Ribosomes and ER
advertisement
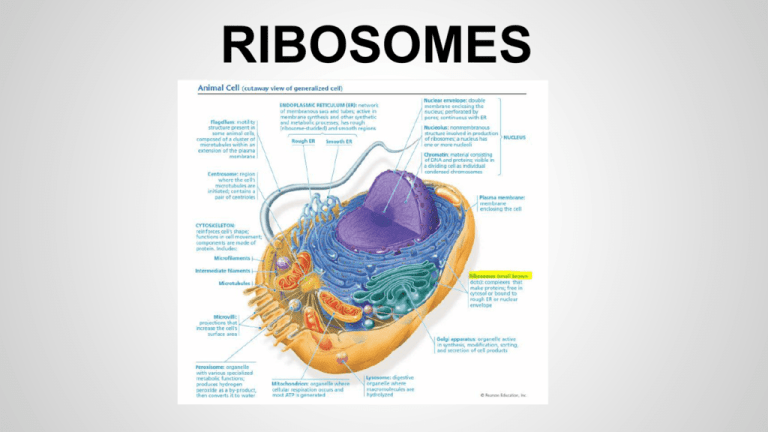
RIBOSOMES Location -Free Ribosomes: in cytosol -Bound Ribosomes: outside of ER or Nuclear Envelope -Smooth ER has no ribosomes -Rough ER has ribosomes Functions of Ribosome -Main function: carry out protein synthesis More Functions -Most Ribosomes in cytosol make enzymes that catalyzes the first step in sugar breakdown. -Bound Ribosomes make proteins usually ready for insertion into membrane, packaging with certain organelles, and secretion. Endoplasmic Reticulum Alila Medical Media What is the Endoplasmic Reticulum? - The “ER” is a network of membranes and sacs that is found in the inner core of the cytoplasm and is connected to the nucleus of the cell. Its primary function is to modify protein, make macromolecules, and transfer substances throughout the cell. ER is only found in eukaryotic cells There are two basic types of ER - Rough ER - Smooth ER Designua Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum(RER) - The RER is also attached to the nuclear envelope that surrounds the nucleus which allows for the movement of molecules through both membranes. Ribosomes are attached to some parts of the ER which is why it's called “Rough”. Ribosomes main purpose is to create proteins and then send it to the RER which processes them and passes them on to the Golgi Apparatus. Chris Hawes, The Research School of Biology & Molecular Sciences, Oxford Brookes University, Oxford, UK Darryl Leja, NHGRI Protein Synthesis Process - Transcription - - - The process of protein synthesis starts when RNA is transcribed from a DNA gene in the nucleus to create mRNA. The mRNA leaves the nucleus through tiny pores and then travels to the surface of the RER Transferal - In this stage, an enzyme attaches an amino acid to one end of transfer RNA (tRNA). On the other end of tRNA is a codon which will be used to bind when it reaches the mRNA. Translation - A ribosome attaches to the mRNA and reads the (AUG) codon. tRNA then brings the corresponding (UAC)anticodon as the ribosome moves down the mRNA strand. The molecule is then read, resulting in amino acids being joined together and the release of proteins. Smooth ER (SER) - - Regions not containing ribosomes. SER synthesizes carbohydrates and lipids as well as male and female hormones in brain cells Produces certain enzymes that detoxifies compounds in the cell by metabolizing the natural and ingested toxins. - Example: The SER of liver cells metabolize a commonly ingested toxin: alcohol. When the SER is not metabolizing a compound, it acts as a storage site until metabolism does begin again. Work Cited Reece, Jane B., and Neil A. Campbell. Campbell Biology / Jane B. Reece ... [et Al.]. Boston: Benjamin Cummings / Pearson, 2011. Print. Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, n.d. Web. 15 Sept. 2015.