business lending.
Analysis of Financial Information for Lending Propositions
The role and use of financial information. Going vs. gone concern. Analysis and
interpretation of financial information from different financial statements. Financial ratios.
Assessment of financial strengths and weakness of borrowers for the purpose of bank
lending.
Evaluation of Financing Propositions
Feasibility of projects. Risk analyses, e.g. resources, marketing, completion, operation ...
etc. Country risk. Evaluation of the types and amount of finance required. Analyses of offbalance sheet items.
Analyses of non-quantitative data, e.g. management quality,
appropriateness of technology, motivation, political / social variables. Legal aspects and
valuation of securities. Viability of repayment scheme / funds flow.
Monitor and Control of Loan Account
Objectives and procedures of monitor & control of loan account. Loan classification and
causes of problem loans. Indicators of problem loans. Prevention and approaches in
handling problem loans.
Credit Risk Management
Loan policies of banks. Traditional methods of managing credit risk of loan portfolios. Credit
risk modeling such as Altman’s Z-score model and KMV’s model. Credit risk management
with the application of securitization and credit derivatives. Legal requirements on bank
lending in Hong Kong.
INDICATIVE READING
Recommended Textbook
Rouse, C.N., Banker’s Lending Techniques, 3rd Edition, Global Professional Publication,
2008.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
52
References
Fraser, L.M. and A. Ormiston, Understanding Financial Statements, 7th Edition, Prentice
Hall, 2003.
Koch, T.W. and S.S. MacDonald, Bank Management, 5th Edition, Dryden, 2003.
Checkley, K. and K. Dickinson, Problem Loans – A Banker’s Guide, Euromoney, 2000.
Coyle, B., Corporate Credit Analysis, CIB Publishing, 2000.
Rouse, C.N., Applied Lending Techniques, 2nd Edition, Lessons Financial Publications 2005.
Caouette, J.B., E.I. Altman, and P. Narayanan, Managing Credit Risk – the Next Great
Financial Challenge, Wiley, latest edition.
Terry, B. J., The International Handbook of Corporate Finance, CIOB, latest edition
HKIOB, The Lending Cases in Hong Kong, 1995.
Hough, V.H. Accounting & Finance for the Lending Banker, Oak Tree Press, latest edition.
Hong Kong Banking Ordinance (Sections related to bank lending)
Hong Kong Monetary Authority, Lending Guidelines and various publications on bank
lending activities.
Journal of Commercial Lending
Journal of Managerial Finance
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
53
Subject Code
:
AF3313
Subject Title
:
Business Finance
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Tutorials
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
Financial Accounting (AF2108) or equivalent
Assessment
:
Coursework
40%
Final Examination
60%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Outcomes by enabling students to
develop strong analytical skills and critical thinking (Outcome 4), and apply financial methods
to analyze business problems (Outcome 7) and apply basic financial theories, analyze
financial reports and understand the operations of financial markets (Outcome 9) and
present and communicate in English effectively (Outcome 1 and Outcome 2).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
•
•
Identify the major responsibilities of financial managers;
Apply different investment appraisal techniques and evaluate the limitations;
Apply the portfolio theory to construct a diversified portfolio;
Determine the corporate cost of capital and
Analyze the key characteristics of working capital and its individual elements.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
The mass lectures cover the basic concepts and theories. Tutorial sessions allow students to
discuss the lectures and present the applications of financial methods in smaller groups.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
A variety of assessment tools, including written assignments, presentations, midterm test
and final examination will be used.
In-class presentations show whether students can apply the financial methods to analyze
business problems (Outcome 7) and apply the basic financial theories (Outcome 9) and
present in English effectively (Outcome 1).
Written assignments assess the analytical skills (Outcome 4) and English writing skills of
students (Outcome 2).
Midterm test and final examination evaluate whether the students can apply the financial
methods to analyze business problems (Outcome 7) and apply the basic financial theories
(Outcome 9) and communicate in written English effectively (Outcome 2).
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
54
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Introduction
Corporate Goal. The Agency Problem and Control of the Corporation
Valuation of Securities
Time value of money. Valuation of Stocks and bonds.
Investment Appraisal Techniques and the limitations
Payback period. Average Accounting Return. Internal rate of return. Net present value.
Profitability Index. Incremental cash flows and Capital Budgeting. Investments of unequal
lives.
Risk Analysis, Real Options and Capital Budgeting
Decision trees, Real Options. Sensitivity Analysis. Scenario Analysis. .Breakeven Analysis
Portfolio Theory
Risk statistics. Opportunity Set and Efficient set. Capital Market Line. Capital Asset Pricing
Model. The Security Market Line.
Cost of Capital
Beta. Cost of Equity. Cost of Debt. Weighted Average Cost of Capital.
Net Working Capital Management
Short-term Finance and Planning. Cash Management. Credit Management
Indicative Reading
Ross, S.A., R.W. Westerfield, J. Jaffe and B. Jordan, Modern Financial Management, 8th
Edition, Irwin/McGraw-Hill, 2008.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
55
Subject Code
:
AF3314
Subject Title
:
Financial Institutions and Markets
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Seminars
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
Business Finance (AF3313)
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(Grade D)
Final Examination
(Grade D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Outcomes by enabling students to
analyze business situations and problems within the financial system by applying concepts
from Accounting, Finance, Economics, Law and Quantitative methods (Outcome 7), critically
assess the performance of financial institutions by applying theories in finance, financial
markets and financial reporting (Outcome 9), identify and analyze various aspects of the
domestic and global business environment that set the parameters of choice within which
financial institutions set objectives and take actions (Outcome 12). It also requires students
to communicate effectively in English either in individual report writing or group presentation
(Outcome 2).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
•
identify the key differences in different financial systems and evaluate the implications on
the operations of the principal financial institutions and markets;
apply appropriate tools to analyze the movements of funds in financial markets and the
determination of interest rates;
critically assess the different roles performed by different financial institutions and the
different management problems faced by different financial institutions;
evaluate the rationale for financial regulation and its impact in the financial system.
Indicative Teaching / Learning Approach
Lectures will be used to discuss concepts and issues relating to the financial system. Case
studies and / or mini projects will be used in seminars to reinforce students’ learning by
illustrating that techniques discussed in lectures have application to real-life problems.
Students will be asked to analyze and provide solutions to cases / projects which should
reflect understanding and ability of applying the knowledge covered in this subject.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
56
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Seminar presentation of discussion questions will help students to apply concepts (Outcome
7), mini projects / case studies will require students to critically assess the performance of
financial institutions (Outcome 9) and identify and analyze the risks involved in the
management of financial institutions (Outcome 12). Group seminar presentation, individual
report and the final examination will require students to communicate effectively in English.
Indicative Content / Outline Syllabus
Functions of Financial System and Institutional Structure
Functions of financial system. Savings, financial investment vs real investment. Factors
shaping the institutional structure of financial system.
Determination of Interest Rates
Loanable fund analysis. Valuation of financial securities. Term and risk structure of interest
rates.
Financial Markets
Money markets. Capital markets. Derivative markets. Institutional structure of financial
markets and market efficiency.
Financial Institutions
Insurance companies. Investment funds. Commercial and investment banks.
Management of Financial Institutions
Risk management. Interest rate and credit risk. Gap analysis. Risk management with
derivatives.
Regulation of the Financial System
Regulatory framework. Protective and preventive regulation. Regulatory dialectic.
Indicative Reading
Textbooks
Miskin, F.S. and Eakins, S.G. (2009) Financial Markets and Institutions, 6/e, Pearson.
Rose, P.S. and Marquis, M.H. (2008) Money and Capital Markets, 10/e, McGraw Hill.
References
Articles from newspapers, magazines and journals. Examples are Financial Times,
Hong Kong Monetary Authority and Financial Analyst Journal…etc.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
57
Subject Code
:
AF3315
Subject Title
:
Foreign Exchange and Finance of International Trade
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Tutorials
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Outcomes by enabling students to
examine the theory and practice of international trade and foreign exchange and train
students to explain methods of payment for imports and exports, documentation and
shipping terms, international payment systems, sources of finance for exports and foreign
currency hedging techniques (Outcomes 5 and 13).
Learning Outcomes
On completion of the subject, students should be able to:
1.
Analyse how spot and forward foreign exchange markets work and evaluate their
importance in international trade;
2.
Compare the techniques, both internal and external, used by corporations to manage
foreign exchange risk;
3.
Discuss the methods and risks of payment involving letters of credit and documentary
collections and the ability to apply ICC Uniform Rules for Collections and ICC Uniform
Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits; and
4.
Compare and evaluate different sources of finance for exports.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
Lectures are used for imparting theoretical principles. In the seminars students will have the
opportunity to examine actual documents used in documentary credits and documentary
collections in order to understand the practice of uniform rules and customs for international
trade.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Assessment components include written problem/case assignments, seminar participation
and presentation of problems/cases and final examination with practical problems/cases.
These assessment components require students to effectively interpret international rules,
customs and practice, and apply the knowledge to provide practical solutions/explanations of
international trade and foreign exchange (Outcomes 5 and 13).
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
58
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
An Overview of International Trade
An overview of needs of importers and exporters. Risks associated with international trade
and how these may be mitigated. Terms of payment. Major shipping terms (Incoterms).
Documentary Credits
Operations of a documentary credit. Roles and liabilities of various parties to a documentary
credit. Types and uses of documentary credit.
The importance of documents in
documentary credits. Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits (UCP 600).
Documentary Collections
Operations of a documentary collection. The legal and practical position regarding the
duties of various parties to a documentary collection. Risks to exporters and importers.
Uniform Rules for Collection (ICC 522).
Finance of International Trade
Methods of international settlement through banks. Finance for exporters and importers.
Non-financial services for exporters and importers.
Foreign Exchange
Quotation of exchange rates. Spot rates and forward rates. Managing transaction, translation
and economic exposure. Foreign exchange hedging strategies.
Indicative Reading
Recommended Textbook
Cowdell and Hyde, International Trade Finance, 8th Edition, Financial World Publishing,
2003.
References
Steiner Bob, Foreign Exchange and Money Markets: Theory, Practice and Risk
Management, Butterworth-Heinemann, 2002.
International Chamber of Commerce, Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary
Credits, ICC Publication No. 600, 2007.
International Chamber of Commerce, Uniform Rules for Collections, ICC Publication No.
522.
Euro Money, Video Cassette: Documentary Letters of Credit: Parts I and II.
Euro Money, Video Cassette: An Introduction to Foreign Exchange Advanced Foreign
Exchange: Parts I and II.
International Chamber of Commerce, Case Studies on Documentary Credits under UCP
500.
Hong Kong Export Credit Insurance Corporation, Protect Yourself against Export Risk,
Latest Edition.
International Chamber of Commerce, Managing Exchange Rate Risks, ICC Publication No.
549.
International Chamber of Commerce, Guide to Documentary Credit Operations, ICC
Publication No. 515.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
59
Subject Code
:
AF3316
Subject Title
:
Investments
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lecture/Seminar
Pre-requisites
:
Business Finance (AF3313)
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
42 hours
Role and Purpose
This course provides a comprehensive coverage of the basic concepts, theories,
applications and decision-making rules for financial investments. It is a complement to
modules in Financial Markets and Institutions, Securities Regulation, Risk Management,
Principles of Insurance, and Management of Financial Institutions.
While this subject contributes towards the achievement of almost all of the BBA program
objectives, more direct contribution is towards enabling students to (i) analyze business
situations by applying conceptual frameworks drawn from finance (Outcome 7), (ii) apply
basic financial theories, analyse financial reports, and understand the operation of financial
markets (Outcome 9), and (iii) communicate their analyses verbally and in writing in English
(Outcomes 1 & 2).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
•
•
Explain the different types of securities and their risk and return profiles;
Understand the security analysis and portfolio analysis process;
Plan, manage and review client portfolios according to customer profile and needs in
order to recommend and justify appropriate types of savings and investment;
Recognize ethical and environmental issues that they might face in real world situations;
Demonstrate an ability to recognize, analyze, and deal with global issues relating to
investments.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
The three contact hours per week will be divided into a 2-hour lecture for the whole class,
and a 1-hour tutorial for smaller groups. The lecture would be used to impart the knowledge
base, and enable students to learn and apply financial concepts to solve investment-related
problems (Outcomes 7 & 9). The tutorial sessions would be used flexibly by the instructor for
discussing key concepts, going through assignments, tutorial questions, and student
presentations. Students are expected to share their views and experiences actively with their
instructors and other classmates, allowing the students to improve their communication skills
(Outcomes 1 & 2).
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
60
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Individual participation during tutorial sessions would require students to demonstrate their
ability to apply investment and finance theories (Outcome 9), to think critically and creatively
(Outcomes 7), and to communicate their analysis effectively (Outcome 1). The mid-term test
and the final examination would test student’s ability to apply finance theories to business
situations (Outcome 9).
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Basics of Financial Investments
The process of portfolio management. Trading mechanisms. Mutual funds, hedge funds and
other investment vehicles. Asset classes and financial instruments. Asset allocation
Risk and Return
Risk and expected Return. Benefits of diversification. Efficient frontier. Capital asset pricing
model. Multifactor models of risk and returns.
Efficient Market Hypothesis
Theory and empirical evidence in favour of and against market efficiency. Limits to arbitrage.
Behavioural finance.
Equity Valuation
Fundamental analysis. DCF models. Relative valuation.
Fixed-Income Securities
Bond Basics, Interest rate sensitivity, Duration, Convexity, Term structure of interest rates,
Immunization, Managing fixed income portfolios
Introduction to Derivatives
Basic terminology. Option payoffs. Option strategies. Futures contracts and strategies. Use
of derivatives in portfolio management.
Performance Evaluation
Time-weighted versus dollar-weighted returns. Risk adjustment in performance evaluation.
Performance attribution analysis.
Indicative Reading
Recommended Textbook
Bodie, Zvi, Alex Kane and Alan J. Marcus, Essentials of Investments, 7th edition, 2008,
McGraw-Hill, International edition.
References
Reilly, Frank K. and Keith C. Brown, Investment Analysis and Portfolio Management, 8th
edition, 2006, Thomson South-Western.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
61
Subject Code
:
AF3317
Subject Title
:
Risk Management
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Seminars
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
Business Finance (AF3313) AND
Quantitative Methods for Business (AMA2101)
Assessment
Minimum Pass Grade
:
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Outcomes by enabling students to
apply concepts in Economics, Finance, Quantitative Methods and Business Law to give the
students an insight into how a business can identify and measure its loss exposures and
select appropriate tools for the management of that exposure (Outcome 7). It also requires
students to demonstrate critical and creative thinking (Outcome 4) work effectively with and
through others (Outcome 1&2&8). This subject is to prepare the students to establish the
body of knowledge necessary for independent risk management analysis and decisionmaking.
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
explain the principles of risk management in relation to Economics, corporate Finance,
investment, and corporate governance
•
evaluate the role of risk management in business firms
•
apply all tools to identify, measure and control risk exposures related to operation,
financing and investment in a global market
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
Lectures will be used to provide theoretical concepts. During seminar sessions, students will
be required to apply the theory to solve risk management problems in the real world.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Coursework, including the project, will help students to apply concepts, and think critically
and creatively (Outcome 4&7). Effective communication (Outcome 1&2) will be assessed the
group project.
The project is carried out in groups and the ability to work with others (Outcome 8) is
assessed through a form of Evaluation of Group Performance.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
62
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Introduction to Risk
Definition of Risk. Various concepts of risk and uncertainty. Classifications of Risks
Basic Concepts of Risk Management
Definition of Risk Management. Importance of Risk Management. Risk management process
and Risk control tools. Risk Management Today. Crisis Management. Economic Theories.
Financial Theories.
Risk Identification
Risk identification. Identification of Risk Exposures. Risk Identification Methodologies. Risk
Identification Tools.
Risk Evaluation
Importance of Risk Exposures. Risk Measurement. Value at Risk.
Risk Control
An Introduction of Risk Control. Reasons for Risk Control. The Relationship between Risk
Control and Risk Evaluation. The Relationship between Pre-event Risk Control and Postevent Risk Financing. Risk Control Tools.
Applications of Risk Management
Portfolio risk management. Case studies.
Indicative Reading
Marthinsen, John E., Risk Takers: Uses and Abuses of financial Derivatives, Pearson
Addison-Sesley, 2005.
Lam, James, Enterprise Risk Management:
Sons, 2003.
From Incentives to Controls, John Wiley &
鄭子云,司徒永富著,企業風險管理,商務印書館(香港)有限公司,2001年(CS)。
Skipper, Harold D., International Risk and Insurance: An Environmental – Managerial
Approach, Irwin/McGraw-Hill, 1998.
Smithson, Charles W., Managing Financial Risk-A Guide To Derivative Products, Financial
Engineering and Value Maximization, 3rd Edition, Irwin McGraw-Hill ,1998.
Williams, Smith & Young, Risk Management and Insurance, 8th Edition, Irwin McGraw-Hill,
1998 (WSY).
Jorinon, Philippe, Value at Risk: the new benchmark for controlling market risk, Irwin
Professional Pub 1997.
(http://www.gsm.uci.edu/~jorion/)
Fink, Steven, Crisis Management, Planning for the Inevitable, American Management
Association, 1986.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
63
Subject Code
:
AF3318
Subject Title
:
Principles of Insurance
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Seminars
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Outcomes by providing students with
general knowledge of insurance both in principle and in practice, and demonstrate critical
and creative thinking (Outcome 4). It is designed to help students understand the theory, the
practical operation procedures, and the major products of insurance. After successful
completion of this course, students should be able to use insurance as a tool for financial
consultation to manage personal and/or group assets (Outcome 7). It also requires students
to work effectively with and through others (Outcome 1&2&8).
LEARNING OUTCOMES
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
•
•
explain what insurance is, why insurance works and how to determine insurance needs;
explain insurance operation: functions of insurance, insurance markets, insurance
regulation and financial assessment and know how insurance works along with its
practical operation procedures;
apply major insurance products, such as life insurance, health insurance, property and
liability insurance;
evaluate various kinds of insurance plans as well as the contract selection criteria from a
cost-benefit point of view; and
use insurance as a tool for personal financial consultation to manage personal and/or
group assets.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
Lectures will be used to provide theoretical concepts. During seminar sessions, students will
be required to apply the theory to solve practical situations relating to insurance contacts.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Coursework, including the project, will help students to apply concepts, and think critically
and creatively (Outcome 4&7). Effective communication (Outcome 1&2) will be assessed the
group project.
The project is carried out in groups and the ability to work with others (Outcome 8) is
assessed through a form of Evaluation of Group Performance.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
64
INDICATIVE CONTENT/OUTLINE SYLLABUS
Introduction to Insurance and Risk
Principles of Risk: introduction to risk, insurance and risk
Principles of Insurance: fundamental legal principle, analysis of insurance contracts
Property and Liability Insurance
Personal property and liability insurance, liability risk and personal property and liability
insurance, homeowners insurance, automobile insurance, personal accident, travel, major
illnesses
Commercial Property Insurance
Commercial property, commercial liability insurance, crime insurance and surety bonds
Life and Health Insurance
Life insurance, fundamentals of life Insurance, types of life insurance, life insurance
contractual provisions, choosing life insurance, applications of life insurance, annuities and
individual retirement accounts, individual health insurance and disability insurance
The Insurance Industry
The insurance company, types of insurance and marketing systems, insurance company
operations, insurance pricing
Insurance Regulations
Government regulation, industry self regulation, other legal regulation
INDICATIVE READING
Recommended Textbook
Rejda, George E., Principles of Risk Management and Insurance, 10th Edition, AddisonWesley, 2008
References
Insurance Intermediaries Quality Assurance Examination Scheme Study Notes: Principle
and Practice, Published by Office of Insurance Commissioner, Hong Kong, 2004
Insurance Intermediaries Quality Assurance Examination Scheme Study Notes: Long-term
Insurance, Published by Office of Insurance Commissioner, Hong Kong, 2007
Insurance Intermediaries Quality Assurance Examination Scheme Study Notes: General
Insurance, Published by Office of Insurance Commissioner, Hong Kong, 2005
Insurance Intermediaries Quality Assurance Examination Scheme Study Notes: Investmentlinked Long Term Insurance, Published by Office of Insurance Commissioner, Hong Kong,
2004
Insurance Intermediaries Quality Assurance Examination Scheme Study Notes:
Travel Insurance Agents, Published by Office of Insurance Commissioner, Hong
Kong, 2006.
Insurance Intermediaries Quality Assurance Examination Scheme Study Notes:
Study Notes for the Mandatory Provident Fund Schemes Examination (2007 Edition)
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
65
Subject Code
:
AF3321
Subject Title
:
Global Financial Markets
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Seminars
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
Financial Services Environment (AF2303)
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA in Financial Services Programme
Outcomes by enabling students to enhance their global outlook (Outcome 3) through studies
on financial globalizations, apply finance and economics (Outcome 9) to analyze the
operations of global financial markets, and analyze the implications for decision-making of
management in a changing business environment (Outcome 12).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
Compare the operations of global money, stock, bond and foreign exchange markets
Analyze the effect of monetary policies on the operation of international financial markets
Evaluate the effectiveness of financial regulations in a global setting
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
The key concepts and the institutional arrangements of the global financial markets will be
explained in lectures. Students will be split into small groups with each delivering a
presentation on pre-set questions on each topic. They are encouraged to participate in group
discussions.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
The presentation and report will require students to apply concepts (Outcome 3) and to
demonstrate an effective understanding of the financial globalization (Outcome 9).
Discussions, quizzes can enhance students’ awareness of the changing business
environment and its implications for management (Outcome 12). A mid-term test seeks to
reinforce the above learning outcomes.
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Financial Markets in a Global Marketplace
Foreign exchange and Eurocurrency markets; international money and capital markets; their
operations and pricing
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
66
Role of International Organizations
The International Monetary Funds, World Bank, Bank for International Settlements and the
International Organization of Securities Commissions; their roles in the global financial
market
Problems of the Global Financial Markets
Inflation risks, default risks, interest risks and currency risks. Global financial crisis
Regulations of the Global Financial Markets
Theories of Regulation, Regulation of hedge funds and international banks
Changing Environment and Management
Changing risks & regulations and their implications for management
Indicative Reading
Recommended Textbook
Rose, P.S and Marquis H.M. Money and Capital Markets – Financial Institutions and
Instruments in a Global Marketplace, 10th edition, McGraw Hill, 2008
References
Miskin, F.S. and S.G. Eakins, Financial Markets and Institutions, 5th Edition, Addison Wesley
Longman, 2006.
Valdez, S., Introduction to Global Financial Markets, 5th Edition, Palgrave Macmillan, 2007.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
67
Subject Code
:
AF3507
Subject Title
:
Company Law
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Seminars
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
Introduction to Business Law (AF2504)
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
The subject builds upon the general principles of business law studies at level 2 and in
particular focuses on business associations in the form of a registered company. The
purpose of the subject is to focus on those aspects of company law which are of particular
significance and relevance to the accountancy profession and also to focus on the
interaction of company law and business practices (Outcome 13). It contributes to the
achievement of BBA Programme Outcomes by enabling students to identify and resolve
legal and ethical issues in companies (Outcome 5), and analyze business situations and
problems by applying legal concepts in company law (Outcome 7).
Learning Outcomes:
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Explain the principles of Hong Kong Company Law relevant to the discipline of
accountancy.
Explain the laws applying to companies which are established overseas but establish a
place of business in Hong Kong.
Advise clients on various means by which a company may raise capital and provide
security for its lending
Critically evaluate the roles and responsibilities of officers of the company and also of
shareholders
Explain the regulatory framework applying to private and public companies and analyze
its effectiveness
Identify and resolve legal and ethical issues in companies
Analyze business situations and problems by applying legal concepts in company law.
Indicative Teaching/ Learning Approach
Legal principles and concepts will be introduced through lectures. In seminars, students will
be required to analyse and apply the legal principles to various issues involving companies
in the form of case study.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
68
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Assessment components include written company law problems/cases in coursework, midterm test and a final examination set with company law problems/ cases. These assessment
components require students to demonstrate their ability to interpret up-to-date company law
statute, including the Companies Ordinance and Securities and Futures Ordinance, and
case law principles and analyze practical company law issues (Outcome 7), apply company
law concepts to provide legal and ethical advice to clients (Outcome 5). Students’ ability to
identify and resolve ethical and legal issues in companies will be assessed in their
explanations/ advices through assessment components and final examination (Outcome 13).
Indicative Content / Outline Syllabus
Formation of a Company
The process of formation and the documentation required. The legal nature of corporation
and the doctrine of separate legal entity. The significance of the memorandum and articles of
association. Overseas companies regulation in Hong Kong.
Share and Loan Capital
Types of share capital and methods of raising and re-organising share capital including
prospectuses and the legal responsibilities of promoters. Debt financing from a corporation’s
perspective. Company debentures and registration.
Officers of the Company
Appointment and removal of directors and company secretary; powers and duties of
directors and company secretary. Disclosure requirements.
Limitation and Control of Company
Types of company’s meetings and their significance. The role and function of auditors and
inspectors. The protection of minority members.
External Regulation of Companies
Insider dealing provisions. The role of the Stock Exchange. Powers and functions of the
Securities and Futures Commission. Powers and duties of the Financial Secretary.
Indicative Reading
Recommended Textbook
Stott V., Hong Kong Company Law, Hong Kong: Pitman, 12th Edition, 2008.
Students are advised to obtain a copy of the Companies Ordinance (Cap.32) from the
Government Stationer or download an electronic copy from BLIS.
References
Cheng Po Wah, The Hong Kong company secretary's handbook : practice and procedure,
8th Edition, 2008
Sealey, L.S., Cases and Materials in Company Law, Butterworths, 8th Edition, 2008.
Smart P. Sd. J, Kathrine L, Anna Y.M.T., Hong Kong Company Law: Cases, Materials and
Comments, Butterworths Asia, 1997.
Lipton & Herzberg’s Understanding Hong Kong Company Law, Law Book Company, 1996.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
69
Subject Code
:
AF 3508
Subject Title
:
Employment Law
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures and Tutorials 42 hours
Pre-requisites
:
AF2504 - Introduction to Business Law
Co-requisites
:
None
Exclusion
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50 %
Final Examination
50 %
Coursework
D
Final Examination
D
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Management Outcomes by enabling
students to analyze employment problems by applying conceptual frameworks drawn from
case law and legislation (Outcome 7), demonstrate critical and creative thinking in the
business setting (Outcome 4), identify and resolve ethical issues arising in the workplace
(Outcome 5) and communicate effectively (Outcomes 1 and 2)
Learning Outcomes:
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
Examine and resolve employment-related legal problems by analyzing case law and
legislation
•
Identify and evaluate the practical actions required for implementing ethical and legal
compliance
•
Follow future legal developments
Indicative Teaching/ Learning Approach
This subject is built around a role-play, which students develop in and out of the classroom.
Lectures will introduce legal principles, legislation, case law and codes of conduct, which
students will be required to apply in the context of their role-plays.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
An individual employment contract drafting task, will help students to demonstrate critical
and creative thinking (Outcome 4), apply appropriate legislation and common law principles
(Outcome 7 ) and communicate effectively (Outcome 2), as will the role-play. The role-play
will also help students to demonstrate effective spoken English (Outcome 1) and identify and
resolve ethical issues arising in the work place (Outcome 5). Rubrics will be used for
assessing learning outcomes for both assessment tasks. The examination will enable
students to demonstrate their legal knowledge, legal reasoning and critical thinking skills by
analyzing business problems and applying the law to resolve the problem (Outcome 7).
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
70
Indicative Content / Outline Syllabus
Legal Framework and Institutions
The Hong Kong legal framework, Labour Tribunal and Equal Opportunities Commission.
Employment Relationship
Distinction between employees, apprentices and independent contractors.
Discrimination: Gender, Disability, and Family Status
Ethical issues, and codes of conduct. Starting a claim under the anti-discrimination
legislation. Rights and remedies.
Form and Terms of Employment Contracts
Contracting-out of statutory obligations. Rights and duties of the employer and the
employee. Remuneration, maternity rights, sickness benefits. Mandatory Provident Fund
(MPF).
Trade Unions
Membership and industrial action.
Health and Safety at Work
The duties of employers and employees under legislation and at common law, legal
exemptions and remedies. Compensation for employment related injuries and diseases.
Disciplinary Action and Termination of Employment
The legal obligations of employers in relation to staff appraisal and references. Dismissal
and remedies for unfair dismissal. Severance payments and long service payments.
Indicative Reading
Textbooks
Michael J. Downey (2004) Hong Kong Employment Law Manual, Hong Kong: Lexis Nexus,
Butterworths
Bruckhaus Deringer (Freshfields, 2006) Employment law in Hong Kong, CCH Hong Kong
Ltd.
Legislation
The Laws of Hong Kong
Halsbury’s Annotated Ordinances
http://www.justice.gov.hk
Law Reports
Hong Kong Law Reports
Hong Kong Law Reports and Digest
Hong Kong Cases
Final Court of Appeal Cases
All England Law Reports (UK)
Weekly Law Reports (UK)
Appeal Cases (UK)
HK Electronic Citations (Westlaw)
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
71
Subject Code
:
AF3511
Subject Title
:
Aspects of Insolvency Law
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Seminars
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
Company Law (AF3507)
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject is specifically designed for students studying in the Faculty of Business. Today
it is generally recognized that a strong and advance insolvency regime does not only create
and protect confidence in the business community but it also has an important role in the
economic recovery process of any jurisdiction in serious economic recession. Thus the
purpose of the subject is to equip the students with the fundamentals of the law and practice
relating to the insolvency of individuals and corporations (Outcome 13). It is expected that at
the end of the course the students will thoroughly understand their role in the existing
insolvency regime and understand the ethical and legal issues (Outcome 5) and problems
surrounding the insolvency of individuals and corporations, and cross-border insolvencies
and how they may be resolved under the current legal framework (Outcome 7).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Explain Hong Kong’s insolvency regime for both individuals and for companies.
Explain the process of being adjudicated bankrupt and the consequences of such an
order.
Explain the alternative voluntary procedure/scheme of arrangement of a debtor’s affairs.
Advise clients on various options a debtor, who is in financial difficulty, may have.
Explain the process of winding up a company, the role of the liquidator and the
dissolution of companies.
Analyze business situations and problems by applying legal concepts in insolvency law
Identify the ethical and legal issues arising in cross border insolvency.
Critically Evaluate the need for reform of insolvency law and explain the various form
such reform may take.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
The lectures will explain and emphasize the fundamental principles and will assist students
in the application of the legal principles in the practical environment. Lectures will constantly
use practical examples to show the important role and function of professional accountants
in the field of individual and corporate insolvency.
The seminars will promote student participation in the learning process through discussion
and case analysis. The emphasis throughout seminars will be on the practical application of
legal theory.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
72
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Assessment components include written individual bankruptcy law and corporate insolvency
law problems/cases in coursework, mid-term test and a final examination set with insolvency
law problems/ cases. These assessment components require students to demonstrate their
ability to interpret up-to-date insolvency law statute, including the Bankruptcy Ordinance and
Companies Ordinance, and case law principles and analyze practical insolvency law issues
(Outcome 7), apply insolvency law concepts to provide legal and ethical advice to clients
(Outcome 5). Students’ ability to identify and resolve ethical and legal issues in insolvency
situation will be assessed in their explanations/ advices through assessment components
and final examination (Outcome 13).
Indicative Content
Introduction to Hong Kong Insolvency Legal Framework
Purpose of Insolvency Law. Nature of Insolvency, Bankruptcy and Liquidation.
Individual Insolvency
Bankruptcy Administration: Courts; Official Receiver; and Trustees. Alternative procedure
to bankruptcy. Bankruptcy proceedings: the statutory demand; bankruptcy petition; the
hearing; bankruptcy order; and proof of debts. Consequential effect of bankruptcy over
person and property of bankrupt. Criminal law and bankruptcy.
Corporate Insolvency
Liquidation Administration: Courts; Official Receiver; Liquidator; Registrar of Companies;
and the Financial Secretary. Distinction between voluntary and compulsory liquidation.
Corporate rescue and alternative to liquidation. The process of compulsory winding up:
winding up petition; consequences of petition; the hearing; winding up order; and proof of
debts. Consequences of winding of order and subsequent proceedings on the corporate
entity and property. The process of voluntary winding by members and creditors.
Consequences on directors and others.
Cross Border Insolvencies
Classification of types of insolvency regimes: e.g. the United Kingdom, the United States
and the People’s Republic of China. Legal and practical problems relating to recovery of
debts and enforcement of securities in different insolvency regime. Legal and practical
problems of competing jurisdictions in parallel insolvency proceedings.
Reforms
Overview of future reforms of Insolvency Laws from the domestic and international
perspectives.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
73
Indicative Reading
Recommended Textbook
Stott V., Hong Kong Company Law, 12th Edition, Hong Kong: Pitman, 2008.
Chan, S., Hong Kong Bankruptcy Law Handbook, 3rd Edition, Butterworths Asia, 2007.
References
Goode, R. Principles of corporate insolvency law, 3rd Edition, Sweet & Maxwell, 2005.
Fletcher, I. F., Law of Insolvency, 3rd Edition, Sweet & Maxwell, 2002.
Stephen, S. M., Personal insolvency : law and practice, 4th Edition, LexisNixis, 2008.
Tomansic, R. and Little, Insolvency Law & Practice, FT Law & Tax Asia Pacific,
Hong Kong, 1997.
Legislation
The Bankruptcy Ordinance (Cap. 6).
The Bankruptcy Rules.
The Companies Ordinance (Cap. 32).
The Companies Winding Up Rules.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
74
Subject Code
:
AF3601
Subject Title
:
Managerial Economics
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Tutorials
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
None
Co-requisites
:
None
Exclusion
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
D
Final Examination
D
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Outcomes by enabling students to
analyze business situations and problems by applying conceptual frameworks drawn from
Economics (Outcome 7); and to identify and resolve ethical issues as they arise generally
and in the specific business settings for which they are being prepared (Outcome 5).
Learning Outcomes:
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
apply economic analysis to major categories of business decision.
identify and resolve ethical issues in the principal-agent problem.
present (individually and with others) economic arguments in a logically consistent
manner.
Indicative Teaching/ Learning Approach
The instructor will provide students with structured lectures on the underlying economic
concepts and their applications in business decisions. Students will be required to participate
in discussion in lectures, to undertake guided reading and case analyses, and to make group
presentations in the seminars.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Group project and case analyses will require students to apply economic concepts (Outcome
7) to different categories of business decisions. Presentations will require them to present
economic arguments logically (Outcome 7). Individual problem sets will assess their ability to
choose and use the appropriate economic frameworks (Outcome 7), while a mid-term test
and the final examination will assess their ability to evaluate practical business issues,
including ethical issues in business decisions (Outcome 5).
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
75
Indicative Content/ Outline Syllabus
The Scope of Managerial Economics
Model-building, theories and assumptions.
Models of the Firm
The profit-maximizing model, managerial and behavioural models.
The Nature of the Firm
Coasian analysis and Williamson’s analysis.
Ownership and Control of the Firm
The extent of managerial discretion. Diversifications, mergers and acquisitions.
Consumer Demand and Production
Estimating and forecasting demand. Production functions, cost curves and cost drivers.
Pricing Decisions
The simple model and its extensions; price discrimination; pricing new products and pricing
to deter entry; pricing in practice.
Game Theory and Strategic Behaviour
The prisoners’ dilemma and collusion; entry deterrence; new product development. The
impact of network effects.
Competition and Competition Policies
Competition law, government regulation, deregulation and privatization.
Indicative Reading
H. Davies and P.L. Lam (2001) Managerial Economics: An Analysis of Business Issues,
London: Prentice Hall.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
76
Subject Code
:
AF3604
Subject Title
:
Monetary and Financial Systems
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Tutorials
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
Introduction to Economics (AF2601) OR equivalent
Co-requisites
:
None
Exclusion
:
Assessment
:
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
D
Final Examination
D
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Outcomes by enabling students to
analyze business situations and problems (Outcome 7) by applying conceptual frameworks
drawn from Economics, and to apply basic financial theories and understand the operation of
financial markets (Outcome 9).
Learning Outcomes:
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to
•
•
•
•
•
Apply the concept of risk-return tradeoff in financial economics.
Analyze the determinants of interest rates.
Explain the importance and operations of the banking system.
Examine the implication of monetary policy.
Evaluate the role and functioning of various financial markets and institutions.
Indicative Teaching/ Learning Approach
Lectures are used to explain the basic concepts related to the subject. Tutorials involve
small groups of students working on a series of presentations and problem set solving.
Students are also required to write individual essays and to discuss findings from published
research articles.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
During tutorials, students will be required to present and discuss problem set questions to
test their ability to analyze business situations and problems (Outcome 7). Students are also
required to present empirical issues relating to the monetary and financial systems in Hong
Kong and to conduct data analysis. These activities will help students to apply basic financial
theories and understand the operation of financial markets (Outcome 9).
Mid term test and final examination are used to test students’ ability in understanding and
applying the concepts learnt from the subject.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
77
Indicative Content/ Outline Syllabus
Basic Financial Economics
Economic analysis of risk and uncertainty. Risk-return tradeoff.
Money and Interest Rate
What is money? Concept and behaviour of interest rates. Risk and term structure of interest
rates.
Banking System and Monetary Policy
Economic analysis of banking system. The money supply process. Central banking. Tools
and conduct of monetary policy.
Monetary Theory
Theories of demand for money. Transmission mechanisms of monetary policy. Monetary
and fiscal policy in the IS-LM model. Theory of rational expectation.
Financial Markets
Nature of financial markets and financial intermediation. Economic analysis of financial
structure. The role of transaction cost and asymmetric information. Concept of market
efficiency.
Financial Institutions
Banking and non-banking institutions. Regulation of financial institutions.
Indicative Reading
Recommended Textbook
Miskin, Frederic S., The Economics of Money, Banking, and Financial Markets, Eighth
edition, Pearson Addison-Wesley, 2007.
References
Publications of Hong Kong Monetary Authority.
Publications of the U.S. Federal Reserve Bank.
The Journal of Money, Credit and Banking.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
78
Subject Code
:
AF3901
Subject Title
:
Economics for Engineers
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Tutorials
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
None
Exclusion
:
AF2617
Role and Purpose
This
subject
aims
to
provide
students
with
fundamental
concepts
of
economics/mathematics/engineering and to develop students’ ability to analyze the
economic situations or solve problems by application of these concepts. It also aims to
explain how these concepts can be applied to affect the functioning of an engineering
company and contribute to decision making in engineering operations. It broadens students’
global outlook by introducing economic issues in Hong Kong and worldwide context.
Assessment tools of the subject help students to enhance their oral and written skills and to
communicate and work effectively with others.
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
understand the fundamental concepts of economics/mathematics/engineering.
understand the concepts of costs and revenues in global business operation.
develop the ability to understand economic and engineering issues in reality.
develop the budgetary planning and capital budgeting skills to deal with economic and
financial problems in engineering operations.
identify, formulate and solve scientific and engineering problems in suitable
mathematical or computable forms.
build up the skills to think innovatively, critically and creatively.
assess the strategies and behaviors of firms operating under various market structures in
the global economy.
understand the ethical dimension and responsibility of business and engineering
decisions and the social consequences of any decisions made.
communicate effectively via graphic, numeric, verbal and written media.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
There will be a lecture of two hours per week that will be structured to help students to
understand engineering economics concepts. Besides, there will be an one-hour tutorial per
week, for which students are required to present answers from tutorial questions and discuss
relevant cases and examples relating to the subject.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
79
Indicative Assessment Tasks
A variety of assessment tools will be used, including in-class exercises, group projects and
presentations and mid-term test. The in-class exercises will help students to understand the
fundamental concepts of economics/mathematics/engineering, to develop students’ critical
thinking and analytical skills and to provide a foundation and broaden the global outlook for
decision making in reality. Group projects and presentations help to strengthen students’
knowledge and application and enhance teamwork, and oral and written communication
skills.
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Part I
Basic Principles of Economics; Price Mechanism; Theory of Demand and Supply; Behaviour
of the Firm; Organisation of Industry.
Part II
Economic model of an engineering company; Composition of costs; Costing systems;
Activity and time based costing; Profit and loss control. Budgetary planning and control;
Investment and sources of finance; Time value of money and Investment appraisal.
Indicative Readings
Chan, Park, Contemporary Engineering Economics, 4th Edition, Prentice Hall, 2007.
Parkin, Michael, Economics, 8th Edition, Addison Wesley, 2008.
Drury, Colin, Management and cost accounting, 6th Edition, London: Thomson Learning,
2008.
Dyson, John R., Accounting for Non-Accounting Students, 6th Edition, Harlow: Financial
Times Prentice Hall, 2004.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
80
Subject Code
:
AF4106
Subject Title
:
Advanced Financial Accounting
Level
:
3
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
Intermediate Accounting 2 (AF3111)
Co-requisites
:
None
Exclusion
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50 %
Final Examination
50 %
Coursework
D
Final Examination
D
Minimum Pass Grade
:
42 hours
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Outcomes by enabling students to
apply financial theories and analyze financial reports (Outcome 9), demonstrate a global
outlook in analyzing business situations and problems (Outcome 3) and identify and resolve
ethical issues (Outcome 5). In addition, the subject will provide students with sufficient
professionally-specific skills and knowledge in management accounting to make an
immediate contribution to the organization in which they are first employed (Outcome 13).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
Explain and compare different types of business combinations.
Prepare group accounts.
Identify and resolve accounting issues of consolidation and foreign currency translation.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
THIS SUBJECT USES A MIX MODE OF TEACHING WITH ABOUT TWO-HOUR LECTURE
AND ONE-HOUR TUTORIAL.
LECTURES WILL INTRODUCE PERSPECTIVES,
CONCEPTS AND TECHNIQUES WHICH STUDENTS WILL BE REQUIRED TO APPLY
FINANCIAL THEORIES AND PREPARE GROUP ACCOUNTS.
TUTORIALS WILL
INITIATE STUDENTS FOR IDEAS, CONCEPTS AND TECHNIQUES OF THE TOPICS.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Classwork, including the use of tutorial questions, will help students to apply financial
theories and analyze financial report (Outcomes 9 and 13). Cases and problems will enable
students to demonstrate global outlook in analyzing business situations and problems
(Outcomes 3 and 13) and identify and resolve ethical issues (Outcomes 5 and 13).
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
81
Indicative Content/ Outline Syllabus
Business Combination
Different types of business combination. Corporate expansion and accounting for business
combinations.
Consolidation of a Group of Companies
Formation of a group. Features of consolidation. The reporting entity and consolidated
financial statements. Consolidation of wholly owned subsidiaries and partially owned
subsidiaries. Consolidation of indirect ownership interests. Reporting intercorporate
investments in ordinary shares. Consolidation as of the date of acquisition. Consolidation
following acquisition. Intercorporate transfers of noncurrent assets. Intercompany inventory
transactions, intercompany indebtedness and intercompany provision of services. Reverse
acquisitions. Equity method of accounting. Proportional consolidation.
Multinational Accounting
Foreign currency transactions and financial instruments. Translation of foreign entity
financial statements. Different methods of foreign currency translation. Accounting
practices of foreign currency translation for individual companies and group of companies.
Indicative Reading
Pearl Tan Hock Neo and Peter Lee Lip Nyean, Advanced Financial Accounting: An IAS and
IFRS Approach, McGraw Hill.
Keith Alfredson, Ken Leo, Ruth Picker, Paul Pacter, Jennie Radford, Applying International
Accounting Standards, Wiley.
Craig Deegan, Australian Financial Accounting, McGraw Hill.
Lynne Chow, Shirley Kan, Dennis Taylor, Christina Tsui, Advanced Financial Accounting in
Hong Kong, Longman.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
82
Subject Code
:
AF4107
Subject Title
:
Financial Statement Analysis (Elective subject)
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
Intermediate Accounting 2 (AF3111) AND
42 hours
Business Finance (AF3313)
Assessment
Minimum Pass Grade
:
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Role and Purpose
This subject aims to introduce an analytical framework for carrying out business analysis and
valuation by using information provided in financial statements. It is primarily designed for
accountancy students who wish to qualify as a professional user of financial statements at
an entry level.
It contributes to the achievement of 02002 and 21045 Programme Outcomes by enabling
students to analyse business situations and problems by applying conceptual framework
drawn from Accounting and Finance (Outcome 5), apply accounting and financial theories to
analyze financial reports (Outcome 9) and function as a professional user of financial
statements (Outcome 13).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
Develop a framework for analysis that sets accounting and financial analysis in the
context of competitive strategies adopted by a company;
•
Analyze accounting choices, combine them into meaningful financial analyst reports and
use this information in assessing company value and
•
Demonstrate skills and knowledge as a professional user of financial statements.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
The three hours per week will be used flexibly by the instructor for discussing both concepts
and applications with students and carrying out other learning activities. Students will be
encouraged to share their views and experiences actively with the instructor and other
classmates.
To maximize learning, students are requested to read the assigned textbook chapter(s), do
exercises and cases before they come to the seminar. It normally requires 4-5 hours
preparation for a 3-hour seminar.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
83
Indicative Assessment Tasks
50% Continuous assessment
-
contribution in discussions to demonstrate students’ knowledge on application of
accounting and finance concepts/theories (Outcome 5, 9 and 13),
-
mid term test, a direct approach to test students’ understanding and application of
accounting and financial concepts (Outcome 5 & 13) and
-
written analysis on assigned cases to demonstrate students’ ability to analyze financial
reports in the context of a company’s strategies and produce meaningful financial analyst
reports so as to qualify as professional users of financial statements (Outcome 5, 9 and
13).
50% Final examination
Problems/cases to test students’ understanding on various types of analysis, their ability to
process, interpret and professionally use relevant information from financial reports
(Outcome 5, 9 and 13)
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
A Framework for Business Analysis
Structure of a corporation: Board, Ownership and Capital structure; Incentives, moral hazard
and adverse selection; Corporate reporting – Financial Statements, Business Analysis, Tools
for Analysis
Business Strategy Analysis
Business Environment analysis; Actual and potential competition; Sources of competitive
advantages; Achieving and sustaining competitive advantage; Formulation and deployment
of strategy through operations, investment, financing and reporting
Accounting Analysis
Factors affecting accounting quality; Assessing accounting flexibility; Potential red flags.
Financial Analysis
Common-sized financial statements; Ratio analysis; Cash flow analysis.
Prospective Analysis and Valuation
Forecasting; Cash-flow and Accounting-based valuation techniques.
Indicative Readings
Recommended Textbooks
J. Wild and K. Subramanyam, Financial Statement Analysis, 10th Edition, McGraw-Hill,
2009 (Wild)
R. Lundholm and R. Sloan, Equity Valuation & Analysis, 2nd Edition, McGraw-Hill,
International Edition, 2007 (L)) [Must buy – cases are chosen from this book. Cases will not
be distributed in class]
Reference
K.G. Palepu, V.L. Bernard, P.M. Healy and E. Peek, Business Analysis and Valuation:
IFRS Edition Text and Cases, South-Western/International Thomson, 2007
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
84
Subject Code
:
AF4108
Subject Title
:
Issues in Management Accounting
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
Management Accounting 1 (AF2110) AND
42 Hours
Management Accounting 2 (AF3112) AND
Accounting Information Systems (AF3211)
Assessment
Minimum Pass Grade
:
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
Final Examination
(D)
(D)
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA (Hons) Programme Outcomes by
enabling students to analyze strategic management problems by applying conceptual
frameworks drawn from accounting, finance, economics, behavioral science and quantitative
methods (Outcome 7), by identifying and analyzing those aspects of the domestic and global
business environment that set the ‘parameters of choice’ within which business
organizations set objectives and take actions (Outcome 12). It will prepare students for using
current information technology effectively and evaluating new technologies as they emerge
in the management accounting context (Outcome 6). This subject will also prepare students
to develop ethical awareness from the managerial accounting and information technology
perspectives (Outcome 5). This subject will contribute to build students’ professionallyspecific skills and knowledge to 1) enable them to make an immediate contribution to the
organization they are first employed and 2) base the process of continuous professional
development (Outcome 13).
Learning Outcomes:
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
Indentify problems and formulate alternatives for strategic management decisions.
Apply the recent global development in management accounting techniques to
management control and decision making.
Design and evaluate information systems for planning, control and performance
measurement.
Indicative Teaching/ Learning Approach
Using active and problem-based learning approaches, a three-hour seminar will be
conducted each week to develop students’ knowledge through case analyses, discussions,
presentations and team projects. This subject adopts “real-life” organization-based cases in
teaching. Through case analysis and presentation, students are provided with the
ambiguous issues and problems found in actual organizations, enabling them to apply
management accounting theory to these problems. This approach encourages students to
think in terms of management accounting theory as a way of conceptualizing problems and
prescriptions for management accounting systems design. Computer laboratory sessions will
be organized to provide students’ hands-on experience in retrieving information from
management accounting information systems for planning, control and decision making.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
85
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Assessment components include group-based case analysis with report and presentation;
mid-term examination; participation; an information system design project and final
examination. The assessment tasks require students to demonstrate their understanding
and critical application of the appropriate concepts and techniques in management
accounting to help management in organizational planning, control and decision-making
processes (Outcome 7); ability to identify and analyze aspects of the domestic and global
business environment when proposing strategic actions in meeting corporate objectives
(Outcome 12); ability to use current information system to aid management for decisionmaking and internal control (Outcome 6); and ability to evaluate ethical issues from a
management accounting and information technology perspective and suggest appropriate
responses (Outcome 5); and ability to build professionally-specific skills and knowledge
(Outcome 13).
Indicative Content/ Outline Syllabus
Cost Management Concepts and Cost Behaviour
Use of product cost information. Expenditure, costs and expenses. Product costs. Cost
behaviour. Organization life-cycle and cost creation. Cost structure.
Traditional Cost Management System
Job order. Job costs and markup. Recording actual job costs. Process costing. Comparison
between process costing and job order costing.
Activity Based Costing and Activity Based Management
Activity cost drivers. Limits of traditional costing system. Using ABC for pricing and analyzing
customer profitability.
Management Accounting Information for Activity and Process Decisions
Sunk cost. Relevant cost. Make-or-buy decisions. Facility layout system. Inventory costs and
processing time. Quality issue. Just-in-time manufacturing.
Cost Information for Pricing and Product Planning
Role of product costs in pricing and product mix decisions. Short-term product mix and
pricing decisions. Opportunity cost. Capacity constraint. Long-term product mix and pricing
decisions.
Management Accounting and Control Systems: Assessing Performance over the
Value Chain
Management accounting and control systems. Characteristics of MAC. Value Chain. Totallife-cycle costing. Target costing. Kaizen costing. Environment costing.
Motivating Behavior in Management Accounting and Control Systems
Ethical code of conduct. Goal congruence. Performance measures. Intrinsic and extrinsic
rewards. Reward system. Incentive compensation plans.
Financial Control
Decentralization. Responsibility centers. Evaluating unit performance. Transfer pricing.
Assessing productivity using financial control. External financial control. Financial Ratio
Analysis.
Using Budgets to Achieve Organizational Objectives
Budgeting process. Operating budgets. Financial budgets. Sensitivity Analysis. Variance
Analysis. Behavior implication of budgeting.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
86
Management Control System Design
The nature of management control systems. The management control environment and
process. Contingency approach to system design. Computer technology in management
control system design.
Strategy and the Balanced Scorecard
The Balanced scorecard, the strategy map and the balanced scorecard. Balanced scorecard
objectives and measures.
Indicative Reading
Textbook(s)
Atkinson A.A., Kaplan, R.S., Matsumura, E.M. and Young, S.M., Management Accounting,
5th Edition, Prentice-Hall, 2007.
References
Young, S.M., Readings in Management Accounting, 5th Edition, Prentice-Hall, 2007.
Blocher, E.J., Stout, D.E., Cokins, G., and Chen, K.H., Cases and Readings Manual (for use
with Cost Management – A Strategic Emphasis), 4th Edition, McGraw Hill, 2008.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
87
Subject Code
:
AF4109
Subject Title
:
International Accounting
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
Advanced Financial Accounting (AF4106)
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(Grade D)
Final Examination
(Grade D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
42 hours
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of BBA Outcomes by enabling students to obtain
sufficient accounting skills and knowledge to make an immediate contribution to their
employer (Outcome 13) and broaden their global outlook (Outcome 3) through evaluating
the diversity of accounting practices across countries It also enables the students to identify
and resolve the consequent international accounting issues facing the professional,
investors, multinational companies and regulators.
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
Identify the impact of environmental and cultural factors on the evolution of the
accounting system of a country.
•
Make a comparative analysis of accounting systems in various countries.
•
Evaluate accounting concepts on significant technical issues in financial reporting and
managerial accounting for multinational corporations.
•
Apply analytical skills and critical thinking on key international accounting issues.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
The three hours per week will be used flexibly by the instructor for seminar-based teaching,
case studies and discussion. To maximize benefits, students are expected to develop their
global outlook and apply their knowledge on international accounting through a combination
of research, discussion, individual assignments and group project.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
The assignments and the group project will help students to develop their global outlook
(Outcome 3), accounting skill and knowledge, analytical skills and critical thinking through
identifying and resolving international accounting issues. The students will also be required
to demonstrate the accounting skills and knowledge (Outcome 13) suitable for their future
career through unstructured essay questions and structured computational questions in the
Final Examination.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
88
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Overview
Meaning of international accounting. Classification of world accounting standards and
practices.
International Accounting Standards and Organisations
Pressures for convergence of accounting standards. Major organizations involved in
convergence of accounting standards.
Comparative Accounting Systems
Environmental and cultural factors that influence national accounting systems and lead to
accounting diversity. Comparison of accounting and reporting practices in a sample of
developed countries.
Financial Reporting and Disclosure Issues for Multinational Corporations
Foreign currency transaction and translation. Accounting for price changes and inflation.
Segment Reporting.
Managerial accounting issues for Multinational Companies
Multinational business strategy and accounting. International budgeting. Formulation and
implementation of performance evaluation system.
Indicative Reading
Recommended Textbook
Doupnik, T. and H. Perera, International Accounting, Latest Edition, McGraw-Hill Education
(Asia).
Recommended References
Choi, F.D.S. and G.K. Meek, International Accounting, Latest Edition, Prentice Hall,
Nobes, C. and R. Parker, Comparative International Accounting, Latest Edition, Prentice
Hall.
Alfredson, Leo, Picker, Radford and Wise, Applying International Financial Reporting
Standard, Latest Edition, John Wiley & Son Australia Ltd.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
89
Subject Code
:
AF4212
Subject Title
:
International Tax Planning and Management
Level
:
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
Hong Kong Tax Framework (AF3204)
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
4
42 hours
Objectives
This subject aims:
(a)
to impart students the principles and techniques in international tax planning and the
commonly used tax avoidance devices. The concepts will be illustrated by up-to-date
cases pertaining to the business practices and tax laws in Hong Kong, in selected
countries which have close economic ties with Hong Kong, and in Mainland China.
(b)
to enhance students’ understanding and appreciation in applying the tax knowledge
in business and investment decisions.
(c)
to provide students a background knowledge in the PRC taxation system and its
implications to foreign investors.
(d)
to arouse students’ appreciation of the contemporary issues in taxation both within
and outside Hong Kong.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
The three hours per week will be used flexibly by the instructor for discussing key concepts
and their applications with students and carrying out other learning activities with them. To
maximize benefits, students are encouraged to share their views and experiences actively
with their instructors and other classmates.
Indicative Content
International Taxation – Concepts and Principles
Purposes of taxation. Jurisdictional bases for taxing persons and property. Company and
personal income taxes. Computation of income. Double taxation.
Taxation Of Inbound and Outbound Investments
Concept of permanent establishment. Source of business and property income. Tax
incentives and implications for foreign direct investment and for choice of investment
vehicles. Equity versus loan financing. Withholding taxes on investment income and profit
repatriation. Foreign tax credit. Foreign tax exemption and deduction. Tax treaty. Tax
sparing. Exchange of information.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
90
International Tax Planning – Principles, Practices and Anti-Avoidance Provisions
Conceptual principles for international tax planning. Basic tax mitigation strategies. Tax
avoidance devices: re-invoicing, transfer pricing, tax haven companies. Offshore
incorporations. Treaty shopping. Use of trusts and holding companies. Investment in shares
and property. Transfer pricing rules. Thin capitalization rules. Controlled foreign corporation
rules. Controlled company provisions, and general anti-avoidance provisions, international
cooperation and harmonization, tax planning for expatriates.
PRC Tax and Investment Implications
Forms of investments. Enterprise income tax. Individual income tax. Turnover tax. Real
property gain tax. Tax incentive and planning opportunities. Double tax arrangement.
Current Issues in Taxation
Other forms of taxation, electronic commerce, tax agency, and latest taxation development
in Hong Kong and at international scene.
INDICATIVE READING
Recommended Textbook
Arnold, B.J. and M.J. Mclntyre, International Tax Primer, most recent edition, The Hague:
The Netherlands, Kluwer Law Internationa.
CCH, Hong Kong Master Tax Guide, most recent edition, Hong Kong, CCH Hong Kong
Limited.
Smith, D.G. and A. Macpherson, Hong Kong Taxation: Law and Practice, most recent
edition, Hong Kong, The Chinese University Press.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
91
Subject Code
:
AF4215
Subject Title
:
Information Systems Audit and Control
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
Computer Systems for Accountants (AF3205) OR
42 hours
Management of Accounting Information Systems
(AF4203) OR ANY IT subject deemed as appropriate
Assessment
Minimum Pass Grade
:
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Role and Purpose
The main purpose of this subject is to introduce the various contemporary concepts,
approaches, and techniques of auditing information systems (IS) and information
technologies (IT), as well as the application of IT in auditing. This subject is especially useful
for those students who want to pursue a career in IT auditing or IT security administration.
Learning Outcomes
On successful completion of this subject, students should be able to:
•
Understand the relationship between IS auditing and general auditing, and the roles of
an IS auditor in the Audit Department as well as the whole business organization.
•
Familiarize with the various types of IS audits and their associated auditing concepts and
techniques.
•
Evaluate how IT can be used to improve the efficiency of general audit reviews.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
Seminars are used to discuss the key IS audit, security and control concepts. A group
presentation, an individual assignment, and a test will be used to reinforce students’
learning. Hands-on experience, such as the use of a commercial computer audit software
package, will be provided if possible.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
92
Indicative Content
IT audit management
Conducting IS audits
Auditing systems development
Auditing application systems
Using IT in auditing
Contingency planning and disaster recovery
Computer fraud and abuse
Indicative Reading
J.A. Hall and T. Singleton, Information Technology Auditing and Assurance (2nd edition),
Thomson / South-Western, 2005 (prescribed textbook).
R. Weber, Information Systems Control and Audit, Prentice Hall, 1999 (or the latest edition)
(prescribed textbook).
R. Cascarino, Auditor’s Guide to Information Systems Auditing, Wiley, 2007.
J. Champlain, Practical IT auditing (2nd edition), Warren, Gorham and Lamont, 2004.
F. Gallegos, S. Senft, D.P. Manson, and C. Gonzales, Information Technology Control and
Audit (2nd edition), Auerbach, 2004.
J.J. Champlain, Auditing Information Systems (2nd edition), Wiley, 2003.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
93
Subject Code
:
AF4216
Subject Title
:
Auditing and Assurance 1
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
14 hours
Seminars
28 hours
Pre-requisite
:
None
Co-requisite
:
None
Exclusion
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(Grade D)
Final Examination
(Grade D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
ROLE AND PURPOSE
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA (Hons) Outcomes by enabling
students to apply basic business financial theories, analyze financial reports and understand
the operation of financial markets (Outcome 9), analyze business situations and problems by
applying conceptual frameworks drawn from accounting, finance, economics, behavioural
science, law and quantitative methods (Outcome 7), and identify and resolve ethical issues
as they arise generally and in the specific business settings of auditing (Outcome 5). In
addition, this subject also contributes to the achievement of the BBA (Hons) Outcomes by
enabling effective written and verbal communications in English (Outcomes 1 and 2) and
working effectively in groups (Outcome 8).
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Upon successful completing this subject, the students will be able to:
•
apply the agency theory to the role of auditing in understanding the operation of the
financial market;
•
analyze audit and assurance situations and problems by applying conceptual framework
on financial reporting; and,
•
identify and resolve ethical issues arisen from auditor independence.
INDICATIVE TEACHING/LEARNING APPROACH
LECTURES WILL INTRODUCE THE VARIOUS CONCEPTS AND TECHNIQUES OF
AUDIT AND ASSURANCE. THESE ARE TO BE REINFORCED BY TUTORIAL EXERCISE,
CASE STUDIES, AND SMALL SCALE RESEARCH INTO TO CURRENT ISSUES.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
94
INDICATIVE ASSESSMENT TASKS
ASSESSMENT COMPONENTS INCLUDE SOLVING AUDIT AND ASSURANCE CASES IN
PRESENTATIONS, TERM TEST(S) AND FINAL EXAMINATION. THESE ASSESSMENT
COMPONENTS REQUIRE STUDENTS TO DEMONSTRATE THEIR ABILITY TO
ANALYZE AND SOLVE PROBLEMS BY APPLYING RELEVANT LAW AND PRINCIPLES
IN AUDIT AND ASSURANCE (OUTCOME 7) AND TO COMMUNICATE EFFECTIVELY IN
ENGLISH (OUTCOMES 1 AND 2). STUDENTS ARE ALSO REQUIRED TO DELIVER
THEIR PRESENTATIONS IN GROUPS AND THEIR ABILITY TO WORK AS A TEAM WILL
BE INDIRECTLY ASSESSES IN THE PRESENTATION COMPONENTS (OUTCOME 8).
THEIR ABILITY TO IDENTIFY ETHICAL ISSUES IN BUSINESS SETTINGS (OUTCOME 5)
AND AUDITOR INDEPENDENCE ISSUES IN CORPORATE REPORTING AS THEY
APPLY TO THE OPERATION OF THE CAPITAL MARKET (OUTCOME 9) WILL BE
ASSESSES THROUGH THEIR WORK IN PRESENTATION, TERM TEST(S) AND/OR
FINAL EXAMINATION.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
95
Subject Code
:
AF4217
Subject Title
:
Auditing and Assurance 2
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
Auditing and Assurance 1 (AF4216)
Co-requisites
:
None
Exclusion
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(Grade D)
Final Examination
(Grade D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
42 hours
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA (Hons) Outcomes by enabling
students to effectively communicate verbally in English (Outcome 1), and work effectively
with and through others (Outcome 8). It also equips students with sufficient professional
skills and knowledge (Outcome 13), enabling them to analyze business situations and
problems in providing auditing and assurance services (Outcome 7), and to identify ethical
issues as they arise (Outcome 5).
Learning Outcomes:
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
understand thorougly the major auditing and assurance services;
•
compare other assurance and related services provided by auditors;
•
apply the knowledge learnt in conducting auditing and assurance in a supervised
manner; and
•
keep abreast of and evaluate the current developments in auditing, assurance and
corporate governance.
Indicative Teaching/ Learning Approach
The three hours per week classes will be used flexibly by the instructor for discussion of
concepts and their applications with students and for carrying out other learning activities
with them. To maximize benefits, students are encouraged to share their views and
experiences actively with their instructors and their classmates.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
96
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Classwork, including the use of cases, problems, research topics and current issues, written
test and examination will enable students to apply professional skills and knowledge
(Outcome 13) to analyze business situations and problems (Outcome 7) and to identify
ethical issues (Outcome 5). Effective communication in English (Outcome 1) will be
assessed in class presentation and participation. Class presentations are carried out in
groups and students’ ability to work with others (Outcome 8) is assessed.
Indicative Content
Advanced Topics on Auditing and Assurance
Auditing and assurance issues related to conglomerates including group entities, related
parties, reliance on other auditors and experts.
Assurance of Other Historical Financial Statements
Review of interim financial statements and other financial information.
Other Assurance and Non-assurance Services
Reporting on prospective financial information. IPOs and due diligence. Agreed-upon
procedures. Compilation of financial statements.
Assurance on Non-Financial Information
Internal audit and operational audit. ISO audit. Reporting on an entity’s internal control over
financial reporting.
IS Audit
The impact of information technology (IT) on internal controls and auditor’s control
evaluation and risk assessment. IT system organization and internal controls. IT-based
audit tools.
Current Issues
Current trend and development in auditing and assurance.
corporate governance matters.
Other current issues and
INDICATIVE READING
Lau, P.T.Y. and N.C.Y. Lam, Auditing and Assurance in Hong Kong, latest edition, Pilot
Publishing Co Ltd.
Gul, F.A., Hong Kong Auditing: Economic Theory and Practice, City University of Hong Kong
Press, latest edition.
Auditing, Assurance and all other relevant Standards, and Code of Ethics for Professional
Accountants issued by Hong Kong Institute of Certified Public Accountants.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
97
INDICATIVE CONTENT
Auditing and Assurance
Auditing, corporate governance and institutions; agency theory and the economic demand
for auditing; auditor independence and professional ethics; responsibilities and legal
liabilities of auditors; auditing standards
Audit planning, Materiality, Audit Risk, Sample Testing and Evidence
Engagement planning and its importance, the assessment of materiality and audit risk, the
audit-risk model, sample testing and evidential matters.
Internal Control
Corporate governance and internal controls; evaluating internal controls; effects of
information technology on internal control system and audit testing.
Auditing the Financial Statements
Audit methods and approaches, the audit of the transactions and balances, performing
analytical review and completing the financial statement audit.
Reporting
Audit qualifications and different types of audit reports.
INDICATIVE READING
Gul, F., Hong Kong Auditing – Economic Theory and Practice, City University of Hong Kong
Press, latest edition.
Knapp, Michael C. Auditing Cases, 7th Edition (International Edition), South-Western
Cengage Learning, 2009.
All relevant up-to-date Standards on Auditing and Code of Ethics issued by the Hong Kong
Institute of Certified Public Accountants.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
98
Subject Code
:
AF4218
Subject Title
:
Financial Reporting Framework in China
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
AF2108 Financial Accounting
Co-requisites
:
None
Exclusion
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
D
Final Examination
D
Minimum Pass Grade
:
42 Hours
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Outcomes by enabling students to
applying accounting framework to analyze business enterprises in China (Outcome 7), more
specifically, to apply accounting knowledge to analyze financial reports of China’s listed
companies and understand the operation of stock market in China (Outcome 9). With a
focus on Chinese market, this course enables students to get professionally-specific skills
and knowledge to deal with China-related clients and make an immediate contribution to the
organization in which they are first employed; these skills may also form a base for future
professional development (Outcome 13). This course also enables them to demonstrate a
global outlook and an understanding of cultural difference between China and western
countries (Outcome 3). It also requires students to work effectively as a team, carry out selfreview and peer review to enhance the team performance (Outcome 8) and to communicate
both orally and in writing for effective business communication (Outcome 2).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
z
Analyze financial reporting framework in the context of accounting and auditing
framework for PRC firms and foreign-invested entities operating businesses in mainland
China.
z
Evaluate the laws and practices of various types of accounting and auditing reporting in
mainland China.
z
Evaluate the achievements and problems in the economic reform since 1978 especially
in accounting and auditing industry, as well as the contemporary issues in mainland
China.
Indicative Teaching/ Learning Approach
The three hours per week will be used flexibly by the instructor for discussing key concepts
and their applications with students and carrying out other learning activities with them. To
maximize benefits, students are encouraged to share their views and experience actively
with their instructors and other classmates.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
99
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Short discussion topics will be given to students on selected weeks, which will help students
to apply accounting framework to analyze business enterprises (Outcome 7) and to
understand the culture differences (Outcome 3). Quizzes will be conducted on selected
weeks for students to apply accounting knowledge to accounting transactions (Outcome 9).
A case analysis will also be given to students for analysis and a report in the form of a
business recommendation letter is required, which will help students improve their ability to
communicate in writing for business communication (Outcome 2) and get ready for handling
real business situation (Outcome 13). The short discussion and the case analysis are done
on group basis with an aim to enhance students’ ability to work with others and effective
communication skills (Outcome 8). Students will be required to assess their own
performance and other team members’ performance through peer review.
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Chinese Market Overview
Economic reform in China. An introduction to the State-owned enterprises in mainland China,
their structural transformation in the economic reform.
Financial Reporting Framework
Basics of financial accounting in mainland China. Financial statements and reporting
requirements for listed and non-listed state-owned enterprises. Regulatory framework of
financial reporting, establishments of accounting standards, and recent accounting reform.
Practices of Auditing
Auditing practices and framework in mainland China. Contemporary issues in auditing,
including recent CPA firm ownership reform and independent auditing standards.
Contemporary Accounting Issues in the Mainland China
Contemporary accounting and auditing issues mainly related to listed companies in China
(such as earnings management, corporate governance, audit quality, etc.).
Indicative Reading
Recommended Textbook
Tang, Y.W., L. Chow and B.J. Cooper, Accounting and Finance in China: A Review of
Current Practice, 5th Edition, Hong Kong, Sweet & Maxwell Asia, 2003.
References
Selected journal articles, rulings, regulations, reports, cases and newsletters.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
100
Subject Code
:
AF4220
Subject Title
:
Forensic Accounting
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
14 hours
Seminars
28 hours
Pre-requisites
:
Auditing and Assurance 1 (AF4216)
Co-requisites
:
None
Exclusion
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(Grade D)
Final Examination
(Grade D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
ROLE AND PURPOSE
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA (Hons) Outcomes by enabling
students to identify and invoke mechanisms for the simulations of creative thinking in the
business setting (Outcome 4), identify and resolve ethical issues as they arise generally and
in the specific business settings for which they are being prepared (Outcome 5), and,
analyze business situations and problems by applying conceptual frameworks drawn from
accounting, finance, economics, behavioural science, law and quantitative methods
(Outcome 7). In addition, this subject also contributes to the achievement of the BBA (Hons)
Outcomes by enabling effective written and verbal communications in English (Outcomes 1
and 2) and working effectively in groups (Outcome 8).
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Upon successful completion of the course, the student will be able to:
•
identify and invoke mechanisms for the simulation of fraud investigation in the business
setting;
•
identify and resolve ethical issues as that arise in the prevention of fraud in a business
setting; and,
•
analyze business situations and problems by applying conceptual framework drawn
from accounting, finance, economics, behavioural science, law and quantitative
methods
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
Lectures will introduce the various concepts and techniques of fraud examination. These are
to be reinforced by tutorial exercise, case studies of financial statement fraud, and online
fraud investigation exercises.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
101
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Assessment components include identifying issues and resolving problems relating to fraud
in online fraud investigations, computer labs, term test(s) and final examination. These
assessment components require students to demonstrate their analytical skill and ability in
creative thinking in resolving online fraud cases (Outcome 4), as well as by applying relevant
principles for identifying symptoms of financial statement frauds in computer labs (Outcome
7), and to communicate effectively in English (Outcomes 1 and 2). Students are also
required to carry out their online investigation and computer labs in groups and their ability to
work as a team will be indirectly assesses in these components (outcome 8). Their ability to
identify ethical issues in business environments as they relate to fraud prevention (Outcome
5) will be assesses through their work in term test(s) and/or final examination.
INDICATIVE CONTENT
Financial Reporting and Fraud
The relationship between financial reporting structure, earnings management and fraudulent
accounting. Fraud schemes and audit failures.
Types of Fraud
The taxonomy of economic crimes. The fraud triangle focuses in assessing fraud – incentive,
opportunity and rationalization. Definition of financial statement fraud. Economic crime
survey reports and a perspective on recent fraud cases.
Fraud Realization, Prevention and Detection
Organizational considerations in controlling fraud – corporate governance, audit, and
assurance. The legal and regulatory frameworks / agencies in fraud prevention and
detection.
Fraud Examination
Fraud examiners – their roles and functions. The nature and characteristics of forensic and
investigative assignments
Information Technology and Fraud
Introduction to the impact of information technology on financial statement fraud. Using
Computer-based Analysis Techniques for Fraud Detection.
INDICATIVE READING
Recommended Textbook
Albrecht, Steve, W., C.C. Albrecht, C.O. Albrecht, and M. F. Zimbelman, Fraud Examination,
latest edition, CENGAGE.
References
Beasley, Mark, Frank Buckless, Steven Glover and Douglas Prawitt, Auditing Cases:
An Interactive Learning Approach, latest edition, Prentice Hall.
Knapp, Michael, C., Contemporary Auditing: Issues and Cases, latest edition,
Thomson.
Kwok, B.K.B., Accounting Irregularities in Financial Statements: A Definitive Guide for
Litigators, Auditors and Fraud Investigators. latest edition, Gower Publishing.
KPMG, 2003 Fraud and Misconduct Diagnostic Survey: Hong Kong, KPMG, 2003.
PricewaterhouseCoopers, Economic Crime Survey 2003, PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2003.
PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC), Economic Crime Survey 2003: Asia Pacific, PwC, 2003.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
102
Robertson, Jack C., Fraud examination for managers and auditors, FEMA, Latest
Edition.
Rezaee, Zabihollah, Financial Statement Fraud, John Wiley and Sons Inc. Latest
Edition.
OTHER RESOURCES
Journal of Forensic Accounting: http://edwardspub.com/journals/JFA/consider.html
Association of Certified Fraud Examiners: http://www.cfenet.com/home.asp
Forensic Accountants’ Society of North America: http://www.fasna.org/
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
103
Subject Code
:
AF4221
Subject Title
:
Strategic Tax Planning and Management
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
Hong Kong Tax Framework (AF3210)
Co-requisites
:
None
Exclusion
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50 %
Final Examination
50 %
Coursework
(Grade D)
Final Examination
(Grade D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
42 hours
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA (Hons) Outcomes by enabling
students to communicate effectively in both verbal and written English (Outcomes 1 & 2),
demonstrate a global outlook and an understanding of cultural diversity (Outcome 3),
demonstrate creative thinking (Outcome 4), apply taxation concepts to analyze business
situations and problems (Outcome 7), and carry out and act upon self-appraisal and
reflective thinking, in the areas of creativity, teamwork, leadership and learning to learn
(Outcome 8). In addition, it requires students to identify and analyze taxation aspects of the
domestic and global business environment (Outcome 12).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
apply advanced aspects of the corporate and individual tax laws, rules and practices in
the Hong Kong context to real life scenarios, taking into account also the latest
development of the tax laws in the neighboring tax regimes that may affect tax planning
decisions on cross-border investment and trading;
•
explain the impact of changes in tax laws and tax cases on business transactions,
organizations and individuals with particular reference to Hong Kong situation;
•
evaluate the development of international tax principles and practices and how it
impinges on business structures and transactions that are organized on a global basis;
and
•
identify tax planning opportunities and integrate appropriate tax strategies in corporate
and personal business planning decisions.
Indicative Teaching/ Learning Approach
The three hours of seminar per week will be used flexibly by the lecturer for discussing key
concepts and their applications with students and carrying out other learning activities with
them. To maximize benefits, students are encouraged to share their views and experiences
actively with their lecturers and other classmates.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
104
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Group Presentation, Group Critique Reports on other classmates’ presentation and an
Individual Case Study will help students to think critically and creatively (Outcome 4), to
analyze business situations (Outcome 7), to carry out self-appraisal and reflective thinking
(Outcome 8), and to analyze domestic and global business environment (Outcome 12).
Effective communication (Outcomes 1&2) and global outlook (Outcome 3) will be assessed
against rubrics in the Group Presentation, Group Critique Reports and Individual Case
Study.
Indicative Content/ Outline Syllabus
Taxation Concepts and Principles
Purposes and classification of taxation. Jurisdictional bases for taxing persons and property.
Source of business and property income. Computation of income. Deduction rules.
Taxation of Inbound and Outbound Investments
Concept of permanent establishment. Forms of investments. Non-residents persons. Equity
versus loan financing. Withholding taxes on investment income and profit repatriation.
Double taxation reliefs. Tax treaty. Tax Sparing. Tax incentives. Exchange of information.
Taxation on Instruments, Wealth and Individuals
Scope of charge, assessment, exemptions and tax planning opportunities of Hong Kong
stamp duty. Tax planning for individuals and expatriates working in Hong Kong.
Strategic Corporate Tax Planning – Principles, Practices and Anti-avoidance
Provisions
Basic tax planning principles and mitigation strategies. Tax avoidance devices: re-invoicing,
transfer pricing, tax haven companies, treaty shopping, use of trusts and holding companies.
Thin capitalization rules. Controlled foreign corporation rules. Harmful tax practices. General
and special anti-avoidance provisions.
Current Issues in Taxation
Electronic commerce. Offshore funds. Goods and sales tax. Latest taxation development
in other Asian Pacific countries.
Indicative Reading
Textbook(s)
Arnold, B.J. and M.J. Mclntyre, International Tax Primer, latest edition, The Hague: The
Netherlands, Kluwer Law International.
Smith, D.G. and A. Macpherson, Hong Kong Taxation: Law and Practice, latest edition,
Hong Kong, The Chinese University Press.
Ordinance(s)
Inland Revenue Ordinance (Chapter 112) and Inland Revenue Rules, Revised Edition and
Amendments, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Government.
Stamp Duty Ordinance (Chapter 117), Revised Edition and Amendments, Hong Kong
Special Administrative Region Government.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
105
Subject Code
:
AF4222
Subject Title
:
China Tax Framework
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
Financial Accounting (AF2108) OR equivalent
Exclusion
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(Grade D)
Final Examination
(Grade D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
42 hours
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA (Hons) Outcomes by enabling
students to communicate effectively in both verbal and written English (Outcomes 1 and 2),
demonstrate a global outlook and an understanding of cultural diversity (Outcome 3), identify
planning mechanisms of creative thinking (Outcome 4) and apply established tax principles
and practices to analyze business situations and problems (Outcome 7) for making their
business operation and investment decisions in the specific business setting of the mainland
China. In addition, students are able to work effectively with other classmates upon selfappraisal and reflective thinking in the teamwork assignments (Outcome 8).
LEARNING OUTCOMES
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
analyze various tax scenarios and prepare tax computations for individual and foreigninvested entities operating business in the mainland China
•
evaluate the tax consequences of various types of structure of business transactions and
provide professional advices on the China tax system and its operation as well as tax
implications on individuals and business entities.
•
formulate and carry out basic China tax planning ideas and strategies in relation to
individual and business transactions in order to minimize their explicit tax liabilities or
enhance their tax efficiency and effectiveness.
INDICATIVE TEACHING / LEARNING APPROACH
The three hours of seminar per week will be used flexibly by the lecturer for discussing key
concepts, techniques and their applications with students and carrying out other learning
activities with them. To maximize benefits, students are encouraged to share their views
and experiences actively with their lecturers and other classmates.
INDICATIVE ASSESSMENT TASKS
Group Presentation, Group Critique Reports on other classmates’ presentation and an
Individual Case Study will help students to think critically and creatively (Outcome 4), and to
analyze business situations (Outcome 7). Effective communication (Outcomes 1 and 2),
global outlook (Outcome 3) and teamwork (Outcome 8) will be assessed against rubrics in
the Group Presentation, Group Critique Reports and Individual Case Study.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
106
INDICATIVE CONTENT / OUTLINE SYLLABUS
Overview of PRC Taxation System and Tax Administration
Forms of business establishment in China. Current tax structure and types of tax. Structure
of PRC tax laws and regulations. Structure of PRC tax administrative system. Tax
collection and administration law and implementing rules.
Corporate Income Tax and Tax Incentives
Forms of business presence of foreign investment in China. Scope of charge – foreign
invested enterprises and domestic enterprises. Assessment and exemptions. Applicable
tax rates. Preferential tax treatments. Tax incentives – location and industry. Tax holidays.
Reforms of corporate income taxes. Special tax adjustments.
Individual Income Tax
Scope of charge. Types of income. Non-taxable benefits. Deductions. Applicable tax rates.
Tax reforms.
Turnover Tax System
Scope of taxation – value added tax, business tax and consumption tax. Exemption and
reliefs. Determination of taxable amount. Calculation of tax liabilities. Applicable tax rates.
Turnover tax administration. Tax refunds on export. Tax reforms.
Transfer Pricing Rules
Transfer pricing audits. Rules and regulations. Target transactions and target enterprises.
Audit adjustments and methods.
Contemporaneous documentation. Corresponding
adjustments. Defense pricing strategy. Recent developments.
Double Taxation Arrangement
Application of Memorandum of Understanding between the Mainland China and the HKSAR
for the Avoidance of Double Taxation.
Comprehensive agreement and protocols.
Implementation issues.
Other Types of Taxes and Issues
Land value appreciation tax. Real estate tax. Urban land and house tax. Vehicle and
vessel license tax. Stamp tax. Deed tax. Motor vehicle acquisition tax. Resource tax. New
proposed taxes and their feasibility – fuel tax, social security tax, share transaction tax and
estate duty.
Other Special Forms of Investment
Representative offices. Contract manufacturing vs. import processing. Chinese holding
companies. Investment headquarters. Investments in free trade zones and bonded areas.
Export processing zones.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
107
Strategic Tax Planning
Tax minimization and tax avoidance. Tax audits and penalty. Tradeoff between tax factors
and non-tax factors. Planning opportunities for expatriates. Planning opportunities for
foreign invested enterprises. Anti-treaty shopping.
INDICATIVE READING
Textbook(s)
Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu, China Master Tax Guide, latest edition, Singapore, CCH Asia
Pte Limited
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
108
Subject Code
:
AF4223
Subject Title
:
Analysis and Design of Accounting Information Systems
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
Accounting Information Systems (AF3211) and
42 hours
Information Technology for Business (MM2421)
Assessment
Minimum Pass Grade
:
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Outcomes by enabling students to
use and evaluate information technology effectively (Outcome 6). It also requires students to
analyze business situations and problems by applying conceptual frameworks drawn from
the subject (Outcome 7). It helps accounting students master the techniques of analysis,
design, development and management of accounting systems, and get sufficient
professionally-specific skills and knowledge to make an immediate contribution to their future
employers (Outcome 13).
Learning Outcomes
On successful completion of this subject, the student will be able to:
•
Explain the roles of an accountant in a systems development project;
•
Analyze the strengths and weaknesses of the systems development approaches and
methodologies used by the systems personnel;
•
Design the interface and database of accounting systems; and
•
Communicate effectively and efficiently with systems professionals and business users
in relation to systems development.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
Seminars are used to discuss the key concepts and issues related to the topics listed in
INDICATIVE CONTENT. These may be supplemented by assignments, small projects, and
a mid-term test when appropriate. Students are required to learn how to use the relevant
software, e.g. ACCESS, in developing accounting systems.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Assessment components include projects, assignments, midterm test and final examination.
These assessment components require students to demonstrate their ability to use and
evaluate information technology effectively (Outcome 6), to analyze business situations and
problems by applying conceptual frameworks drawn from the subject (Outcome 7), and to
apply professionally-specific skills and knowledge in business cases (Outcome 13).
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
109
Subject Code
:
AF4224
Subject Title
:
Information Systems Audit and Control
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisite
:
Accounting Information Systems (AF3211)
Co-requisite
:
None
Exclusion
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework *
50%
Final Examination
50%
42 hours
* Hands on experience of using a commercial audit
software system will be provided if possible.
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Coursework
(Grade D)
Final Examination
(Grade D)
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA (Hons) Outcomes by enabling
students to apply the concepts/techniques of auditing information systems (IS) and
information technologies (IT) (Outcomes 6 and 13), analyze the use of IT in financial auditing
(Outcomes 6 and 13), and demonstrate creative thinking (Outcome 4).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
apply the concepts and techniques of IT audit in organizations
apply the appropriate IT audit tools in financial auditing
analyze the current development of IT and its impact on various security and control
issues
Indicative Teaching / Learning Approach
Lectures will introduce the various concepts and techniques of IT audit. A commercial audit
software system will be used to demonstrate the use of IT in financial auditing.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Programme Outcomes 4, 6 and 13, and the three Learning Outcomes listed above will be
assessed by means of a group presentation, an individual assignment, and a test. The
group presentation and its question-and-answer session will also be used to assess the
creative thinking of the students (Programme Outcome 4).
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
110
Indicative Content / Outline Syllabus
IT Audit Management
Need for control and audit of information systems. Types and consequences of computer
abuse. Impact of IT auditing on organizations. Effects of computers on internal controls.
Information security policy. Staffing the IT audit function.
Conducting IT Audits
Nature of controls. Analyzing risks and controls. Dealing with complexity. Audit risks.
Major steps in an IT audit. Audit-around-the-computer approach. Audit-through-thecomputer approach.
Auditing Systems Development
Waterfall and prototyping models. Pre-implementation audit of systems development.
Auditing Application Systems
Boundary controls. Input controls. Database controls. Output controls.
Using IT in Auditing
Motivations for audit software. Typical system functions of audit software. Major audit tasks
using audit software. Limitations of audit software.
Contingency Planning and Disaster Recovery
Types of IT asset. Securing IT assets. Analysis of exposures. IT threats. Disaster recovery
plan.
Computer Fraud and Abuse
Overview of computer abuse. Prosecution of computer abuse.
Prevention and detection of computer abuse.
Perpetrator’s style.
Indicative Reading
J.A. Hall and T. Singleton, Information Technology Auditing and Assurance (2nd edition),
Thomson / South-Western, 2005 (prescribed textbook).
R. Weber, Information Systems Control and Audit, Prentice Hall, 1999 (or the latest edition)
(prescribed textbook).
R. Cascarino, Auditor’s Guide to Information Systems Auditing, Wiley, 2007.
J. Champlain, Practical IT auditing (2nd edition), Warren, Gorham and Lamont, 2004.
F. Gallegos, S. Senft, D.P. Manson, and C. Gonzales, Information Technology Control and
Audit (2nd edition), Auerbach, 2004.
J.J. Champlain, Auditing Information Systems (2nd edition), Wiley, 2003.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
111
Indicative Content
Overview of Accounting Information Systems
Files versus databases; different business cycles; data processing; role of accountants in
accounting information systems
Project Management
Initiating, planning, executing, and closing down the project; representing and scheduling
project plans
Systems Development Approaches
Systems development life cycle (SDLC); waterfall model; rapid prototyping
Requirements Analysis and Specification for Accounting Systems
Process of determining and structuring requirements; traditional and modern methods for
requirements determination
Structural Analysis and Design for Business and Accounting Processes
Identifying business and accounting processes for reengineering; process modeling;
conceptual data modeling; alternative design strategies; human interface design
Database Modeling & Design
Relational database model; entity-relationship (E-R) diagram; functional dependencies and
primary keys; database normalization
Systems Implementation
Concepts of systems implementation; testing and operation; systems documentation; user
training and support. (Extensive programming knowledge is not required for this subject)
Indicative Reading
Valacich, J.S., Essentials of Systems Analysis and Design, Latest Edition, Pearson, Upper
Saddle River, NJ. (Textbook)
Kendall, K.E. and J.E. Kendall, Systems Analysis and Design, 6th Edition, Prentice Hall,
Upper Saddle River, NJ, 2005.
Perry, J.T. and G.P. Schneider, Building Accounting Systems Using ACCESS 2000, 4th
Edition, South-Western, 2001.
Begg, C. and T. Connolly, Database Systems: A Practical Approach to Design,
Implementation, and Management, 3rd Edition, Addison Wesley, Reading, MA, 2001.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
112
Subject Code
:
AF4300
Subject Title
:
Introduction to Derivative Securities
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
Introduction to Finance (AF3308)
Assessment
:
Continuous Assessment
50%
Mid-term Examination
35%
Presentation, Participation
15%
Final Examination
50%
Continuous Assessment
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
42 hours
ROLE AND PURPOSE
The objective of the subject is to introduce students to the theory and practice of derivative
securities.
LEARNING OUTCOMES
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
Understand the issues in pricing, hedging, and arbitrage in the derivative securities
markets.
Familiarise with various derivative products, including exotic over-the-counter
derivatives.
Able to apply various trading and hedging strategies in real life situations to
enhance portfolio returns.
INDICATIVE CONTENT
Introduction
What derivatives are and their economic role. The organisation of derivatives markets and
how derivatives are traded. Recent development of derivatives in Hong Kong will be
discussed.
Options
The structure of options markets. Principles of option pricing. Option pricing models. Basic
option strategies. Advanced option strategies.
Futures and Forwards
The structure of forward and futures markets. Principles of spot pricing. Principles of
forward and futures pricing. Futures hedging strategies. Advanced futures strategies.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
113
TEACHING/LEARNING APPROACH
Lectures are given on the topics of the syllabus. The three hours per week will be used
flexibly for discussing key concepts and their applications with students and carrying out
other learning activities with them. To maximize benefits, students are encouraged to share
their views and experiences actively with their lecturers and other classmates. Seminars
provide students with the opportunity to strengthen their understanding of the concepts
taught in lectures and to apply the theories to the real-life situations. The activities in
seminars include student presentations and discussions of problem sets and case studies
(to develop students’ critical thinking, analytical skills, teamwork, and oral and written
communication skills).
INDICATIVE READING
Essential Readings
Don Chance, An Introduction to Derivatives & Risk Management, 6th Edition, SouthWestern, 2004.
Supplementary Readings
Hull, John, Fundamentals of Futures, Options Markets, 4th Edition, Prentice Hall, 2002.
An Introduction to Derivatives, John Wiley, 1999.
Mastering Finance, FT Pitman, 1998.
Journals
Journal of Future Markets
Journal of Derivatives
Derivatives Quarterly
Review of Derivatives Research
Financial Analysts Journal
SUBJECT CO-ORDINATOR
CHUNG Alan
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
114
Subject Code
:
AF4306
Subject Title
:
International Finance
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
Introduction to Finance (AF3308)
Assessment
:
Coursework
45%
Final Examination
55%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
42 hours
ROLE AND PURPOSE
This module builds on the basic principles of finance and put them under an international
context. The aim is to introduce students to various international financial markets and
instruments, and examine their implications for financial management.
LEARNING OUTCOMES
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
•
•
Understand the functions and characteristics of various markets and instruments in
international finance;
Understand how different exchange rate systems (especially Hong Kong’s currency
board system) function;
Appreciate the sources of risks in international transactions;
Manage and hedge those risks;
Understand how the international debt and equity markets can be utilized by companies
and investors.
INDICATIVE CONTENT
Introduction
Characteristics
management.
of
multinational
corporations.
Features
of
multinational
financial
The Foreign Exchange Market
Exchange rate defined. Spot and forward markets. Interest rate parity relationships.
Exchange Rate Systems
Fixed vs. Floating exchange rates. How to maintain a fixed exchange rate? Pros and cons of
fixed exchange rates. How does Hong Kong’s currency board work?
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
115
Exchange Rate Determination
Using the interest rate parity relationship. Purchasing Power Parity considerations. Current
account considerations. Fundamental approach. Technical approach. Forecasting
performance of professional forecasters.
Foreign Exchange Risk Management
The Instruments: Foreign exchange futures and options. Transaction exposure. Economic
exposure. Long-term interest rate and currency risk management. The use of swaps.
International Financial Markets: The Manager’s Perspective
International capital structure and the cost of capital. International corporate governance.
International Financial Markets: The Investor’s Perspective
International portfolio investments. The benefits of international diversification. The effects of
exchange rate movements. Home bias in portfolio holdings.
International Capital Budgeting
The NPV and the real options approaches
Multinational Cash Management
Transfer pricing
TEACHING/LEARNING APPROACH
The three hours per week will be used flexibly by the instructor for discussing key concepts
and their applications with students and carrying out other learning activities with them. To
maximize benefits, students are encouraged to share their views and experiences actively
with their instructors and other classmates.
INDICATIVE READING
Bodie, Z., A. Kane and A.J. Marcus, Essentials of Investments, 6th Edition, McGraw-Hill,
2007.
Eun, C.S. and B.G. Resnick, International Financial Management, 4th Edition, McGraw-Hill,
2007.
Eiteman, D.K., A.I. Stonehill and M.H. Moffet, Multinational Business Finance, 11th Edition,
Addison Wesley, 2007.
Shapiro, A.C., Multinational Financial Management, 8th Edition, Wiley, 2006.
SUBJECT CO-ORDINATOR
CHUE Timothy K.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
116
Subject Code
:
AF4314
Subject Title
:
Company Valuation and Analysis
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminar
Pre-requisites
:
Intermediate Accounting 2 (AF3111) OR
42 hours
Corporate Accounting 2 (AF3106) AND
Business Finance (AF3313) OR
Introduction to Finance (AF3308)
Assessment
Minimum Pass Grade
:
:
Coursework
60%
Final Examination
40%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
ROLE AND PURPOSE
This course is about how to use financial information – particularly firms’ financial statements
– to value and to analyze firms. The primary focus is on Company or Business Valuation
using different Valuation Techniques. It is designed for accountancy students who wish to
qualify as a professional user of financial statements at an entry level.
LEARNING OUTCOMES
By the end of the course, students should be able to:
•
•
•
•
•
Understand the relationship between accounting/financial statements and company
valuation;
Analyze accounting and financial statements in the context of strategies adopted by a
company;
Apply analysis to make forecasts and review a range of valuation techniques that are
available;
Choose appropriate valuation models in specific decision contexts like securities
analysis, credit assessment and acquisition and merger and
Value a business and present to appropriate readers/audiences in effective manners.
INDICATIVE CONTENT
Valuation Models
Methods of Fundamental Analysis, Discounted Cash-flow Analysis, Accounting-based
Valuation, Use of multiples
Analysis of Information for making forecasts
Diagnosing accounting quality and red flags, Analysis of Shareholders’ Equity, Profitability,
Sustainable growth and Value generation, Risk and the Cost of Capital
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
117
Forecasting and Valuation
Analysis of strategy, Forecasting earnings and cash flows, Choice of Valuation Models
TEACHING/LEARNING APPROACH
The three hours per week will be used flexibly by the instructor for discussing key concepts
and carrying out exercises and case assignments with students. Heavy emphasis is placed
on the students’ oral and written communication skills. Active participation is expected from
every student. To maximize benefits, students are requested to read the assigned textbook
chapter(s), do exercises and cases before they come to the seminar.
INDICATIVE READING
Prescribed Text
Wild, Subramanyam and Hasley, Financial Statement Analysis, 9th Edition, McGraw Hill,
2007.
Palepu, Bernard and Healy, Business Analysis and Valuation: Using Financial Statements,
3rd Edition, Thomson South-Western, 2004.
Supplementary Text
Penman, Stephen H., Financial Statement Analysis & Security Valuation, International
Edition, McGraw Hill, 2007.
Aswath Damodarn, Investment Valuation: Tools and Techniques for Determining the Value
of Any Asset, 2nd Edition, John Wiley & Sons, 2002.
SUBJECT CO-ORDINATOR
LAI Karen
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
118
Subject Code
:
AF4317
Subject Title
:
Derivative Securities
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
AF3313 Business Finance
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
42 hours
Role and Purpose
The subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA outcomes by enabling students to
think critically in the application of the uses derivatives markets and the underlying operation
of financial markets (Outcome 9) and to identify and resolve the ethical issues as they arise
in the context of derivatives (Outcome 5).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
Evaluate the issues in pricing, hedging, and arbitrage in the derivative securities
markets.
•
Evaluate the price determination of derivatives and derive the price of derivatives by
using different models
•
Apply various trading and hedging strategies in real life situations to enhance
portfolio returns
•
Evaluate the real-life situations in which financial derivatives resulted in success or
failure while exploring everyday uses of financial derivatives
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
In the first part of each class, the lecturer will provide students with a structured lecture on
the underlying concepts and their applications and highlight the importance of each topical
area exemplified with real-world situations. Students are required to participate in discussion
in the lectures, and undertake guided reading, which will form the basis for student
presentations in the later part of each class.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Presentations, independent essay and case analyses will require students to apply concepts
(Outcome 9) and to demonstrate the application and techniques of the uses of derivative
markets. Problem sets, mid-term test, project/essay, and the final examination will assess
their ability to evaluate the concepts, strategies, theories, techniques and the ethical issues
covered in this subject (Outcome 5).
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
119
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Introduction
What derivatives are and their economic role. The organisation of derivatives markets and
how derivatives are traded. Recent development of derivatives in Hong Kong will be
discussed.
Options
The structure of options markets. Principles of option pricing. Option pricing models. Basic
option strategies. Advanced option strategies.
Futures and Forwards
The structure of forward and futures markets. Principles of spot pricing. Principles of
forward and futures pricing. Futures hedging strategies. Advanced futures strategies.
Management Risk in Corporations
Risk management function in a company. Avoiding derivatives losses.
Indicative Readings
Essential Readings
Don Chance and Robert Brooks, An Introduction to Derivatives & Risk Management, 7th
Edition, South-Western, 2008.
Supplementary Readings
John Hull, Fundamentals of Futures, Options Markets, 5th Edition, Prentice Hall, 2004.
John Marthinsen, Risk Takers: Uses and Abuses of Financial Derivatives, Pearson
Addison Wesley, 2005.
Journals
Journal of Future Markets
Derivatives Quarterly
Review of Derivatives Research
Financial Analysts Journal
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
120
Subject Code
:
AF4318
Subject Title
:
Financial System in China
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Seminars
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA in Financial Services Programme
Outcomes by enabling students to enhance their global outlook (Outcome 3) through studies
on the internationalization of the Chinese financial sector. It also applies finance and
economics (Outcome 9) to analyze the operations of Chinese financial markets and
institutions.
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
Compare the institutional arrangements of financial markets and institutions in China with
those in developed financial sectors
Identify and evaluate the problems underlying the operations of financial institutions and
markets in China
Assess the prospects for the internationalization of the China’s financial system.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
Basic theories and the institutional arrangements of the Chinese financial sector will be
covered in lectures. Students will be split into small groups with each delivering a
presentation on pre-set questions on each topic. They will be required to participate in
discussions.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Discussions, quizzes can allow students to evaluate the development of the Chinese
financial sector with an international perspective (Outcome 3). The presentation and report
will require students to apply the economics and finance theories to analyze the operations
of the Chinese financial sector (Outcome 9).
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Financial Institutions and Markets
Commercial banks, insurance firms, and other non-bank financial institutions, money
markets, bond markets and stock markets, foreign exchange markets
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
121
Efficiency of the Chinese Financial Sector
Administrative versus economic controls, interest rate control, foreign exchange control,
state ownership of financial institutions
Problems of Monetary Control
Inadequate financial regulations and rules, limitations of monetary policy tools, exchange
rate stability and growth
Internationalization of the PRC Financial System
Foreign financial institutions in Mainland, outward investment of Chinese financial institutions
Role of Hong Kong
Issues of H shares and Rmb bonds, Hong Kong and Shanghai as an international financial
centre
Indicative Reading
Neoh, A., Toward Sound Capital Market in China. Beijing University Press, 2001.
Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). 2002. China in the
world economy the domestic policy challenges. OECD, Paris. [Electronic source]
The Economists Intelligence Unit (EIU). 2008. China Hand – The complete guide to doing
business in China. Chapter 2: Trade (February 2008); Chapter 3: Finance (March 2008);
Chapter 4: Investing (April 2008); and Chapter 5: Investing location (May 2008) EIU. [Electronic
source]
Journals
Almanac of China’s Finance and Banking
Year book of China’s Insurance
The China Quarterly
China Information
Journal of Contemporary China
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
122
Subject Code
:
AF4320
Subject Title
:
Corporate Finance
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
Business Finance (AF3313)
Assessment
:
Coursework
40%
Final Examination
60%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
42 hours
Role and Purpose
This subject builds on the AF3313 Business Finance and covers some advanced topics of
corporate finance. This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Outcomes by
enabling students to apply basic financial theories, analyze financial reports and understand
the operations of financial markets (Outcome 9) and identify ethical issues as they arise
(Outcome 5) and communicate in English effectively (Outcome 1 and Outcome 2).
Learning Outcomes
On completion of this subject, students should be able to:
z
z
z
Identify the major responsibilities of financial managers;
Apply financial theories to maximize firm value or shareholders’ wealth
Identify ethical issues of corporate finance.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
The seminars mainly cover the key concepts and theories in Corporate Finance. Students
have opportunities to present the applications of financial theories.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
A variety of assessment tools, including written assignments, presentations, midterm test
and final examination will be used. In-class presentations show whether students can apply
the basic financial theories (Outcome 9) and present in English effectively (Outcome 1).
Written assignments are designed to test whether students can identify the ethical issues of
corporate finance (Outcome 5) and communicate in written English effectively (Outcome 2).
The midterm test and final examination test whether students are able to apply the basic
financial theories, analyze financial reports and understand the operations of financial
markets (Outcome 9) and communicate in written English effectively (Outcome 2).
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Corporate Governance
Corporate goal. Agency problem and Control of the Corporation.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
123
Fisher Separation Theorem
Consumption decisions and utility theory. Capital markets and production opportunities.
Implications of Fisher Separation Theorem.
Efficient Market Hypothesis
Three forms of efficiency. Implications for corporate finance. Market Anomalies and empirical
challenges.
Long-term Financing in Hong Kong Capital Market
Different types of equity and debt securities. Alternative equity and debt Issue methods.
Cash and Rights offerings. Bond refunding
Capital Structure
Theories of capital structure. MM propositions. Taxes, Costs of Financial distress. Agency
costs of equity. Agency costs of debt.
Valuation and Capital Budgeting for the Levered Firms
Adjusted Present Value approach, Flow-to-Equity approach, Weighted Average Cost of
Capital (WACC) approach.
Dividend Policy
Dividends and stock repurchases. Stock dividends and stock splits. Theories of dividend
policy. Dividend policies in practice.
Options
Option Basics. Put-call parity, Option Pricing. Stocks and Bonds as options.
Mergers and Corporate Restructuring
Motives for mergers. Financial analysis for mergers. Defence tactics.
Indicative Reading
Ross, Westfield, Jaffe and Jordan, Modern Financial Management, 8th Edition, McGraw-Hill.
McGuinness, P.B., A Guide to the Equity Markets of Hong Kong, Oxford University Press,
1999.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
124
Subject Code
:
AF4321
Subject Title
:
Case Study in Finance
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
Business Finance (AF3313) and
42 hours
Corporate Finance (AF4320)
Assessment
Minimum Pass Grade
:
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Role and Purpose
This subject provides a platform for students to integrate financial and business analysis
skills and apply them systematically in solving multifaceted case problems. It contributes to
the achievement of the BBA(Hons) Outcomes by enabling students to apply the theories and
principles in finance to solve finance-oriented cases problems (Outcome 9), exercise critical
and creative thinking in analyzing multifaceted business problems from the perspective of
finance, accounting, economics and management to generate sound financial strategies to
address them (Outcome 7), communicate the analysis and recommendations effectively
(Outcome 1).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing the subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
Integrate and expand upon the concepts they have learnt in earlier courses, such as
business strategy, management, business law, accounting, investment banking etc.
Identify the prioritize business and finance issues from complex business cases and
address them in a systematic manner.
Apply appropriate finance principles and business analysis techniques in analyzing
complex case problems.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
Key concepts and issues will be introduced through lectures. Case discussions will be used
extensively throughout this course to enable students to stimulate critical thinking and to
integrate the concepts which they have learned in prior finance, accounting, economics and
management courses in solving case problems.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Individual participation on case discussions requires students to demonstrate their ability to
apply finance theories and business knowledge (Outcome 9), to think critically and creatively
(Outcomes 7), and to communicate their analysis and the recommended course of action
effectively (Outcome 1). The group case write-up and presentation, along with the final
exam case report and further reinforce these learning objectives.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
125
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Introduction to the Course
Financial Analysis Basics
Optimal Capital Structure
Cost of Capital Concepts
Valuation and Capital Budgeting
Payout Policy
Dividends. Share repurchases. Leverage. Signalling and valuation.
Derivative Instruments and Risk Management
Financing Decisions and Tactics: Convertibles
Initial Public Offering (IPO)
Hostile Takeovers
Valuing Projects
Indicative Reading
Bruner, Case Studies in Finance, 5th Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2007.
Ross, Westerfield, Jaffe and Jordon, Modern Financial Management, 8th Edition, McGrawHill, 2008.
Donald H. Chew, Jr., The New Corporate Finance: Where Theory Meets Practice, 3rd
Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2001.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
126
Subject Code
:
AF4322
Subject Title
:
Management of Financial Institutions
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Seminars
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
Business Finance (AF3313)
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(Grade D)
Final Examination
(Grade D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Outcomes by enabling students to
analyze the management of assets and liabilities of financial institutions by applying
concepts from Accounting, Finance, Economics, Law and Quantitative methods (Outcome
7), critically assess the performance of financial institutions by applying theories in finance,
financial markets and financial reporting (Outcome 9), identify and analyze various sources
of risks in financial intermediation in implementing strategies across all types of financial
institutions (Outcome 12). It also requires students to communicate effectively in English
either in individual report writing or group presentation (Outcome 2).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
•
•
critically assess the specialness and the roles of financial institutions;
evaluate the impact of different regulatory and ethical issues on the management of
financial institutions;
apply appropriate tools to assess financial institutions performance;
identify the various sources of risks in financial intermediation and the methods for
measuring and managing such risks.
identify and evaluate the different strategies of assets and liabilities management of
financial institutions.
Indicative Teaching / Learning Approach
Lectures will be used to discuss concepts and issues arising in respect of the management
of financial institutions. Case studies and / or mini projects will be used in seminars to
reinforce students’ learning by illustrating that techniques discussed in lectures have
application to real-life problems. Students will be asked to analyze and provide solutions to
cases / projects which should reflect understanding and ability of applying the knowledge
covered in this subject.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
127
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Seminar presentation of discussion questions will help students to apply concepts (Outcome
7), mini projects / case studies will require students to critically assess the performance of
financial institutions (Outcome 9) and identify and analyze the risks involved in the
management of financial institutions (Outcome 12). Group seminar presentation, individual
report and the final examination will require students to communicate effectively in English.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
128
Subject Code
:
AF4323
Subject Title
:
International Finance
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
AF 3313 Business Finance
Co-requisites
:
None
Exclusion
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
45 %
Final Examination
55 %
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
42 hours
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Programme Outcomes by:
developing students’ ability to analyze aspects of the global business environment (Outcome
12) and to apply their understanding of financial theories and markets (Outcome 9) in
making international financial management decisions.
Learning Outcomes
On completion of this subject, students will be able to:
1. Understand the structure and characteristics of various international financial markets
and instruments;
2. Understand how different exchange rate systems (especially Hong Kong’s currency
board system) function and how they affect an economy’s business environment;
3. Identify the sources of risks in international transactions and understand how these
risks can be managed;
4. Identify and analyze the international dimensions of the debt and equity markets, and
understand their implications for a company’s financing decisions and investment
policies.
These four Subject Learning Outcomes all contribute to the BBA Programme Outcomes 9
and 12 as discussed above.
Indicative Teaching/ Learning Approach
In the first part of most classes, the instructor will provide students with a lecture on the
underlying concepts and their application in practical settings. Students will be required to
participate in the lectures and class discussions, to solve analytical problems and case
studies, to make presentations, and to submit written reports.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
129
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Students will be required to solve problems that test their understanding of how exchange
rates are determined, the relationship between exchange rates and interest rates, the
characteristics of international financial instruments, the impact of different exchange rate
systems on the business and economic environment, and of what the sources of risks are in
international financial transactions. There will also be cases and problems that test if
students can make use of financial instruments and/or operational hedges to manage risks
in international financial transactions, and understand the implications of the international
nature of the debt and equity markets for corporate financial decisions. These problems and
cases will test students’ ability to apply concepts (Outcome 9) and test if students possess
the global outlook (Outcome 12) to appreciate the financial linkages between international
economies, how various international financial markets can be utilized from a corporate
financial perspective, and how the risks that arise from international transactions can be
effectively managed.
Indicative Content
The Foreign Exchange Market
Exchange rate defined. Spot and forward markets. Interest rate parity relationships.
Exchange Rate Systems
Fixed vs. Floating exchange rates. How a fixed exchange rate is maintained? Pros and cons
of fixed exchange rates. How does Hong Kong’s currency board work?
Exchange Rate Determination
Using the interest rate parity relationship. Purchasing Power Parity considerations. Current
account considerations. Fundamental approach. Technical approach. Forecasting
performance of professional forecasters.
Foreign Exchange Risk Management
The Instruments: Foreign exchange futures and options. Transaction exposure. Economic
exposure. Long-term interest rate and currency risk management. The use of swaps.
International Financial Markets: The Manager’s Perspective
International capital structure and the cost of capital. International corporate governance.
International Financial Markets: The Investor’s Perspective
International portfolio investments. The benefits of international diversification. The effects of
exchange rate movements. Home bias in portfolio holdings.
Indicative Reading
Eun, C.S. and B.G. Resnick, International Financial Management, 4th Edition, McGrawHill, 2007.
Bekaert, G. and R.J. Hodrick, International Financial Management, 1st Edition, Pearson
Prentice Hall, 2009.
Bodie, Z., A. Kane, and A.J. Marcus, Essentials of Investments, 6th Edition, McGraw-Hill,
2007.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
130
Indicative Content / Outline Syllabus
Specialness and Roles of Financial Institutions
Differences between of financial institutions and non-financial firms. Social, economic,
financial, technological, and demographic forces affecting the financial services industry.
Performance Assessment of Financial Institutions
Financial statements analysis. CAMEL model. Du Pont analysis of ROE.
Risk Measurement & Management
Risks of financial intermediation. Risk measurement models. Risk management techniques.
Assets & Liabilities Management of Financial Institutions
Assets management. Liabilities and liquidity management.
adequacy. The Basel II.
Deposit insurance.
Capital
Strategic Planning and Management
Strategic planning process. Product & geographic diversification. Economies of scale and
scope. Merger and acquisition.
Indicative Reading
Textbooks
Saunders, A. & Cornett, M.M. (2008) Financial Institutions Management – a Risk
Management approach, 6/e, McGraw Hill.
Rose, P.S. and Hudgins, S.C. (2008) Bank Management & Financial Services, 7/e, McGraw
Hill.
Gardner, M.J., Mills, D.L. and Cooperman, E.S. (2005) Managing Financial Institutions, 5/e,
Thomson South-Western.
References
Annual reports of various financial institutions.
Articles from US Federal Reserve, Bank for International Settlement, Hong Kong Monetary
Authority, and various newspapers such as Financial Times.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
131
Subject Code
:
AF4324
Subject Title
:
Financial Planning
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Seminars
14 hours
Assessment
:
Continuous Assessment 50%
Final Examination
Minimum Pass Grade
:
50%
Continuous Assessment (D)
Final Examination
(D)
Role and Purpose
This is an introductory course on financial planning and a course that has been recognized
by the Institute of Financial Planners of Hong Kong (IFPHK) as a substitute for Module One
in its education program (i.e., those who have passed this course will not be required to take
Module One of the education program for Certified Financial Planners).
It contributes to the achievement of BBA Programme Outcomes by enabling students to
understand, analyze and apply the elements and steps relevant in practicing financial
planning services. This module will set the background of financial planning for students and
equip them with the essential knowledge and skills to perform financial planning services for
clients. Topics including the major steps of financial planning, job knowledge requirement of
CFPCM and the latest financial planning tools and techniques will be covered.
Learning Outcomes
After successfully completing this module, students should be able to:
z
z
z
z
z
z
Identify and resolve ethical issues relevant in the context of financial planning, by
complying with Code of Ethics (Outcome 5);
Identify roles of regulators and scopes of regulations that govern the financial services
industry, and interpret regulations of financial markets of Hong Kong;
Analyze real-life situations and problems encountered by financial planners by applying
conceptual frameworks drawn from the different context areas such as investment
planning and estate planning areas (Outcome 7);
Carry out and act upon self-appraisal and reflective thinking in the areas of teamwork,
leadership and career selection to equip students with the skills and knowledge
(Outcome 8) for continuous development;
Apply the essential concepts in investment planning, insurance planning, risk
management, retirement planning, estate planning, and tax planning;
Apply the six-step financial planning approach to construct a financial plan in the
different personal planning areas, and analyze the means by which value is created in
delivery process of financial planning services (Outcome 8);
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
Lectures will be used to provide theoretical concepts. During seminar sessions, students
would be asked to discuss and solve real-life issues related to the topics.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
132
Subject Code
:
AF4325
Subject Title
:
Wealth Management
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Seminars
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
Any ONE of the finance theory related subjects (AF3313
Business Finance, AF3314-Financial Institutions and
Markets, AF3316-Investments, AF4320-Corporate
Finance, AF4324 Financial Planning)
Assessment
Minimum Pass Grade
:
:
Coursework
50%
Examination (3-hour unseen examination)
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
ROLE AND PURPOSE
This subject examines the basic principles and skills for wealth management. It covers all
the important concepts for a financial planner and a wealth manager on managing the
financial wealth for individual clients. After completing this subject, the student is expected to
master wealth management knowledge, understand risk profile of Asian clients, understand
effective ways to communicate with clients, and integrate economics, accounting and
finance concepts in preparing the wealth management report.
LEARNING OUTCOMES
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
z
Comprehend the principles of wealth management in relation to Economics,
Accounting, and Finance (BBA Outcome 7)
z
Understand the comprehensive view of wealth management
z
Adopt a six-step financial planning evaluation process in wealth management (BBA
Outcome 9)
z
Apply risk profiling in the context of Asian culture (BBA Outcome 3)
z
Understand various aspects of asset allocation strategies
z
Develop all-roundedness skills by integrating interpersonal skills, communication skills,
and subject knowledge (BBA Outcome 2)
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
133
INDICATIVE CONTENT
General Overview
z
z
z
z
z
An Overview of Financial Planning and Wealth Management Profession
Basic Concepts, Professional Ethics and Practice Standards
Step 2 –Determining Client Goals and Expectations and Gathering Client Data
Step 3 – Determining Client’s Current Financial Status
Step 4 –Developing and Presenting the Financial Plan
Wealth Management
z
z
z
z
Profiling and Life-cycle Analysis
Investment Techniques (Part I)
Investment Techniques (Part II)
Asset Allocation Strategies
Advanced Topics and Conclusion
z
z
Total Wealth Index
Cases, Application and Conclusion
INDICATIVE TEACHING/LEARNING APPROACH
In addition to classroom discussion and exam evaluation, a research project and individual
assignments are designed to educate and evaluate students.
Research project:
The students are required to form groups to conduct a case study on risk profiling (BBA
Outcome 3) and portfolio allocation for high net worth clients. Both qualitative and
quantitative analyses are expected (BBA Outcome 7). A comprehensive financial planning
approach with emphasis on investment planning is required (BBA Outcome 9). Section 1:
Group report of 12-15 pages and a presentation are expected. Section 2: Individual report of
3 pages (300 – 400 words) (BBA Outcome 2)
Individual assignment:
You are required to conduct a case analysis on financial planning and wealth management.
The case report should include the 6-step financial planning analysis using personal profiling
(BBA Outcome 7) and some basic quantitative analysis on investment for goals.
INDICATIVE READING
Recommended Textbook
Cheng, Louis, Leung, Tak Yan, and Wong, Yiu Hing, Financial Planning and Wealth
Management: An International Perspective, McGraw-Hill, 2009
References
1) Harold R. Evensky, Wealth Management: The Financial Advisor's Guide to Investing and
Managing Your Client's Assets, McGraw-Hill, 1996
2) Ross Levin, The Wealth Management Index: The Financial Advisor's System for
Assessing & Managing Your Client's Plans & Goals, McGraw-Hill, 1996
STAFF RESPONSIBLE
Louis Cheng
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
134
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Coursework, including the project, will help students to apply concepts, and think critically
and creatively (Outcome 4 & 7). Effective communication (Outcome 1& 2) will be assessed
in the group project.
Discussions and presentations are carried out in groups and the ability to work with others
(Outcome 8) is assessed through a form of Evaluation of Group Performance.
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Fundamental Concepts of Financial Planning
The financial planning areas and the roles of financial planners
Overview of the Financial Planning Market
Ethical Financial Planning Practice
Practicing Ethics and Professional Responsibilities
Application of Time Value of Money concepts in financial planning
Basic concepts and applications in real-life examples
Regulatory Framework of the Financial Services Industry
Hong Kong Regulations Related to Financial Planning
The Planning Components and Life Cycle Analysis
The Concept of Life-Cycle Analysis
Short-term and Medium Term Investment Planning
Risk Management and Insurance Planning
Retirement Planning, and Tax Planning Estate Planning
The Financial Planning Process
The Six-step approach in practice
Applications
Financial planning cases
Indicative Reading
Cheng Louis, Leung Tak Yan and Wong Yiu Hing, Financial Planning & Wealth Management
An International Perspective, McGraw-Hill, 2009.
George, Rejda, Principles of Risk Management and Insurance, 6th Edition, Addison Wesley,
1998.
Bodie, Kane and Marcus, Essential of Investments, 3rd Edition, Irwin, 1998.
Williams, Smith and Young, Risk Management and Insurance, 8th Edition, 1998.
Burton T. Beam and John J. McFadden, Employee Benefits, 5th Edition, Irwin, 1998.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
135
Subject Code
:
AF4326
Subject Title
:
Fixed Income Securities
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures / Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
Investments (AF3316)
Co-requisites
:
None
Exclusion
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
42 hours
Role and Purpose
This course is concerned with fixed income securities and interest rate risk management. It
will introduce tools used to explore the theoretical and empirical aspects of fixed income
securities and their derivatives. It contributes to the achievement of the BBA programme
outcomes by enabling students to understand and analyze real life issues related to fixed
income securities (Outcome 7), and apply relevant concepts and tools to solve problems on
fixed income investment (Outcome 9).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
•
Understand, explain and analyze the issues in pricing, hedging, and arbitrage in the
fixed income securities markets.
Evaluate various types of fixed income products and analyze their potential risk and
return.
Apply theories and concepts learned and analyze fixed income investment decisions.
Understand and explain the recent developments and issues of the fixed income
markets.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
Lectures and seminars will be conducted on the topics of the syllabus. Lecture time will be
used flexibly for discussing key concepts and their applications with students and carrying
out other learning activities with them. Such activities include group discussions and student
presentations of their work. To maximize benefits, students are encouraged to share their
views and experiences actively with their lecturer and classmates.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Coursework, including assignments, an Individual Essay and a Group Presentation, will help
students to identify and analyze real life issues in fixed income markets (Outcome 7) and to
apply relevant concepts and theories to solve fixed income problems (Outcome 9).
Exams will test students’ understanding of and ability to apply taught concepts and theories.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
136
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
The Basic Products
Bond price arithmetic. Treasury bills, notes, bonds and strips. Organization of government
bond markets. Spot rates, par rates and forward rates. Constructing zero curves.
Risk Management
Measures of price sensitivity. Simple hedging strategies using fixed income derivatives.
Eurodollar futures. Bond futures. Interest rate swaps.
Pricing Interest Rate Claims
Theories of the term structure. Arbitrage free pricing.
Corporate Bonds and Credit Risk
Credit ratings. Default risk and credit spread. Credit derivatives.
Mortgages and Their Derivatives
Residential mortgages and mortgage backed securities. Prepayment risk.
Bonds with Embedded Options
Basic pricing principles. Static spread and option-adjusted spread. Negative convexity.
Effective duration and convexity.
Indicatve Reading
Fabozzi, F., Bond Markets, Analysis, and Strategies, 6th edition, Prentice Hall.
Altman, Edward I. (2006) “Credit Risk and the Link between Default and Recovery Rates.”
CFA Institute Conference Proceedings Quarterly, vol. 23, no. 3 (September):35-43.
Taylor, Michael C. (2007) “Emerging Market Debt: Not So Emerging Anymore.” CFA Institute
Conference Proceedings Quarterly, vol. 24, no. 1 (March):55-63.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
137
Subject Code
:
AF4328
Subject Title
:
Mergers and Acquisitions
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
Business Finance (AF3313) and
42 hours
Corporate Finance (AF4320)
Assessment
Minimum Pass Grade
:
:
Coursework
50%
Final examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Role and Purpose
This subject aims to provide a theoretical framework as well as practical knowledge on
mergers and acquisitions. It contributes to the achievement of BBA Programme
Outcomes by enabling students to demonstrate a global outlook and an understanding of
cultural diversity, as evidenced by an understanding of globalization, the dimensions along
which cultures vary and the implications of both for merger business (Outcome 3).
Besides, students have to apply and analyze merger situations and problems by using
conceptual frameworks drawn from Accounting, Finance, Economics, Behavioral Science,
Law and Quantitative Methods (Outcome 7). A lot of real case examination will
demonstrate that there is strong linkage on the capital market action and the merits of
M&A transactions. In this connection, students are required to apply basic financial
theories, analyze financial reports and understand the operation of financial markets as
well (Outcome 9).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
•
•
Evaluate the economic functions played by M&A activities and the importance of capital
markets in supporting such activities;
Examine various valuation methods used in M&A process;
Review the regulatory framework governing M&A-related activities in Hong Kong;
Assess the strategies and tactics of different forms of takeovers and acquisitions, offers
and defenses; and
Enhance their global outlook and cultural awareness in cross-border takeover deals and
negotiations
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
The 3-hour seminar per week will be used flexibly by the instructor for discussing key
concepts and their applications with students and carrying out other learning activities. To
maximize benefits, students are encouraged to participate actively in the discussions and
share their views with their peers. This course also places a lot of emphasis on team work.
Students will be organized into teams and assigned to work on problem sets and real-life
case studies.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
138
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Assessment components include written merger problems/cases in coursework and
subject final examination set with merger problems/cases. The coursework will cover
cases from Hong Kong, China, Japan, India, Europe and the US in order to provide
students a global perspective and how different cultural issues have affected merger
decisions (Outcome 3). These assessment components require students to demonstrate
their ability to apply and analyze merger situations and problems by using conceptual
frameworks drawn from Accounting, Finance, Economics, Behavioral Science, Law and
Quantitative Methods (Outcome 7). Besides, students will be assessed by how they apply
basic financial theories, analyze financial reports and understand the operation of financial
markets as well (Outcome 9).
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Overview of Mergers and Acquisitions
Types of acquisitions; dynamics of the M&A process; merger theories and empirical
evidence.
Takeover Regulation in Hong Kong
Substantial shareholding; Takeovers Code; Securities Ordinance; Companies Ordinance;
SEHK Listing Rules.
Valuation Issues
Valuation methodologies; valuation of target firms; valuation issues for the offeror.
Structuring M&A Deals
Consideration; method of payment; impact of financial strategy.
Bid Strategies and Tactics
Choice of offer consideration and conditions; management and board considerations.
Takeover Defenses
Resistance motives; defense strategies; impact and cost of strategies; right of minority
shareholders.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
139
Indicative Reading
Weston, J. Fred, Mark L. Mitchell and J. Harold Mulherin, Takeovers, Restructuring &
Corporate Governance, 4th Edition, Prentice Hall, 2003.
Patrick A. Gaughan, 4th edition, Mergers, Acquisitions, and Corporate Restructurings
University Edition, John Wiley and Sons, 2007
Sudi Sudarsanam, Creating Value from Mergers and Acquisitions: The Challenges, Prentice
Hall, 2003.
Lang, Larry H.P., Cases of Mergers and Acquisitions in Hong Kong, Prentice Hall, 2000.
Norman, David and Denise Jong, M&A: mergers and acquisitions in Hong Kong, THC Press,
2000.
Gaughan, Patrick A., Mergers, Acquisitions and Corporate Restructuring, 2nd Edition, John
Wiley and Sons, 1999.
Dirk HACKBARTH & Erwan MORELLEC, “Stock returns in mergers and acquisitions”, The
Journal of Finance 63 (3), June 2008, pp.1213-1252
Matthew RHODES-KROPF & David T. ROBINSON, “The market for mergers and the
boundaries of the firm”, The Journal of Finance 83 (3), June 2008, pp. 1169-1211
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
140
Subject Code
:
AF4331
Subject Title
:
Business Valuation
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures and Seminars 42 hours
Pre-requisites
:
Corporate Finance (AF4320)
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of BBA (Hons) Outcomes by enabling students
to evaluate the economic, legal, regulatory, and industry environment, in which both
domestic and international firms operate (Outcome 7), and understand the function of firms
by analyzing financial reports (Outcome 9) for valuing different kinds of businesses. It
requires students to present and communicate effectively so as to provide a solid foundation
for students to advance further into the field of business valuation as investment analysis
(Outcome 1 and 2). It provides a solid foundation for students to advance further into the
field of business valuation as investment analysts (Outcome 13).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
Assess a firm’s financial condition through analyzing financial statements;
•
Apply analytical tools to make forecasts and value firms and projects using different
valuation techniques;
•
Evaluate and compare corporate valuation decision in specific contexts like securities
analysis, credit assessment and acquisition and merger.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
The three hours per week will be used flexibly by the instructor for discussing key concepts
and carrying out exercises and case assignments with students. Heavy emphasis is placed
on the students’ oral and written communication skills. Active participation is expected from
every student. To maximize benefits, students are expected to share their views actively
with instructors and other classmates.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
141
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Assessment components include mid-term examination, written report/cases in coursework
and subject final examination set with cases. These assessment components require
students to demonstrate their ability to evaluate the economic, legal, regulatory, and industry
environment in which firms operate (Outcome 7), and understand the functions of firms by
analyzing financial reports (Outcome 9) for valuing different kinds of businesses.
Project and presentation are carried out to assess the student’s both written and oral
communication skills. (Outcome 1 and 2). These are designed to assess students’ ability to
apply techniques of equity valuation which serve as a base for continuous development as
investment analysts (Outcome 13).
Indicative Content
Essential Principles and Valuation Techniques
The equities market; meaning of value; common techniques used in valuation (e.g. ratio
analysis, DCF, FME, capitalisation of dividends, asset-based valuation, WACC, CAPM) of
business and securities.
The Company and its Industry
Private or public firms; sources of information; sector analysis; analysis of management and
company performance reporting.
Application of Valuation Principles
Management structure; historical financial performance, segmental information; analysis of
assets and liabilities; projection of earnings; special valuation situations.
Other Factors affecting Valuations
Impact of accounting treatments; taxation; regulatory requirements; dilution and new issues.
Valuation of Business under Special Situations
Special nature of industries; valuing synergy; corporate control; leveraged buyouts and
takeovers; re-organisation and restructure.
Other Valuation Techniques
Special equity analysis (e.g. charting, QA); break-up valuation; Economic Value Added
(EVA).
Valuing New Economy
The characteristics of new economy; the business models of new economy; the supply and
demand for new economy stocks; valuation methods for new economy companies; IPO of
new economy stocks.
Indicative Reading
K.G. Palepu, V.L. Bernard, and P.M. Healy, Business Analysis and Valuation Using
Financial Statements, IFRS Edition, South-Western/International Thomson, 2007.
J. Wild, K. Subramanyam, and R. Halsey, Financial Statement Analysis, 10th Edition, Mc
Graw Hill, 2009.
T. Copeland, T. Koller, and J. Murrin. Valuation: Measuring and Managing The Value of
Companies, 4th Edition, Wiley, 2005.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
142
Subject Code
:
AF4332
Subject Title
:
Corporate Risk Management
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures / Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
Investments (AF3316)
Co-requisites
:
None
Exclusion
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
42 hours
Role and Purpose
This course is to prepare students to establish the body of knowledge necessary for
independent risk management analysis and decision-making. It builds on basic finance
concepts and gives the students an understanding on how a business can identify, measure
and control its risks. It contributes to the achievement of the BBA programme outcomes by
enabling students to apply relevant tools and concepts to identify and explain real life risk
management issues of non-financial and financial institutions and analyze systematically the
underlying factors that lead to sound risk management (Outcome 7).
It will also help
students improve their ability to communicate verbally in English through discussions and
presentations (Outcome 1).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
Understand the basic principles of risk management and the role of risk management in
business firms.
•
Identify and analyze underlying factors that lead to good/poor risk management of a
business.
•
Apply relevant tools to identify, measure and control risk exposure related to operation,
financing and investment in a global market.
•
Apply Value-at-Risk (VAR) methodology to assess various types of risk for a business.
•
Enhance their ability to communicate verbally in English through discussions and
presentations.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
Lectures and seminars will be conducted on the topics of the syllabus. Lecture time will be
used flexibly for discussing key concepts and their applications with students and carrying
out other learning activities with them. Such activities include group discussions and student
presentations of their work. To maximize benefits, students are encouraged to share their
views and experiences actively with their lecturer and classmates.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
143
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Coursework, including assignments, an Individual Essay and a Group Presentation, will help
students to identify and explain real life risk management issues of business firms and to
apply relevant concepts and theories to analyze systematically the underlying factors that
contribute to a firm’s risk exposures and to manage them (Outcome 7).
Exams will test students’ understanding of and ability to apply taught concepts and theories.
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Basic Concepts of Risk and Risk Management
Definitions of risk and risk management. Risk concepts and processes.
Risk Identification, Measurement and Control
Classification of risk. Basic tools. Value-at-Risk (VAR). Stress testing.
Liquidity Risk
Asset liquidity risk. Funding liquidity risk. Liquidity-adjusted VAR.
Credit Risk
Credit exposure. Default risk. Pricing credit risk.
Operational Risk
Identification, assessment and loss distributions. Data challenge.
Integrated/Enterprise Risk Management
Enterprise-wide risk management, its importance and principles.
Indicative Reading
Jorion, Philippe, Value at Risk: The New Benchmark for Managing Financial Risk, 3rd edition,
McGraw Hill, 2007.
Lam, James, Enterprise Risk Management, Wiley, 2003.
Crouhy, M, D. Galai and R. Mark, The Essentials of Risk Management, McGraw Hill, 2006.
Brown, S. J., & Steenbeek, O. W. (2001) “Doubling: Nick Lesson’s trading strategy”. Pacific
Basin Finance Journal 9, 83-99.
Edwards, F. R. (1999) “Hedge funds and the collapse of Long-Term Capital Management”.
Journal of Economic Perspectives 13 (2), 189-210.
Jorion, P. (2000) “Risk management lessons from Long-Term Capital Management”
European Financial Management 6 (3), 277-300.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
144
Subject Code
:
AF4510
Subject Title
:
Law and Practice of Banking
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Seminars
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
Introduction to Business Law (AF2504)
Assessment
:
Coursework
60%
Final Examination
40%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
The subject builds on students' knowledge acquired in business law and explains the legal
aspects and practice relating to a wide range of daily banking operations. The legal nature of
the various instruments commonly used in banking transactions will be considered in depth
with a view to understanding the complexities of domestic and international banking. Thus
the purpose of the subject is to equip the students with the fundamentals of the law and
practice relating to banking industry (Outcome 13). It is expected that at the end of the
course the students will thoroughly understand their role in the existing banking regime and
understand the ethical and legal issues (Outcome 5) and problems surrounding the banking
industry, the participants in the banking industry, including individuals and corporations and
how they may be resolved under the current legal framework (Outcome 7).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Explain the development and complexity of Hong Kong’s banking industry
Explain the legal principles governing the daily banking operations of commercial banks
Explain the implications of differing types of customers transacting business with bankers
Advise clients on the use of different forms of negotiable instrument and security –
including guarantees, indemnities and charges
Advise clients on the consequences of money laundering and evaluate the various forms
of control
Advise clients to make sound business decisions based on their knowledge of the bank
customer relationship
Critically evaluate the effectiveness of the existing banking law regime
Identify and resolve legal and ethical issues in banking industry.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
Lectures will be used mainly for introducing to students the application of theoretical legal
principles to real life banking operations. Banking practices will be considered in detail and
members of the banking profession will be invited to contribute to the subject.
Seminars will, through case studies and problem based learning, encourage critical analysis
of the course materials and promote debate on current related issues.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
145
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Assessment components include written banking law problems/cases in coursework, midterm test and a final examination set with banking law problems/ cases. These assessment
components require students to demonstrate their ability to interpret up-to-date banking law
statute, including the Banking Ordinance and Bills of Exchange Ordinance, and case law
principles and analyze practical banking law issues (Outcome 7), apply banking law
concepts to provide legal and ethical advice to clients (Outcome 5). Students’ ability to
identify and resolve ethical and legal issues in banking industry will be assessed in their
explanations/ advices through assessment components and final examination (Outcome 13).
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
The Banker/Customer Relationship
The legal definition of a bank. The definition of a customer. Express and implied contractual
terms. Rights and duties of the bank and customer. The banking systems and anti moneylaundering legislation.
Types of Customer
The opening and the conduct of accounts in credit and debit for individuals, joint customers,
executors, administrators and trustees, minors, sole proprietors, partnerships, companies,
solicitors, unincorporated clubs etc.
Effect of death, insolvency, mental disorder, and legal processes on a customer's account.
Banking Operations
Payment by cheques and other instruments. The rights and duties of the various parties of
negotiable instruments. Statutory protection of collecting and paying banker. The Hong
Kong cheque clearing and settlement systems. Electronic banking and its legal impact.
Securities for Advances
Creation and enforcement of individuals' and companies' securities including: stocks and
shares; land and buildings; guarantees; debentures; book debts; fixed deposit receipts;
insurance policies; gold and goods.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
146
Indicative Reading
Recommended Textbook
Chan, S., Annotated Banking Ordinance, Butterworths, 2008.
Chan, S., Halsbury’s Law of Hong Kong – Bills of Exchange and Other Negotiable
Instruments, LexisNexis, 2007
Chan, S., Halsbury’s Law of Hong Kong – Banking and Finance, LexisNexis, 2007.
References
Chan, S., Butterworths Hong Kong Banking Law Handbook, Butterworths, 2003.
Chan, B.C.S., Hong Kong Banking Law and Practice, HKIB, Vol. 1 & 2, 2000.
Ko S.H., Law & Practice of Banking Services in Hong Kong, City University, Hong Kong.
1998.
Ong CA, Legal Decisions Affecting Banks in Hong Kong, CIOB, 1995.
Ong C.A., J. Lee and Others, Law and Practice of Banking in Hong Kong, CIOB, 1993.
Tokley, I., Hong Kong Banking and Practice, Butterworths, 2000.
Roebuck, D., Banking Law in Hong Kong: Cases and Materials, Butterworths Asia, 1995.
Roebuck, D., Law Relating to Banking in Hong Kong, Hong Kong University Press, 1993.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
147
Subject Code
:
AF4511
Subject Title
:
E-Business Law
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
14 hours
Seminars
28 hours
Pre-requisites
:
AF2504 Introduction to Business Law
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA programme outcomes by enabling
students to demonstrate their ability to analyze e-business situations and problems by
applying legal conceptual frameworks (outcome 7). The subject will examine the impact of
electronic services upon the basic concepts of business law already learnt and will introduce
current legal issues relevant to users, managers and providers of e-services and information.
The subject will therefore extend to the laws of other jurisdictions and will enable students to
demonstrate a global outlook to e-business (outcome 3).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
•
•
•
Understand the impact of the continuing developments in the technology of commerce
on the law relating to business
Understand the different approaches taken to governing e-business in different
jurisdictions
Explain the law of defamation in the context of e-business
Appraise the intellectual property issues arising in e-business
Understand the criminal laws applying to the abuse of e-business systems.
Formulate solutions to new problems for businesses brought about by the global nature
of Internet transactions
Indicative Teaching /Learning Approach
Lectures will be used mainly to introduce the essential principles of each subject in the
syllabus.
Seminars will deal with the application of the principles to practical situations by the use of
case studies. Students will be expected to prepare answers to the case studies and actively
participate in the discussions.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
148
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Class work will comprise a series of cases which require that students (working in small
groups) identify the legal issues, research the relevant law and report on for further
discussion by all members of the class. These cases will require that students analyze ebusiness situations and problems and apply legal conceptual frameworks (outcome 7) not
only in the context of Hong Kong but also globally and so require that students demonstrate
a global outlook (outcome 3). The examination will also be case based and to will reinforce
these outcomes.
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
National and International Laws
International and Supra-national organizations concerned with e-business law: the United
Nations, European Union, the USA. The development of Hong Kong and the PRC’s ebusiness laws. Consumer protection – product liability. Jurisdiction – choice of laws, conflict
of laws.
Impact of Electronic Transactions in relation to Contract Law
Formation of electronic contracts. Legal effect of electronic/digital signatures. Electronic
records of contracts.
Impact of Electronic Services in relation to Negligence
Liabilities in relation to on-line advice services.
Principles of Defamation
Basic legal principles of the tort of defamation and problems for information service
providers.
Law of Intellectual Property and Electronic Technology
Domain names, infringement of trade marks and copyright, passing off.
Data Privacy
Legal framework relating to the protection of personal and business data. SPAM.
Criminal Law Issues
Abuse of the Internet system. Fraud, impersonation and forgery of information and
documents. Obscene articles. Criminal damage. Gambling.
New Developments in E-commerce
Alternative payment systems suitable to the electronic format: electronic cash, virtual banks.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
149
Indicative Reading
Wright and Mc Auliffe, Internet law in Hong Kong, Sweet and Maxwell, 2003.
Baumer and Poindexter, Cyberlaw and E-Commerce, 2002.
Stephenson and Kwan, Cyberlaw in Hong Kong, Butterworth, 2001.
Akdeniz, Walker and Weil, The Internet, Law and Society, Longman, 2000.
Bainbridge, Introduction to Computer Law, Longman, 4th Edition, 2000.
Electronic Transaction Ordinance.
Personal Data (Privacy) Ordinance.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
150
Subject Code
:
AF4512
Subject Title
:
Corporate Governance and Compliance
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures/Seminars
Pre-requisites
:
Company Law (AF3507)
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
42 hours
Role and Purpose
This subject aims to impart students with a sound knowledge of the legislative and regulatory
framework of companies registered in Hong Kong and an understanding of the importance of
the corporate governance system (Outcome 7). It contributes to the achievement of the BBA
Outcomes by enabling students to apply the concepts relating to corporate governance
issues of Hong Kong registered companies (Outcome 7), to formulate codes of ethics and
codes of best corporate governance practice (Outcome 5), to comply with and to critically
evaluate the effectiveness of statutory and non-statutory regulations relating to investor and
creditor protection (Outcome 7).
Learning Outcomes:
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
•
•
Interpret the corporate governance system and best practices in Hong Kong.
Identity and evaluate the role and responsibilities of directors, secretary and auditors in
the corporate governance system
Comply with the regulatory requirements and apply them to the current issues and
cases.
Critically evaluate the effectiveness of the statutory and non-statutory regulations in
protecting the interest of the investing public, members and creditors of a company.
Formulate codes of ethics and codes of best practice in relation to the further
development of corporate governance.
Indicative Teaching/ Learning Approach
Lectures emphasize concepts while seminars provide a forum for discussion on the
application of concepts to current issues and cases.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Class discussions, presentations, written assignment/test enable students to apply the
concepts of corporate governance issues (Outcome 7), to apply regulatory provisions to
current issues and cases (Outcome 7), to formulate codes of ethics and codes of best
practice (Outcome 5) and to critically evaluate the effectiveness of the statutory and nonstatutory regulations in investor and creditor protection (Outcome 7).
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
151
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
Corporate Governance System
The historical development of the system of corporate governance. The role of the
Companies Registry, the Stock Exchange and the Securities and Futures Commission in the
corporate governance system of Hong Kong companies.
Business Ethics
Ethics and business. Ethical dilemmas. Corporate responsibility. Corporate standard of
behaviour and corporate codes of conduct.
Incorporation of Companies
The practice and procedures for incorporation of companies.
Share Capital
Classes of securities issued by companies, sources and methods of raising new capital,
alteration of capital, reduction of capital, repurchase of shares, allotment of shares, transfer
and transmission of shares, voting and other rights, variation of rights and disclosure of
substantial ownership.
Share Registration Practice and Transfer and Transmission Procedures
Share registration practice and transfer and transmission procedure, upkeep of statutory
books, court orders, personal representative, power of attorney and procedures for issuing
replacement share certificates for listed and unlisted companies.
Accounts and Annual General Meeting
Basic requirements of company accounts. Contents of directors’ reports. Practical work of a
company secretary before, during and after an annual general meeting. Annual returns.
Directors
The duties and responsibilities of directors (including board committees) and their alternates.
Qualification and disqualification of directors. Appointment of directors and alternate
directors, tenure and vacation of office, remuneration, loans and compensation for loss of
office, disclosure of interests, executive directors and non-executive independent directors.
Secretary
The duties, responsibilities and qualifications of secretaries for listed and unlisted
companies. Secretary’s appointment, resignation and removal.
Auditors
The duties, responsibilities and qualifications of auditors. Auditors’ appointment, termination
and vacation of office.
Law and Procedures of Company Meetings
The law relating to meetings of companies. Types of company meetings include general and
class meetings, board and committee meetings and meetings in winding up. The conduct
and management of company meetings, notices, agenda, quorum, ordinary and special
resolutions, voting, polls, proxies, adjournment, powers and duties of chairman, practical
work of the company secretary before, during and after meetings.
Listing Rules and their Application
Hong Kong Stock Exchange dealing procedures. Procedure for admission of securities to
listing, continuing obligations and reporting requirements of listed companies including
notifiable and connected transactions.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
152
Amalgamation, Reconstructions and Takeovers
Procedures involved in cases of major changes to a company’s ownership or business,
amalgamation, acquisitions and reconstructions, schemes of arrangement and takeovers.
Loan Capital and Registration of Charges
Types of debentures. Procedures for issuing debentures including listing of debentures on
the Stock Exchange. Registration of charges, maintaining and inspection of register of
charges. Release of charges.
Liquidation
Procedures and practice in respect of winding up, appointment, duties powers and
qualifications of liquidators and dissolution of companies.
Non-Hong Kong Companies
Initial registration under Part XI of the Companies Ordinance, Stock Exchange listing,
continuing obligation to file accounts, annual returns and report changes in documents
registered, termination of registration and winding up of non-Hong Kong companies.
Indicative Reading
Cheng, P.W., H.S. Sum and K.T. Yuen, The Hong Kong Company Secretary’s Handbook:
Practice and Procedure, latest Edition, Longman
Stott, V., Hong Kong Company Law, latest edition, Longman.
Crone A., and Matten D., Business Ethics, 2nd Edition, Oxford University Press, 2008.
De George, Richard T., Business Ethics, 6th Edition, Prentice Hall, 2006.
Velasquez, Manuel G., Business Ethics - Concepts and Cases, 6th Edition, Prentice Hall,
2006.
Erismann-Peyer, G., Steger, U., and Salzmann, O., The Insider’s view on Corporate
Governance: The Role of the Company Secretary, Palgrave Macmillan, 2008.
Companies Ordinance, Cap. 32 (and amendments) and all related rules, regulations &
orders
Electronic Transactions Ordinance, Cap. 553
Financial Reporting Council Ordinance, Cap. 588
Securities and Futures Ordinance, Cap. 571
Rules governing the Listing of Securities, The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited.
The Codes on Takeovers and Mergers and Share Repurchases, the Securities and Futures
Commission.
Company Secretarial Practice: The Manual of Chartered Secretaries and Administrators,
ICSA Publishing Ltd.
Hong Kong Ethics Development Centre, Ethics in Management: A Resource Portfolio for
Hong Kong Universities.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
153
Subject Code
:
AF4513
Subject title
:
Corporate Social Responsibility
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures and seminars 42 hours
Prerequisites
:
None
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
Corporate social responsibility has its foundations in the students' knowledge of a diverse
range of business functions and sectors. Whatever the specific business setting
(accountancy, finance, logistics, marketing or management) the examination of corporate
interaction with stakeholders and the notions of social responsibility and ethical behaviour
are a matter of concern. This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA programme
outcomes by enabling students to demonstrate a global outlook (outcome 3), identify and
resolve ethical issues (outcome 5) and the application of conceptual frameworks (outcome
7).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
Understand what is meant by “corporate social responsibility” and appreciate its
development.
•
Analyse “ethical issues” within the framework of corporate social responsibility.
•
Appreciate that ethical issues may need different approaches in differing value systems.
•
Assess the role of a code of ethics, the essential requirements in drafting such a code
and the difficulties of enforcement.
•
Apply appropriate ethical concepts and approaches in realistic corporate and
professional circumstances.
•
Identify the interconnection of this subject with other disciplines.
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
Lectures will introduce ethical issues, theories and the debates concerning the need for
corporations to be socially responsible. Seminars will provide students and opportunity to
consider and debate practical examples and to discuss a wide variety of case-studies
concerning the various aspects of corporate social responsibility. Continuous assessment
will comprise preparation for and contribution to seminar activities, small-group case-study
research and presentations, and a quiz.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
154
Indicative Assessment Tasks
The continuous assessment tasks will comprise two short individual essays; both of which
will concern ethical theories and so will help students to resolve ethical issues (outcome 5)
and apply conceptual frameworks (outcome 7). The quiz will focus on identifying and
resolving ethical issues (outcome 5). Given that many of the case-studies concern
multinational corporations, the seminar presentations will seek to ensure that students
understand cultural diversity as well as help them to gain a global outlook (outcome 3). The
examination will be a separate 3 hour assessment and will reinforce the identified outcomes.
Indicative Content/Outline Syllabus
The Development of Corporate Social Responsibility
The notion of stakeholders; concern for human rights and the environment; ethical and moral
reasoning; the relationship between law, ethics and corporate social responsibility; ethical
dilemmas typically encountered by corporations.
A Framework for Ethical Decision-Making
Ethical concepts and theories; deontological and teleological theories; the notions of fairness
and justice; Chinese, Asian and Western concepts and theories compared.
Corporate / Professional Standards
The conflict between economic performance and social responsibility; relations between
corporations and key stakeholders; deceptive marketing; employee privacy; customer
privacy; intellectual property; secrecy / information privacy; equal opportunities;
discrimination; “whistle-blowing”; codes of conduct.
International Issues
The diversity of cultural values; moral relativism v. moral pluralism; cross-cultural dilemmas
facing corporations; ethnocentric morality; current developments in corporate social
responsibility.
Indicative Reading
Text book: Business Ethics, Crane A. and Matten D, Oxford University Press (2nd ed)
Allouche, J., Corporate Social Responsibility, Vol. 1, Concepts, Accountability and
Reporting, New York, N.Y.: Palgrave Macmillan, 2006.
Cramer, J., Corporate Social Responsibility and Globalization: An Action Plan for Business.
Greenleaf, 2006.
Jonker, J. and de Witte, M. The Challenge and Difficulties in Organizing and Implementing
Corporate Social Responsibility, Houndmills, Hampshire, N.Y.: Palgrave Macmillan, 2006.
Harvard Business Review, Harvard Business Review on Corporate Responsibility. Harvard
Boston, MA: Business School Publishing Corporation, 2003.
Hopkins, M., The Planetary Bargain: Corporate Social Responsibility Matters, London, UK:
Earthscan Publications Ltd., 2003.
Leipziger, D., The Corporate Responsibility Code Book, Greenleaf, 2003.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
155
Journals including
Business and Professional Ethics Journal
Business and Society
Business and Society Review
Business Ethics - A European Review
Business Ethics Quarterly
Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management
Journal of Business Ethics
The Journal of Corporate Citizenship
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
156
Subject Code
:
AF4605
Subject Title
:
Hong Kong – China Business
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Seminars
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
Introduction to Economics (AF2601) or equivalent
Assessment
:
Coursework
50%
Final Examination
50%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
Role and Purpose
This subject is designed to give students an overall view of the business environment in
China and it accounts for Hong Kong's position as the “gateway” between China and the rest
of the world. This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Outcomes by enabling
students to analyze business situations and problems by applying concepts from economics
and finance (Outcome 7), to identify and analyze various business issues of the Chinese and
local environment (Outcome 12), and communicate effectively (Outcomes 1 and 2).
Learning Outcomes
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
Analyze the nature and development of the business environment in China
Examine the role of the Chinese government in the business environment within which
businesses operate in China
Command a view of the role of Hong Kong in China’s economy and the business
implications for Hong Kong companies and other Western firms
Indicative Teaching/Learning Approach
Lectures will provide an overview of the conceptual frameworks and expound major case
studies for illustration of concepts, show video-tapes, and may invite guest speakers.
Seminar work will include the analysis of academic papers and the evaluation of current
business issues.
Indicative Assessment Tasks
Classwork, including learning-to-learn exercises, will help students to apply concepts, and to
identify and analyze various business issues in China mainland and Hong Kong (Outcomes
7 and 12). Effective communications will be assessed through group presentation and class
discussion. Other coursework assessment tools include a presentation, a report and a midterm test (Outcomes 1 and 2).
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
157
Indicative Content / Outline Syllabus
External Economic Relations of the PRC
The direction and structure of trade flows between the PRC, Hong Kong and the rest of the
world. The role of foreign direct investment into the PRC, and its pattern. The central
importance of the Chinese diaspora. The effects of the reform process on trade. China's
trading institutions and its trade policy regime. International technology transfers to China.
The Development of the Financial Sector in the PRC
Banking reform in China and its impact upon Hong Kong as an international financial centre.
The development of financial markets in China.
Aspects of China Business
The nature of the firm in China, alternative forms of enterprise and their changing
importance. The importance of the law in the process of reform. The role of “guanxi” in a
high-context transitional economy. The development of technology. Distribution systems
and the emergence of a retail market. Managing Sino-foreign joint ventures.
Indicative Reading
Zhou, L. (2006) China Business, Prentice Hall.
Davies, H. (ed.) China Business: Context and Issues, Longman Hong Kong, most recent
edition.
Lane, K. and Y. Luo, (eds.) China 2000: Emerging Business Issues, CA, Sage Publications,
most recent edition.
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
158
Subject Code
:
AF4606
Subject Title
:
Economic Development of Asia-Pacific Countries
Level
:
4
Credits
:
3
Mode of Study
:
Lectures
28 hours
Seminars
14 hours
Pre-requisites
:
Introduction to Economics (AF2601) or equivalent
Assessment
:
Coursework
40%
Final Examination
60%
Coursework
(D)
Final Examination
(D)
Minimum Pass Grade
:
ROLE AND PURPOSE
This subject contributes to the achievement of the BBA Outcomes by enabling students to
access economic performance of selected Asia Pacific economies by applying concepts
(Outcome 7) from Economics and Quantitative methods, to evaluate the process of
globalization (Outcome 3) and regional integration in the Asia Pacific region, to develop
students’ ability to analyze critically (Outcome 4) key economics issues facing the region. A
variety of assessment methods will be used to enhance students’ communication skills,
verbally (Outcome 1) and in writing (Outcome 2).
LEARNING OUTCOMES
On successfully completing this subject, students will be able to:
•
•
•
Evaluate the fundamental economic forces that have shaped the economic performance of
the region.
Analyse key economic issues in Asia Pacific countries and in particular their business
implications.
Access how economic integration with countries in the region impacts on Hong Kong.
INDICATIVE TEACHING/LEARNING APPROACH
This subject will be taught in both lecture and seminar formats, emphasising key issues in
the economic development of these countries, economic integration of the region and
importantly, business implications for Hong Kong.
INDICATIVE ASSESSMENT TASKS
Several assessment tools will be used, including group or individual essay, class
presentation and discussion, as well as final examination. Group or individual essay will help
students to develop the ability to evaluate the process of globalization and regional
integration (Outcome 3) by applying concepts (Outcome 7) from Economics and Quantitative
methods and to communicate effectively in writing (Outcome 2). In-class presentation,
together with class discussion, will help develop students’ ability to communicate verbally
(Outcome 1) and to analyze critically (Outcome 4) key economics issues facing the region.
INDICATIVE CONTENT/OUTLINE SYLLABUS
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
159
Hong Kong and the Asia Pacific Economies: A Regional Perspective
The Asia Pacific economies: relative size and diversity; Growth and structural change; FDI
flows; Intra-regional trade; ‘Group miracle’ and Asian financial crisis; Hong Kong’s integration
with mainland China.
Key Issues in Economic Development
Growth and development: the analytical framework; Growth accounting; Growth theory;
Income Distribution; Labour market; Financial sector; Trade and development;
Macroeconomic Management; Industrial Policy; Population.
Economic Development of Japan
Economic growth; Japan’s lost decade; Labour market; Capital market; Industrial structure
and industrial policy; Trade and development.
Economic Development of South Korea and Taiwan
Economic growth; Income distribution; Korean Management System; Financial market;
Industrial structure and industrial policy; International trade; Economic integration between
Taiwan and Mainland China
Economic Development of Southeast Asian Countries
Why did ASEAN economy grow so fast since 1970s? Income distribution; Labor market;
Export-oriented industralization; ASEAN economic integration.
INDICATIVE READING
Recommended Textbook
There is no prescribed textbook. Lecture summaries and supplementary notes will be
distributed from time to time. Books that are on the list of essential readings and additional
references will be placed in Student's Reserve Section of the University Library.
Key References
Athukorala, Prema-chandra. China’s rise and East Asian export performance: is the
crowding-out fear warranted? APEC Economies Newsletter, Vol. 11 No.9, September 2007.
Kuo, Shirley W.Y. and Christina Y. Liu, The Development of the Economy of Taiwan, AsianPacific Economic Literature. 36-49, 1999.
Tongzon, Jose L., The economies of Southeast Asia: the growth and development of
ASEAN economies, Cheltenham; Northampton, Mass: E. Elgar, 1998.
Song, Byung-Nak, The Rise of the Korean Economy, Oxford University Press, 1997.
Gillis, Malcolm, Dwight H. Perkins, Michael Roemer and Donald R. Snodgrass, Economics
of Development, New York: W. W. Norton & Company, latest edition.
Takatoshi Ito, The Japanese Economy, MIT Press, 1992.
Subject Co-ordinator
XU Xinpeng
AF Subjects Syllabi (2008-09)
160