LPE&T Calculations I
advertisement

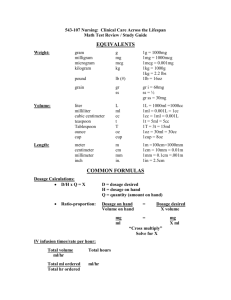
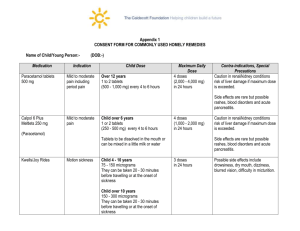
LPE&T Calculations I You have 60 minutes to answer the following 20 calculation questions Q1 What weight of potassium permanganate is required to prepare a 100ml solution such that 10ml diluted to 1 litre will give a 1 in 4000 solution? A 2.5mg B 25g C 1.25g D 2.5g E 250mg 10ml – 1L (1g in 4000ml = 250mg/L) 10ml contains 250mg Therefore x 10 for 100ml = 250 * 10 = 2500mg = 2.5g Q2 A patient is prescribed prednisolone as a descending dose course. The patient is to take 80mg OD reducing by 10mg every 2 days until a dose of 10mg is reached. She is then to take 10mg for 7 days and 5mg for 7 days and then stop. What is the total dose of prednisolone taken? A 725mg B 755mg C 775mg D 805mg E 825mg 80mg – 2 days 70mg- 2 days 60mg – 2 days 50mg- 2 days 40mg- 2 days 30mg- 2 days 20mg- 2 days 10mg- 7 days 5mg- 7 days = = = = = = = = = 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 70 35 Total = 805mg LPE&T 2013 (Questions taken from Drug Calculations 2 compiled by Roy Sinclair and LNR regional training programme) Q3 Pripsen sachets contain 4gms piperazine citrate and 15.3mg sennosides per sachet. It is recommended that they are prepared by dissolving the granules in a glass of water or milk. Assuming that there is no displacement, what is the approximate concentration of sennosides if a standard glass of water is 150mls? A 0.01% B 0.015% C 0.030% D 0.060% E 0.15 % 15.3mg/ 150ml 15.3/3 = 5.1 5.1 * 2 = 10.2 in 100ml Approx 10mg in 100ml = 10/1000 = 0.01% Q4 A patient is to be given infliximab for Crohns disease. The patient weighs 54Kg and is to be given a dose of 2.5mg/kg/dose. Infliximab comes as 100mg in 10ml and should be prepared in an intravenous solution with a final volume of 250ml which is then to be administered over 3 hours (The recommendation is a minimum of 2 hours). At what rate is the infusion actually to be administered in micrograms/minutes? A 1000mcg /minute B 750mcg /minute C 500mcg/minute D 250mcg/minute E 125mcg /minute 54 x 2.5 = 135mg dose Infliximab comes as 10mg/ml 135mg in 250ml = 135mg/3 = 45mg/hour 45000mcg/60 = 4500/6 = 750mcg/minute LPE&T 2013 (Questions taken from Drug Calculations 2 compiled by Roy Sinclair and LNR regional training programme) Q5 A patient is admitted to hospital following a drug overdose. On admission a plasma concentration of 72 micrograms/ml is measured. Given that the half-life of the drug is 18 hours, what would you expect the approximate plasma concentration to be after 45 hours? (You may assume that the distribution is complete and the elimination follows first order kinetics) A 13.5 micrograms/ml B 22.5 micrograms/ml C 25.5 micrograms/ml D 36.5 micrograms/ml E 42.5 micrograms/ml 72mcg/ml – 36mcg/ml – 18mcg/ml after 36 hours Then how much after 9 hours = 18mcg/ml – 9mcg/ml Which is 13.5mcg/ml Q6 A patient is being given pilocarpine eye drops 0.5% for their glaucoma. How much drug is contained in 1 drop if each 1ml contains 20 drops? A 1mg B 500 micrograms C 250 micrograms D 125 micrograms E 62.5 micrograms 0.5g/100ml 500mg/100ml 5mg/ml 5mg/20 = 5000mcg/20 = 250mcg LPE&T 2013 (Questions taken from Drug Calculations 2 compiled by Roy Sinclair and LNR regional training programme) Q7 A six year old child year old child weighing 21kg is to be treated with diclofenac sodium to relive the pain of juvenile arthritis. Which one of the following would you recommend as a treatment option? A 100mg diclofenac sodium suppository bd B 25mg diclofenac sodium tablet tds C 50mg diclofenac dispersible tablet bd D 75mg diclofenac sodium m/r capsules bd E 2 x 50mg diclofenac sodium dispersible tablet bd Answer: c) 50mg bd Patient is 21kg. c-BNF 2013-14, pg 503. Dose for 6 months- 18yrs = 1.5- 2.5 mg/kg bd 1.5 x 21 = 31.5mg 2.5 x 21 = 52.5mg Dose range is 31.5- 52.5mg bd = 63mg – 105mg Option a) dose is too high Option b) within range, but tablets are probably not the most suitable preparation for a 6 year old child Option c) dose within range and dispersible tablets are a suitable preparation Option c) not licensed for a 6 year old Option d) dose over range Q8 What volume of stock solution of chlorhexidine 5% when diluted to 250ml produces a chlorhexidene 1.5% solution. A 75 ml B 125ml C 150 ml D 7.5ml E 55ml 1.5% = 1.5g in 100ml 250ml contains 1.5 x 2.5 (250/100) = 3.75g 5g in 100ml 3.75g in xml LPE&T 2013 (Questions taken from Drug Calculations 2 compiled by Roy Sinclair and LNR regional training programme) 3.75/5 x 100 = 375/5 = 75ml Q9 Drug X, a class 1 anti-arrhythmic is renally excreted. It is administered by intravenous infusion. The data sheet provides the following recommendations: Creatinine Clearance Dosage Frequency: • >50ml/min 5mg/kg 12 hrly • 25-50ml/min 2.5mg/kg 12 hrly • 10-25ml/min 2.5mg/kg 24 hrly • 0-10ml/L kg 1.25mg/kg 24 hrly Creatinine Clearance = (ml/minute) 1.02 x (140- age) x weight (Kg) Serum creatinine (mmol/litre) You have a patient who is a 60yr old non obese female. She weighs 50kg and her last plasma creatinine was measured as 300mmol/L. Which of the following doses of Drug X would be appropriate? A 275mg x 12hrs B 125mg x 12 hrs C 125mg x 24 hrs D 75mg x 12 hrs E 75mg x 24 hrs Crcl = 1.02 * 80 * 50 = 1.02 * 40 = 40.8 = 13.6 300 3 3 2.5mg/kg 24 hourly = 2.5 * 50 = 125mg/ 24 hourly Q10 Mr R has a body surface area of 1.6m2 and has been prescribed Drug X at a dose of 30mg/m2 OD for 5 days. The doctor has told you to round the daily dose to the nearest number of tablets. How many 10mg tablets are required for the 5 day course? A 20 B 25 C 30 D 40 E 48 30 x 1.6 = 48mg 48 x 5 = 240mg 240mg/10mg = 24 tablets LPE&T 2013 (Questions taken from Drug Calculations 2 compiled by Roy Sinclair and LNR regional training programme) Nearest is 25 tablets Q11 A family of two adults and their 6 year old child (who weighs 20kg) ask your advice for malaria chemoprophylaxis for a 3 week holiday to South Asia. You advise a regime of chloroquine and proguanil for the family. The child is able to swallow tablets. Which one of the following options relating to the provision of Avlocor® tablets is correct? A In total you supply 48 tablets for the whole family B The child receives 62mg/kg of chloroquine (expressed as base) over the full course of treatment C In total you supply 6g of chloroquine (expressed as base) for the whole family D The child receives a total of 3g of chloroquine phosphate over the full course of treatment E The total number of tablets to be supplied for the two adults is 20 Answers a) Avloclor® = chloroquine phosphate 250mg tabs (=155mg chloroquine as base). Regime is one tablet weekly starting 1 week before travel, during period of travel and for 4 weeks after. The family will require treatment for 8 weeks (1 week before, 3 weeks away and for 4 weeks after) b) c-BNF 2013-14, pg 337; child 4-8 yrs = dose of 1 tablet weekly BNF 65, pg 426; adults = dose of 2 tablets weekly Child = 8 weeks x 1 tablets = 8 tablets Adult= 8 weeks x 2 tablets =16 tablets Total tablets needed = 16 + 16 + 8 = 40 tablets, therefore a) is incorrect c) Child receives 8 tablets = 155mg base x 8 = 1240mg in total 1240mg / 20 = 62mg/kg, therefore b) is correct d) 8 tablets = 250 x 8 = 2g = chloroquine phosphate, therefore d) is incorrect LPE&T 2013 (Questions taken from Drug Calculations 2 compiled by Roy Sinclair and LNR regional training programme) Q12 A child weighing 5.8kg is prescribed a dose of 8mg/kg/day ciprofloxacin to be given by IV infusion in 2 divided doses. Which of the following is the correct volume of ciprofloxacin infusion 2mg/ml that should be given for each dose? A 10.3ml B 11.2ml C 11.6ml D 12.6ml E 23.2ml 5.8 x 8 = 46.4mg 46.4/ 2 = 23.2 per divided dose 2ml/ml = 23.2/2 = 11.6ml Q13 Miss A is currently on a heparin infusion. It’s 2pm and you notice her pump is bleeping showing an occlusion and she presses the ‘stop’ button. The last rate set on the pump was 2.5ml/hour and it had not altered since it was set up at 8am. How much heparin has Miss A received? Her prescription reads 25,000 units in 50ml sodium chloride 0.9%. A 75 000 units B 750 units C 15 000 units D 1500 units E 7500 units 8am- 2pm = 6hrs 2.5ml/hr = 2.5 x 6 = 15ml 15 x 25000 = 15 x 500 = 7500 units 50 LPE&T 2013 (Questions taken from Drug Calculations 2 compiled by Roy Sinclair and LNR regional training programme) Q14 A patient needs to receive 60mmols Potassium Chloride intravenously as part of their TPN. The maximum dose the patient is to receive is 5mmols / hour and they are to receive it by intravenous infusion over a maximum of 24 hours. 30mls of Potassium Chloride Concentrate Sterile (2mmol/ml) is included as part of a 2.5 litre TPN Infusion bag which is to be administered. Which of the following is the nearest maximum drop rate per minute assuming 20 drops per ml. A 700 drops per minute B 420 drops per minute C 210 drops per minute D 70 drops per minute E 35 drops per minute 30ml KCL = 60mmol So they need to receive 30ml so the entire 2.5L bag 60/5 = 12 hours 2.5L/12 hours 2500ml/12 hours 50,000 = 12 hours 50,000ml = 720ml 5000 = 72ml 69.4ml Approx 70 drops per min Q15 The recommended dose of drug A is 25mg/kg/day in divided doses. On admission, Mrs X says she is on three 250mg capsules twice daily. If the dose is correct, what is Mrs X approximate weight? A 50kg B 55kg C 60kg D 65kg E 70kg 750mg bd = 1500mg daily 1500/25 = 60kg LPE&T 2013 (Questions taken from Drug Calculations 2 compiled by Roy Sinclair and LNR regional training programme) Q16 You have on your dispensary shelf 1 litre stock bottle which is exactly half full of a 4 molar aqueous solution of potassium chloride (KCl). You receive a written order, which requires you to dilute 50ml of the stock solution with 100ml of water. What strength of KCl solution was written on the order? (Relative molecular mass KCL = 75g) A 15% B 5% C 10% D 20% E 40% The fact that the bottle is hall full is irrelevant. 4 molar solution = 4 moles/per litre 1 mole = MW therefore = 75 x 4 = 300g/litre = 30%w/v Method 1: 50ml : 100ml = 1:2 dilution or 1 in 3 dilution 30% / 3 = 10% Method 2: 50ml to 100ml = halving the concentration 30g in 100ml halve concentration = 15g in 100ml, but making 50ml to 100ml, therefore 15g in 150ml = 10% Method 3: C1V1 = C2V2 15 x 100 = C2 x 150 1500 = C2 150 C2 = 10% LPE&T 2013 (Questions taken from Drug Calculations 2 compiled by Roy Sinclair and LNR regional training programme) Q17 You are required to produce 250ml of Potassium Citrate Mixture BP, what is the volume of concentrated chloroform water required? Potassium citrate Citric acid monohydrate Lemon spirit Quillaia tincture Syrup Double strength chloroform water Water A 1.5ml B 3.75ml C 37.5ml D 4.5ml E 15ml 300g 50g 5ml 10ml 250ml 300ml to 1000ml 300ml/4 = 75ml double strength water 75/20 = 3.75ml (conversion 1:20), answer b) is correct Q18 Mrs Smith has been taking 400mg carbamazepine (Tegretol retard) once a day to control her seizures. She is currently on ITU and has a nasogatric tube. The nurse has requested a liquid preparation and asks whether the dose needs to be adjusted. Calculate the dose of the liquid preparation required. Carmazepine liquid is available as 100mg/5ml. Tegretol retard Carbamazepine liquid A 360ml B 14ml C 28ml D 18ml E 3.6ml 400mg = 100g/5ml F= 0.9 F= 1.0 5ml x 4 = 20ml 9/10 of 20ml = 180/10ml = 18ml LPE&T 2013 (Questions taken from Drug Calculations 2 compiled by Roy Sinclair and LNR regional training programme) Q19 A coated tablet has a dry weight of coating of 10mg/tablet. The coating solution is prepared to contain 10% w/v of coating material. How long is needed to coat a batch of 1 milllion tablets at a spray rate of 250ml/min, given that coating efficiency is 100%? A 25 min B 40 min C 100 min D 250 min E 400 min 1 million x 10mg = 10 million mg coating material = 10,000g 10g/100ml = 10,000 = 100L 250ml/min = 0.25L/min So 100/0.25 = 400 min Q20 You receive a prescription that requires you to supply 150g of a 1.5% drug Y in cetomacrogol cream. You only have a 2.5% drug Y in cetomacragol cream preparation. What quantity of the 2.5% cream do you need to dilute to 150g to prepare a 1.5% drug Y cream? A 30g B 45g C 60g D 75g E 90g You want to produce 150g of a 1.5% cream of drug Y. 1.5% = 1.5g in 100g Quantity for 150g would be 1.5 x 1.5 = 2.25g Therefore you can use ratios: = 2.5g 2.25g in 100g in x 2.25/2.5 = 9/10, therefore 9/10 of 100 = 90g and the answer is E Tip if you find it hard to find the ration between 2.25: 2.5, double the figures 4.5: 5 to make it easier or even double it again to get 9:10 LPE&T 2013 (Questions taken from Drug Calculations 2 compiled by Roy Sinclair and LNR regional training programme)