Skin and Body Membranes
advertisement

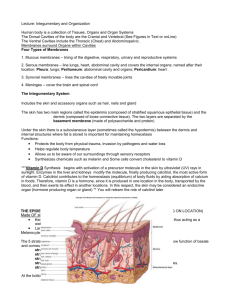
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes ___________________________ Line _________________________ Form ____________________________________________ Classification of Body Membranes _______________________membranes ___________________ membranes _________________ membranes _________________ membranes _____________________ tissue membranes _____________________ membranes Cutaneous Membrane ___________________ membrane = __________ _________ membrane __________________ protective boundary ________________________ epidermis is composed of keratinized _______________________________ epithelium Underlying dermis is mostly ________________ connective tissue Cutaneous Membranes ________________ Membranes Surface epithelium type depends on ____________ _______________ _______________ epithelium (_______, esophagus) Simple ________________ epithelium (rest of ________________ tract) Underlying _____________ connective tissue (lamina _________) Lines all body _________ that _______ to the _______________ body surface Often adapted for ________________ or _________________ _________________ Membranes Surface is a layer of simple _______________ epithelium Underlying layer is a _______ layer of ____________ connective tissue Lines open body cavities that are ___________ to the exterior of the body Serous membranes occur in _________ separated by serous __________ ________________ layer covers the outside of the organ ______________ layer lines a portion of the wall of __________ body cavity ______________ Membranes ______________ serous membranes _____________________ _________________ cavity _______________ Around the _______________ _______________________ Around the heart Connective Tissue Membrane ________________ membrane ____________________ tissue only Lines fibrous capsules surrounding _______________ Secretes a ______________________ fluid _________________________ System ___________ (cutaneous membrane) Skin derivatives Sweat glands ________ glands Hair ___________ Skin Functions Skin Structure _______________________—outer layer ___________________ squamous epithelium Often ________________________ (hardened by keratin) ___________ _____________ connective tissue Subcutaneous tissue (_________________) is deep to dermis Not part of the ___________ Anchors skin to underlying _______________ Composed mostly of __________________ tissue Layers of the Epidermis ________________ ________________ (stratum germinativum) _____________________ layer of epidermis Lies next to _________________ Cells undergoing __________________ ____________________ cells are pushed upward to become the more ________________________ layers Stratum __________________ Stratum _________________________ __________________ ___________________ Formed from ___________ cells of the deeper strata Occurs only in thick, hairless skin of the ___________ of hands and ____________ of feet Stratum ___________________ ______________________ layer of epidermis _________________-like dead cells are filled with ________________ (protective protein prevents water loss from skin) Summary of layers from deepest to most superficial Stratum _____________ Stratum ___________________ Stratum _____________________ Stratum ________________ (thick, hairless skin only) Stratum ___________________ Melanin ______________ (melanin) produced by _______________________ Melanocytes are mostly in the stratum _________________ Color is _______________ to brown to ________________ Amount of melanin produced depends upon ______________ and exposure to ___________________ Dermis _________ layers _____________________ layer (__________ dermal region) Projections called ___________ ____________________ Some contain ____________________ loops Other house _________ receptors and ___________ receptors _____________________ layer (___________ skin layer) ___________ vessels __________ and oil glands Deep _______________ receptors Overall dermis structure __________________ and _____________ fibers located throughout the dermis Collagen fibers give skin its __________________ Elastic fibers give skin ____________________ Blood vessels play a role in body ________________ ______________ Skin Structure Normal Skin Color Determinants ________________ Yellow, brown, or black pigments ________________ Orange-yellow pigment from some vegetables ________________ ________ coloring from blood cells in dermal capillaries ______________ content determines the extent of red coloring Skin Appendages Cutaneous glands are all _______________ glands __________________ glands _____________ glands __________ Hair ___________________ ______________ _________________ glands Produce _________ ___________________ for skin Prevents _____________ hair Kills ___________________ Most have _________ that empty into hair _________________; others open directly onto skin _________________ Glands are activated at __________________ Sweat glands Produce ______________ _________________ distributed in skin Two types _______________ Open via duct to pore on skin surface _______________ Ducts empty into hair follicles Sweat and Its Function Composition Mostly _______________ ___________ and vitamin ____ Some ___________________ waste Fatty acids and _____________ (_____________ only) Function Helps dissipate _____________ _______________ ____________________ waste products Acidic nature ______________ bacteria growth Odor is from associated ____________________ Hair Produced by hair ___________________ Consists of hard __________________ epithelial cells _____________________ provide pigment for hair color Hair anatomy Central ________________ ________________ surrounds medulla _________________ on outside of cortex Most heavily _______________________ Associated hair structures Hair __________________ Dermal and _________________ _____________ surround hair root _____________ ________ muscle ___________________ muscle Pulls hairs _________________ when cold or frightened ____________________ gland _______________ gland Nails __________-like _______________________ of the epidermis Heavily ________________________ Stratum _____________ extends beneath the nail bed Responsible for _________________ Lack of ______________________ makes them colorless Nail structures __________ ______________ Body is the visible _________________ portion ___________ of nail ___________________ in skin ______________ is the proximal nail fold that projects onto the nail body Skin Homeostatic Imbalances Infections ___________________ foot (______________ pedis) Caused by _________________ infection Boils and _________________________ Caused by ____________________ infection Cold sores Caused by _________________ Infections and ______________________ ________________ dermatitis Exposures cause allergic reaction ____________________ Caused by _______________________ infection ______________________ Cause is unknown Triggered by trauma, infection, ______________ Burns Tissue damage and cell death caused by __________, electricity, UV radiation, or _____________________ Associated dangers _______________________ _________________________ imbalance _________________________ shock Rule of Nines Way to determine the _________________ of burns Body is divided into _______ areas for quick estimation Each area represents about ___% of total body __________ __________ Severity of Burns __________-degree burns Only _________________ is damaged Skin is _______ and ___________________ ___________________-degree burns __________________ and ______________ dermis are damaged Skin is red with _______________ _________________-degree burns Destroys ____________ skin layer Burn is _________-white or ____________ Critical Burns Burns are considered critical if Over ____% of body has _______________-degree burns Over ____% of the body has _________-degree burns There are ___________-degree burns of the ________, hands, or feet Skin Cancer Cancer—_____________________ cell mass Classified two ways ________________ Does not spread (encapsulated) ____________________ ________________________ (moves) to other parts of the body ___________ cancer is the most common type of cancer Skin Cancer Types ___________ cell _____________________ ____________ malignant Most ________________ type Arises from stratum ______________ ____________________ cell carcinoma Metastasizes to ____________ nodes if not removed Early removal allows a good chance of __________ Believed to be _______-induced Arises from stratum ____________________ ____________________ melanoma Most _______________ of skin cancers Cancer of ________________________ Metastasizes rapidly to ____________ and ___________ vessels Detection uses ___________ rule ABCD Rule A = ______________________ Two sides of pigmented mole do not match B = _____________ _________________________ Borders of mole are not smooth C = ________________ Different colors in pigmented area D = ____________________ Spot is larger then 6 mm in diameter