WHMIS Workplace Hazards Safety Training Package
advertisement

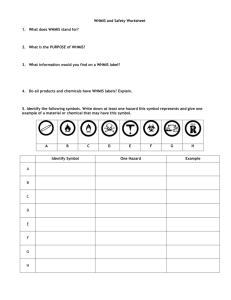
Annual Learning Package Workplace Hazards WHMIS Safety Core Curriculum 2013 WHMIS Did You Know? What does WHMIS provide for us? During the course of the workday health care workers can be exposed to potentially hazardous agents. This may happen while performing: Diagnostic testing Certain procedures Patient care activities Support services e.g. Housekeeping WHMIS is a nationally based hazardous materials workplace information system and forms Canada’s hazard communication standards. It provides workers with improved hazard information through a system of labels and product information sheets called MSDS. It provides: Accurate consistent information for deciding how materials should be stored, handled and used A system for easy hazard recognition WHMIS is the “Right to Know” Legislation WHMIS legislation applies to all workplaces in Canada and both federal and provincial governments have passed supporting WHMIS legislation. WHMIS Means: Federal Legislation Bill C-70 Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System Provincial Legislation Bill 79 MSDS Means: Material Safety Data Sheet Amended the Hazardous Product Act Identifies “controlled Products” Ensures the provinces applies the WHMIS framework Outlines supplier requirements 2013 Safety Core Curriculum – WHMIS 1 Provides specific details about WHMIS Outlines roles and responsibilities of employees and employers to ensure safe work environments WHMIS What is a hazardous or controlled product? It is any substance that can produce adverse effects to the health or safety of a worker Because some materials are covered through other legislation they may be exempt or partially exempt from WHMIS legislation. Fully exempt products include: Wood and wood products Manufactured articles Tobacco or products derived from tobacco Hazardous wastes Products covered by Transportation of Dangerous Goods Legislation Partially exempt products include: Some consumer products Cosmetics and drugs Explosives Pesticides Radioactive substances Controlled Products Classification – Hazard Symbols WHMIS applies only to controlled products. Under the legislation all controlled products are classified by their potential hazard. Products can fall in one or more of the classifications for hazardous materials. Symbol and Name Class A: Compressed Gas Class B: Flammable or Combustible Definition and Risks Precautions and Examples Normally gases are kept in pressurized containers Contents are under pressure and could explode Do not drop/rupture Store away from heat sources Examples: Oxygen, Nitrous Oxide Continue to burn after exposed to a flame or ignition source Potential fire hazard Keep away from heat sources or sparks and other materials that can ignite Ensure electrical sources are safe Examples: Isopropyl Alcohol, Acetone, Xylene, Varsol Store away from heat sources; increased fire and explosive hazard Store in proper containers Examples: Oxygen, bleach pak (Chlorine Bleach) Wear proper protective equipment and handle with care Examples: Gentian violet, formalin Class C: Oxidizing Materials Class D: Materials Causing Immediate and Serious Toxic Effects Can cause other materials to burn or support combustion May cause combustibles to explode or react violently Poisons/potentially fatal materials which cause immediate and severe harm Will cause rapid injury or death on contact Fatal if ingested or inhaled 2013 Safety Core Curriculum – WHMIS 2 WHMIS Symbol and Name Class D: Materials Causing Other Toxic Effects Class D: Biohazardous Infectious Material Class E: Corrosive materials Class F: Dangerously Reactive Materials Definition and Risks Have harmful effects after repeated exposures or over long periods of time May sensitize you so you develop an allergy or rash May cause cancer or birth defects May be contagious, contains bacteria or viruses and lead to infective disease Precautions and Examples Examples: Xylene, Formalin, Crew Klean ‘N Shine, Multi Surface Crème Cleanser Handle with care and adhere to Standard Precautions Examples: Medical wastes, contaminated sharps May react with metal, skin and other body tissue such as lungs Inhaled vapours may cause lung damage Wear protective equipment Avoid eye contact Examples: Iodine, Glance HC (hyperconcentrate), Bleach pak (chlorine bleach) May have unexpected reactions Very unstable and may undergo a rapid chemical change if exposed to shock, increased temperature or pressure May react with other liquids, releasing a toxic gas or cause explosion Avoid sudden temperature changes Do not mix products Examples: Acetylene COMPRESSED GAS A compressed gas is a substance that is a gas at normal room temperature and pressure, and is contained under pressure, usually in a cylinder. Some compressed gases (e.g. acetylene) are stabilized in the cylinder by dissolving the gas in a liquid or solid mix. Hazards of compressed gas: Sudden, uncontrolled release of cylinder contents – damaged cylinders can rocket or spin out of control causing significant injury and damage. Knocking over an uncapped cylinder breaking the cylinder valve can cause this type of incident. Suffocation – a compressed gas cylinder contains a huge volume of chemical. For example a liter of liquid nitrogen forms 700 litres of nitrogen gas at room temperature. A leak in a confined area could displace air and cause people to suffocate. Frostbite— gases escaping from a cylinder may be very cold and cause frostbite. Severe frostbite can lead to permanent skin damage. Other Hazards – a compressed gas may also be labelled with other WHMIS designations such as toxic, explosive, or oxidizing agent. In a health care environment where compressed gas is used often (i.e. oxygen tanks) it is important to remember to utilize safe handling, storage and transport practices. During use and storage tanks must be properly labelled and secured, so as to avoid possible injury due to a rolling, falling, or damaged cylinder. Always store full and empty cylinders in separate locations, and secured in racks, carts, or chained to the wall to prevent cylinders from falling and exploding 2013 Safety Core Curriculum – WHMIS 3 WHMIS Key Elements of WHMIS: 1. 2. 3. Product Listings and MSDS Material Safety Data Sheets Labels Education and Training All products and their accompanying MSDS have been inventoried. The product listings and current sheets are available. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) How to access an MSDS at SMH: Hardcopy There is a WHMIS Binder that has the MSDS for the products used in the hospital located on each floor near the elevator bank. There are master binders of all MSDS sheets located in Materials Management and the Emergency Department. These sheets are an important source of information for all health care workers. The supplier of the controlled/hazardous product provides the information sheet. It consists of 9 categories of detailed information about such areas as: Health hazards First aid Protective equipment Storage of the product On-Line ** NEW They are accessible via the computer network at SMH on the Shared Data Drive. S:\Material Safety Data Sheets The sheets must be kept current and must be less than 3 years old. In addition they must be easily accessible to all employees. Johnson wax PROFESSIONAL Material Safety Data Sheet GOOD SENSE SC LIQUID AIR FRESHENER National Fire Fire Hazard Protection Association (NFPA) Health Protective Clothing Specific Hazard None required Emergency Overview Reactivity Hazardous Material Health 2 Information System Fire Hazard 0 (HMIS) Reactivity 0 Colourless Liquid See Section 8 CAUTION: May be mildly irritating to skin. May cause eye irritation. Section 1. Chemical Product and Company Identification Product Name Good Sense SC Liquid Air Freshener Product Use Industrial/Institutional Air care. This product is intended to be diluted prior to use MSDS # 113915002 U.S. Headquarter s Johnson Wax Professional 8310 16th Street Sturtevant, Wisconsin 53177-0902 Phone (888) 352-2249 MSDS Internet Address: www.iwc.com Canadian Headquarte rs Code PMS# 7826 448696 Validation Date Print Due Supersedes In Case of Emergency 8/2/2002 8/2/2001 7/30/2001 Johnson Wax Professional 100 Matheson Blvd. E. Ste.203 Mississauga ON L4Z 2G7 Phone (905) 755-0913 or (888) 746-5971 Section 2. Composition and Information or Ingredients Ingredient CAS # % by Weight Exposure Limits Water Alcohol Eloxylates 7732-18-5 68439-46-3 60-100 5-10 Not available Not available Sod Xylene Sulfonate 1300-72-7 1-5 Not available 1-5 Not available Fragrance (800) 851-7145 LC50/LD50 Not available ORAL (LD50): Acute 1378 Mg/kg (Rat): DERMAL (LD50); Acute: >2000 mg/kg [Rabbit]: Not available Not available 2013 Safety Core Curriculum – WHMIS 4 WHMIS WHMIS LABELS Workplace Label Product labels are often the first identifier of a WHMIS warning. They provide basic information while the MSDS provides very detailed information. A workplace label must be attached to a hazardous product under the following situations: If a product is purchased in bulk from a supplier and distributed If transferring or decanting a product from the supplier’s container to another container If the supplier or original label is accidentally removed or cannot be read 2 types of WHMIS labels include: Supplier Label Workplace Label The workplace label does NOT have hazard symbols or a hatched border Supplier Labels The manufacturer of a hazardous product must provide supplier labels. All hazardous products of 100 mL or more must be labelled and information must be provided in both French and English. 1 Name of Product The distinguishing features of the supplier label are: the hatched border and square corners one or more hazard symbols product identifier (name of product) name of company that sold the product a statement that an MSDS is available risk phrases (words that describe the main hazards of the product) precautionary measures (how to work with the product safely) first aid measures Statement indicating that a copy of a material safety data sheet (MSDS) is available Safe handling instructions 2 3 How to complete the Workplace Label Information for filling out the workplace label can be found on the supplier label or MSDS. The workplace label is required to have 3 pieces of important information 1. Name of the product 2. A statement indicating that a material safety data sheet is available in the work place 3. Safe handling instructions 2013 Safety Core Curriculum – WHMIS 5 WHMIS Other Types of Labels Products exempt from WHMIS legislation frequently have their own identifying system warning us of potential hazards. For example, consumer products that are hazardous must be labelled if they are poisonous, corrosive, flammable or explosive. Poison Corrosive Flammable The hazard symbols are typically shaped as: Explosive Triangle Diamond Octagon CAUTION DANGER Moderate hazard/long-term or hidden harm Severe hazard/ immediate harm WARNING Special hazard/ special When working with these products it is the employee’s responsibility to: Read the labels and follow warnings with these products Ensure labeling is intact Place a workplace label on the product if placed in a container other then the orginal 2013 Safety Core Curriculum – WHMIS 6 WHMIS Who has Responsibility Under WHMIS? Legislation has placed responsibilities on the Supplier of hazardous materials Employer Employee Responsibilities of a Supplier Suppliers must: Determine which product are designated as “Controlled Products” according to legislation Assign an appropriate WHMIS category or symbol Attach a supplier label to the product Provide an MSDS for every hazardous product Update MSDS and label with new information at least once every 3 years Responsibilities of an Employee Employees must: Participate in training programs Use information learned to protect their own health and safety i.e. wear protective equipment Read labels and refer to MSDS before using a product Apply workplace labels when decanting or if supplier label is defaced Know the location of the MSDS inventory Responsibilities of an Employer Employers must: Ensure products are labelled properly Ensure the MSDS is received from the supplier Maintain an up to date and readily accessible MSDS inventory Advise employees of hazards and required protection Train workers so they understand information on labels and MSDS Have protective equipment available 2013 Safety Core Curriculum – WHMIS 7 WHMIS Exposure to a Hazardous material can occur through: Factors influencing whether a product can affect your health: Inhalation Breathing in hazardous fumes How toxic the material is Amount entering your body How quickly it is absorbed into the bloodstream Where it goes in your body i.e. target site How the body deals with it or eliminates it Four Main Sites Where Disease Can Occur Ingestion Accidentally swallowing or drinking a hazardous liquid At the site of entry (lungs, skin, intestine) In the blood In the nervous, reproductive and digestive systems In the organs (liver, kidney, bladder) *Exposure can lead to acute or chronic effects* Absorption Skin/eye contact with a hazardous material How can you protect yourself: Injection Through blood and body fluids and needlestick injury Be knowledgeable about products you are using at work Read labels and MSDS Never mix controlled products together Wear protective equipment Avoid direct contact with skin, eyes, mucous membranes Avoid inhaling fumes Wash your hands frequently Prevent needlestick injury 2013 Safety Core Curriculum – WHMIS 8 WHMIS WHMIS ANNUAL LEARNING REVIEW TEST 1. Which of the following are the three key elements of WHMIS: a. MSDS’s, controlled products and labels b. Training, labels and SDS’s c. Labels, MSDS’s , education/ training. d. None of the above 2. Which is/are key area(s) of employer responsibility under WHMIS? a. Maintaining MSDS b. Ensuring products are labelled c. Providing protective equipment d. All of the above 3. Hazardous wastes are fully exempt from WHMIS legislation. a. True b. False 4. If you pour an cleaner from a large container into a smaller container for use during the next couple of days you must: a. Label the small container with a workplace label. b. Hide the small container when not in use. c. Store it with other solutions in similar containers in your department. d. Be careful not to inhale while pouring. 5. WHMIS supplier labels …. a. Act to warn workers of the dangers of hazardous products b. Have a distinctive cross-hatched border c. Must be in both English and French d. All of the above 6. What do the letters on WHMIS stand for? a. Workplace Healthy Materials Information System. b. Workplace Hazardous Management Information System c. Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System d. None of the above 7. Which is NOT a key area of employee responsibility under WHMIS? a. Knowing the location of MSDS inventories b. Completing education and training c. Assign an appropriate WHMIS category or symbol d. Reading labels and refer to MSDS before using a product 8. Compressed gas cylinders MUST be stored… a. Free standing b. In one area whether full or empty c. In racks, carts, or secured to the wall, bed, stretcher or wheelchair d. None of the above 2013 Safety Core Curriculum – WHMIS 9 WHMIS 9. What are the four entry methods for chemicals to enter the body: a. Ingestion, intravenous, inhalation, absorption b. Ingestion, absorption, exhalation, injection c. Ingestion, absorption, inhalation, injection d. Ingestion, inhalation, exhalation, intravenous 10. Three hazards which are associated with compressed gas are… a. Sudden release of contents, suffocation and explosion. b. Suffocation, frostbite and explosion c. Sudden release of contents, suffocation and frostbite d. None of the above Answer the following questions using the MSDS found in the reference binders or shared drive S:| 11. What Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is required when using Accel wipes to clean equipment: a. Goggles, gloves, gown b. Gloves c. Respirator face mask d. None 12. A container (large or small) containing Formalin should be transported in a: a. Card box b. Plastic container to contain any spills c. Your pocket d. In your bare hands 13. Match the hazard symbol with the correct statement: Using the Answer Sheet provided, fill in the appropriate answer bubble Example: 13i) = Symbols i ii iii iv v vi vii viii Meanings A. May explode if the container is dropped, falls or is punctured C. Can cause long term effects such as cancer. E. Will burn readily if exposed to sparks or fire G. May contain material that is contagious, contains bacteria or viruses and lead to infectious diseases B. Fatal if eaten or inhaled. D. May react with other liquids, releasing a toxic gas or cause explosion F. Can cause other materials to burn or support combustion H. May react with skin and other body tissue such as lungs 2013 Safety Core Curriculum – WHMIS 10