Unit 10 – Flatworm, Roundworm and Segmented Worms
advertisement

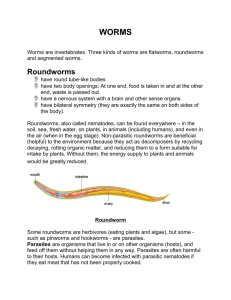
Unit 10 – Flatworm, Roundworm and Segmented Worms Flatworms Characteristics of Flatworms Flatworms (phylum ______________________________) are a step “up” the ladder of evolution being ________________________________________________________. Flatworms have a _____________________________. This body plan means they have ___________________________________________________________________________ __________________________. However, _______________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________. These specialized systems are exemplified by the Planaria which is a heterotrophic free-living flatworm. There are three Classes of flatworms. Class Turbellaria – example Planaria free living, incomplete gut, no suckers or hooks. Class Trematoda – example flukes parasitic, incomplete gut, _____________ _________________________________. Class Cestodae – example tapeworms parasitic, no gut, ___________________ _________________________________ _________________________________. Body Plan Summary - Both primitive and advance characteristics - ____________________________________________. - ______________________________________ - ______________________ - concentration of sensory organ and nervous tissue at anterior end of body - ________________________________________ ___________________________________________ (germ layers). - Ectoderm – forms outer epidermis. - Mesoderm - forms muscle tissue and reproductive, and excretory organs. - Endoderm – forms inner gut. - ____________________________________________ Movement Some larval stages move using cilia while adults move using muscle contractions. Class Turbellaria Planaria __________________________________________________________________ ___________________________. The __________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ on the end of a muscular ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ to the body. Indigestible wastes leave the same way they came in through mouth. There are approximately 4,500 species that live in the ________________. Some live in ________________________ Planaria Digestive System The digestive system in Planaria is similar to that of the cnidarians. It consists of a _________ _____________________________. A pharynx extends from the underside of the flatworm and sucks up food through the mouth. The food is then ______________________________ ___________________________. Wastes are expelled through the same opening. Nutrients can be carried through the organism efficiently by ________________ because the flatworm is so thin. Label Planaria Digestive System Planaria Excretory System Excretion is the expulsion of excess water and wastes. These wastes differ from those expelled from the gastrovascular cavity in that wastes excreted by the excretory system were first digested and entered the body of the flatworm. Planarians have specialized cells called _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ Planaria Reproductive System Planarians are ___________________________, meaning they are ______________________________________, but they ______________________________________ between organisms. Adjacent flatworms will align themselves so that they will simultaneously fertilize each other. Planaria also have amazing _________________________________________. If a planaria is cut lengthwise, it will grow into two separate animals. And, if a planarian is cut down the center, but not completely, it will develop two heads. Label Planaria Reproductive System Planaria Nervous System The nervous system of the planarian consists of ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________. This type of nervous system is referred to as a ___________________________. The cephalization consists of a brain, chemosensitive organs, and two eyespots. The chemosensitive organs guide the flatworm toward food and the eyespots are sensitive to light. Planaria will move away from light probably to avoid predation. The nervous system also controls muscles used for movement. Other Systems in Planaria CIRCULATORY and RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS – not true systems - part of the gastrovascular cavity. - ____________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________. MUSCULAR SYSTEM – a true system. -controlled by longitudinal, circular, and oblique layers of muscle sometimes assisted by secreting a layer of mucus. SKELETAL SYSTEM – NONE Class Trematoda There are an estimated 9000 species of Trematoda. Many of these are ______________ (liver, lung, heart, intestine). Flukes are _________________________. Flukes have _____________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________. They absorb nutrients through the gastrovascular cavity. They have ___________________________ for excretion. Nerve cords and anterior ganglia make up the nervous system. They are _______________________________. Flukes have a _______________________________________ with numerous larval stages that infect a number of hosts. The entire external surface of a fluke is covered by a continuous sheet of fused cells called the ____________________________. The ________________________ consists of a layer of protein and carbohydrates that __________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________. Liver Fluke Life Cycle Class Cestoda There are an estimated 5000 species of Cestoda. An example is tapeworms. Tapeworms are ________________ animals and are specialized for living within a host. Most body systems have been lost as they are not required as the host provides nutrients. There are ___________________ ___________________________________ __________________________. Tapeworms ____________________________________ __________________ through their skin. The ____________________________________ ____________________________________ This adult tapeworm has a _____________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ While the tapeworm grows in the host's intestine, ___________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________. This species occurs most often in rabbits, cats and rodents, but sometimes humans, causing diarrhea, weight loss and abdominal discomfort. Adult tapeworms may grow 5-10 meters in length. Proglottids are body segments specialized for reproduction Tapeworms have a Scolex with hooks and suckers used to attach to the inside wall of the host intestine Tapeworm Life Cycle Tapeworm Reproduction Summary - Carried out by ______________________ ______________________________. - Tapeworms are ____________________ contain both ovaries and testes and ______ ___________________________________. - Zygotes are passed out of host’s body with feces. - Larvae hatch in water and in grass. - Larvae are eaten by a herbivore (________________________________) and the larvae then burrows through the wall of the intestine and into the blood stream. Intermediate hosts contain tapeworm cysts (__________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________. MMmmm Tapeworms As part of a University of Salford experiment to develop a diagnostic test for beef tapeworm, biologist Mike Leahy volunteered to grow this gruesome parasite inside his own gut. Mike swallowed the immature tapeworm cyst with a glass of red wine and the worm started to grow at an initial rate of four centimetres a week. Twelve weeks later he had to call a halt to the unusual experiment because he was getting married! After a dose of anti-worm pill Mike passed out an intact tapeworm three metres long. Parasitic Flatworms Flatworms that are parasitic on humans fall into two categories, _______________________ _________________. Due to the fact that they live in the gut of a host animal these flatworms have an anatomy __________________________________________. Generally, _________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ________________________. Parasitic flatworms will usually have hooks on the scolex (anterior region) to attach it to the wall of the gut and they have an ______________________ ______________________________________________ When a flatworm reproduces, the eggs are passed out with the feces. When consumed by another host the life cycle continues. Flukes and tapeworms can infect many different animal hosts. _________________________ ___________________________________________. One host when sexually mature called the primary host and a secondary host in which the eggs mature to larvae. Roundworms General Characteristics Roundworms Roundworms belong to the Phylum ______________________________ (also called ___________________________). Nematodes are the most speciose phylum after the arthropods. They occur in nearly every habitat including ________________ ___________________________________________________ ______________________ (they don't like dry places however). One species is known that can live in old vinegar (Turbatrix aceti) and another that has only been found in German beer mats. Though only about 80 000 species have been described some scientists estimate there may be as many as a million species all told. They can occur in very dense numbers in the soil and rotting vegetation, as many as 90 000 have been found in a single rotting apple, while millions occur in the top 3cm (1 inch) of a square metre of good quality soil. While there are a huge number of ______________________ Nematodes there are also a large number of __________________________________, many of which cause diseases to man and other animals as well as to plants, nearly every living organism has been found to be parasitised by one species of nematode or another. Most nematodes are reasonably small, they range in size from 100 micrometres in length (1/10th of a mm or 1/250th of an in) to the female Giant Nematode Dioctophyme renale which may be up to 1 metre, or 3 ft long. Body Systems in Roundworms Roundworms (phylum ____________) have a _________________________ _______________________________. This body plan is more advanced than the Platyhelminthes and Cnidarians which, you should recall from previous units, have a single opening functioning as a mouth and anus called a sac plan. Nematodes _____________________ _______________________________. This design allows for ____________ ______________________________ ______________________. At the anterior (head) end there is a mouth which has 3 lips behind which predatory species possess a few teeth, this leads to a ___________________. The pharynx of Nematodes is an efficient pump and forces food into the intestines as it can be used to suck liquid food into the mouth. ________________________________________________________________________. Digestive System Roundworms have a __________________________________________. It is a long tube shaped digestive tract with _____________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________. As food is pushed through digestive tract it is digested and ____________________________ _________________________ into the cells of the body. Undigested remains continue on through tract and are _________________________________________________________ _________________________. Free living round worms are often _______________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________. They excrete metabolic waste through their body walls by __________________. Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Roundworms have __________________________ _____________________________________. They breathe and excrete waste through their body walls. They do not have an internal transport (circulatory) system and rely on ________________________. The _____________________________ is filled with fluid and it distributes digested foods and dissolved oxygen to the body. It also acts as ___________________________________. Excretory System In roundworms, ____________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________. Nervous System Nematodes, especially free living forms generally have a reasonably well developed nervous system. This is comprised of a circum-pharyngeal nerve ring and longitudinal nerves that extend down through the body to the various parts of the gut and the reproductive organs. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________. They have simple sense organs. Reproduction Nematodes are copiously reproductive and most of their body cavity, which is a _________________________________, is filled with paired sets of reproductive organs, either ovaries or testes. _______________________________________________________ _____________________________________. The female has long coiled ovaries that produce thousands of eggs every day. Eggs are stored in a uterus. The vagina leads to an external opening. ____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________. Sperm cells pass through the sperm duct though an opening at the posterior end of the worm. During copulation sperm is released into the vagina resulting in internal fertilization. After fertilization, _______________________ ______________________________________. The females lay eggs over a prolonged time period, thus a female Ascaris lumbricoides may lay her eggs at the rate of 200,000 per day and have had a total 27 million eggs within her at the start of her reproductive career. Summary Primitive Characteristics : - ___________________________. - No circulatory System. - No skeletal system. - ________________________________________________ Advanced Characteristics: - ______________________________________________. - Cylindrical shape (round worms). - _____________________________________________. Ectoderm – produces tough cuticle. Mesoderm – muscle and various organs. Endoderm – digestive tract. - ____________________________________________________ – mouth to anus! - ___________________________ - between the mesoderm and the gut is a fluid filled space. Ascaris Ascaris is usually diagrammed to typify roundworm anatomy. Ascaris is a roundworm that is ___________________________. The entire life cycle can take place in the human body and the eggs can be passed out with feces. Eggs in food or water are _____________________ _____________________________, the eggs hatch in the small intestine, larvae enter the blood vessels and are carried to the lungs, larvae then travel to the throat and are swallowed. Adult ascaris worms live in the small intestine with eggs leaving the host in the feces. With a longitudinal cross section the tube within a tube design can be observed. It can also be observed that the digestive system is not very well developed as the length of the gut after the pharynx is unchanged and reproductive organs are quite large in comparison to the body. This is a characteristic of an internal parasite to have a simple digestive system and well developed sex organs. Ascariasis is the human disease caused by ____________________ with as many as ______________________________________________________. It is common in tropical regions, regions with poor sanitation, poor personal hygiene, and places where human feces are used as fertilizer. Intake of food or drink contaminated with Ascaris eggs causes the infection. The symptoms of Ascariasis are listed below. Passing worms in stool. Vomiting up worms. Worms exiting through the nose or mouth. Low-grade fever. Cough. Bloody sputum. Wheezing. Shortness of breath. Skin rash. Vomiting. Stomach pain. Note: There may be no symptoms. Label Ascaris Other Parasitic Roundworms Even though ________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________ are typically enough to ward off roundworm infection many roundworm diseases are common worldwide including some in North America. _________________________________ are common in North America, while more serious infections such as ______________________________________ are common in Africa and are rarely seen here. Trichina worm causes Trichinosis when the host eats __________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________. Trichinosis forms cysts in the muscles of its victims and causes symptoms such as pain, blisters, muscular weakness, and anemia. The images below show a trichina worm and a cyst formed in muscle around a worm. ...... Pinworms are tiny pin-shaped nematodes known as Enterobius vermicularis to the medical and zoology communities. Also called seatworms or threadworms these small, whitish roundworms are responsible for contagious intestinal _______ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ ____________________________________________ Although adult pinworms inhabit the large intestine, the eggs are laid outside of the anus during the night creating a severe itching sensation. Other symptoms include disturbed sleep, decreased appetite and weight loss. Spread from person to person usually occurs with ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ The eggs can also drift through the air where they are inhaled or swallowed. Once they enter the new host the eggs hatch in the small intestine and travel down to the large intestine for maturation. _________________ _________________ _________________ _________________ _________________ _________________ _________________ _________________ _________________ Filaria worms __________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________. Elephantiasis is transferred by mosquitoes and blocks lymph vessels as the worms increase in size. Lymph vessels return fluid to the bloodstream from the tissues so when the vessels are blocked the limbs increase greatly in size. Loiasis, called eye worm or loa loa, is endemic to the rainforests of central and western Africa where mango flies of the Chrysops species serve as both intermediate host and the parasite vector. About 13 million people are currently infected. This map shows the distribution of eye worm infections. Guinea worms, also known as the stick worm, form ulcerating blisters in human skin. People get infected when they drink standing water containing a tiny water flea that is infected with the even tinier larvae of the Guinea worm. Over the course of a year in the human body, the immature worms pierce the intestinal wall, grow to adulthood, and mate. The males die, and the females make their way through the body, maturing to a length of as much as 3 feet, and ending up near the surface of the skin, usually in the lower limbs. The worms cause ____________________________ __________________________________ __________________. To soothe the burning, sufferers tend to go into the water, where the blisters burst, allowing the ______________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________. In the water, the larvae are swallowed by small water fleas, and the cycle begins again. These parasites can cause long-term suffering and sometimes crippling after-effects. The worms are slowly removed from the body by winding them slowly around a stick to pull them out. Segmented Worms General Characteristics of Annelids The annelids or _____________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________. The general characteristics of an Annelid are similar to those of a roundworm. They are _________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________. However, an Annelid also has a _____________________ ___________________________. Both the coelom and segmentaion allow for greater specification of body parts. _____________________________________________________ and allow structural support by creating a hydroelastic skeleton. ________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ which will be discussed in the anatomy of the earthworm later in this lesson. The ___________ ___________________________________________________________________________ __________________ (filtering organ) in each segment. The Annelid moves by alternating contractions of circular and longitudinal muscles. The circular muscles encompass the body wall and therefore contractions cause the body to become long and thin. The longitudinal muscles run the length of the body and cause the body to shorten and fatten. The Phylum name Annelida means "Ringed in Form". _______________________________ ______________________________________________________________ within the animal for different purposes. The coelom is divided into separate compartments (septa) by partitions. These septa enable different compartments to contract or expand independently. Duplication of some of the organ systems in each segment provides insurance against injury. There are three Classes of Annelids that we will discuss in this book. 1. Class Polychaeta meaning "____________________________". 2. Class Oligochaeta which _________________________________________. 3. Class Hirudinea which ____________________________________. Marine Worms Class Polycaeta are so named because they have many _______ on their segments. These _______________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________. In some marine worms they are arranged like a paddle and are called _______________________________________________ ___________________________________ because Annelids breath through their body wall by _________________ and parapodia expand the surface area of the animal. Some marine worms such as Nereis have a more noticeable cephalization. Nereis has an invertible pharynx that exposes chitinous (made of chitin - a strong complex carbohydrate common to fungi cell walls and some animals) jaws, eyes, and other sense organs. Some marine worms have bristles to aid in defense. Nereis seen below is an example of a free living predatory marine worm. Predatory worms also have ____________________________________________________. Other marine worms live in tubes that may be made of calcium, silica (sand) or protein. These tube worms are filter feeders. Here's what these worms look like when retracted. Earthworms Segmented worms of the class ___________ ___________ (maximum 20 setae per segment) and are exemplified by the common ____________________, Lumbricus terrestris. Earthworms do not have cephalization as advanced as marine worms such as Nereis, but they do _____________ ___________________________________ ______________________________. They do not have eyes, but are capable of detecting and avoiding water without actually coming in contact with it. Earthworms live in soil and freshwater while some types are found in the ocean. Earthworms act as ______________________, maintain the fertility of soil, release nutrients into the soil, loosen and ________________ ________________________________________. Some segmented worms such as the Tubifex (sludgeworm) seen in the third picture can survive in polluted sediments and areas with little oxygen. Earthworm Digestion The digestive system of the earthworm and other annelids is quite advanced. In the earthworm, ______________________________________________ as they burrow ____________________________________________. From the pharynx food moves through the ___________________________________________________________ ____________________________. It ____________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________. The _______________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________. The intestines have a typhlosole, which is a fold that increases surface area for absorption. ____________________ _________________________ (castings that are good for the garden) __________________ _____________________________. Here's an image showing Oligochaeta digestive system. Earthworm Circulation The circulatory system of an Earthworm consists of a ________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ _______________________ that connect the two vessels together behind the head region. The branches _______________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________. Due to the pulsating action of the branches, which is similar to the action of hearts, they are termed "hearts" or pseudohearts. The purpose of this ___________________________________________________ is to transport oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients and wastes throughout the body of the earthworm. Earthworms have _____________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ and into small blood vessels when the skin is moist. Earthworm Excretion As stated in the general characteristics, ____________________________________ ________________________. In earthworms, ____________________________________ ____________________________________ ___________________________________. The cellular wastes and excess water are eliminated through these nephridia. Each segment of the earthworm except the first three and last one have nephridia. Earthworm Nervous System The nervous system of an Earthworm is ____________ ____________________________________________ ______________________. Most body segments have a single ganglion. These worms also have an __________ _____________________________________________ and can respond to light, touch, chemicals, moisture, temperature, and vibrations. Movement in these worms is made possible by segmentation. ________________________________ ____________________________________________ ______________________. To move,______________ ____________________________________________ and contracts circular muscles in front of these segments. Hydrostatic fluid in the coelom increases pressure and elongates the worm. Then longitudinal muscles pull posterior segments forward as they contract and shorten. Earthworm Reproduction Earthworms are ____________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________. The clitellum is the relatively large band around the earth worm. _______________________ ________________________________________ (an individual worm cannot fertilize its own eggs) by aligning head regions with clitellums. Two earthworms press their ventral surfaces together with the anterior ends pointing in opposite directions. _________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ _________________________ as it transfers. Each earthworm injects sperm into the mucus which moves into a pouchlike seminal receptacle of each worm. After several days each worm secretes a tube of mucus and chitin (thick carbohydrate) which picks up the worms eggs and stored sperm. The sperm and egg are then expelled through a slime tube and fertilization takes place. The tube closes up to form a protective case for 2-3 weeks until the young worms hatch. Leeches Class ________________________________________ _____________________________________________ with approximately 300 species. Although ___________ ____________________________________________, many leeches are annelids which are ______________ ________________________________________________ _________________________________________. They ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ _____________________________________. They also ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ ________________________. If undisturbed, a leech can ingest 10 times its own weight in blood. A leech will drop off once finished eating and will not need to eat again for up to a year. Leeches are used in medicine________________________ _________________________ in amputated digits (fingers or toes) that have been surgically reattached. Body Plan comparison in the Worms This lesson compares the body plan of the three classes of worms discussed in this unit. The diagrams below are keyed as follows. Ectoderm: blue Endoderm: yellow Mesoderm: red _________________________ ________________________ _________________________ ________________________ Body cavity filled with Body cavity partially lined with mesoderm. mesoderm. ________________________ ________________________ Body cavity entirely lined with mesoderm.