PNS Lecture Slides PDF
advertisement

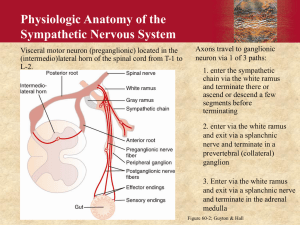
The Peripheral Nervous System Chapter 13-14 Nervous System Structural Overview Peripheral Nervous System • All neural structures outside of the brain and spinal cord. • Includes sensory receptors, peripheral nerves, ganglia, and efferent motor endings. Sensory Receptors • Respond to specific changes in their environment called stimuli • General Sensory Receptors: • Free nerve endings • Tactile (Merkel) discs • Hair follicle receptors • Tactile (meissner’s) Corpuscles • Lamellar (pacinian) corpuscles • Ruffini Endings • Muscle Spindles • Tendon organs Somatosensory Neural Integration • Three main levels of neural integration in the sensory system • Receptor Level • Circuit Level • Perceptual Level Processing at the Receptor Level • • Step 1: Stimulus excites receptor and action potentials reach the CNS • Stimulus must match the specificity of the receptor • stimulus must be applied within the receptor field • stimulus must be converted into a graded potential (transduction) Adaptation Processing at the Circuit Level • Step 2: Impulses must be delivered to the appropriate region of the cortex for localization and perception of the stimulus. Processing at the Perceptual Level • Step 3: Sensory input is interpreted in the cerebral cortex Perception of Pain • Activated by extremes of pressure or temperature • Sharp, then aching/burning. A delta, c fibers • Based on situation • Pain threshold versus pain tolerance Nerves • Cord-like organs composed of bundles of axons. • Connective tissue wrappings: • • endoneurium, perineurium (fascicles), epineurium. Nerves classified by transmission direction: • Sensory nerves, motor nerve, mixed nerves. Peripheral Motor Endings • The Neuromuscular Junction Motor Integration • Levels of Motor Control: • The Segmental Level (reflexes, CPG’s) • The Projection Level (initiate voluntary movement, oversee the segmental level). • The Precommand Level (Cerebellum, basal nuclei: coordination, timing, start/stop) Reflex Activity • The Reflex Arc • inborn or learned Components of a Reflex Arc 1. Receptor 2. Sensory Neuron 3. Integration Center 4. Motor Neuron 5. Effector • Can be either somatic or autonomic Spinal Reflexes • Stretch Reflex Spinal Reflexes • The Tendon Reflex Spinal Reflexes • The Flexor and Crossed Extensor Reflexes Superficial Reflexes The Autonomic Nervous System ANS Divisions and Roles • • Parasympathetic Division • Rest and Digest Division • Keeps body energy as low as possible Sympathetic Nervous System • Fight or Flight System • Prepares body for emergency situations Comparison of Somatic NS and ANS ANS Anatomy • Dual Innervation • Sites of Origin • Relative lengths of their fibers • Location of their ganglia ANS Anatomy • Parasympathetic (craniosacral) Division • • Cranial part • Occulomotor N. • Facial N. • Glossopharyngeal N. • Vagus N. (Multiple Plexi) Sacral Part • Pelvic Splanchic n. • Inferior hypogastric plexus ANS Anatomy • Sympathetic (Thoracolumbar division) • Preganglionic fibers arise from Lateral Horns of segments T1-L2 ANS Anatomy • Sympathetic trunks and pathways 3 Pathways of Synaptic Innervation • Synapse at the Same Level 3 Pathways of Synaptic Innervation • Synapse at a higher or lower level 3 Pathways of Synaptic Innervation • Synapse in a distant collateral ganglion anterior to the vertebral column ANS Physiology • Neurotransmitters and Receptors • Acetylcholine • • Released by all ANS Preganglionic axons and all parasympathetic postganglionic axons (cholinergic fibers) Norepinephrine • Most sympathetic postganglionic axons (adrenergic fibers) Cholinergic Receptors • Nicotinic Receptors • • Found on sarcolemma of skeletal fibers, all postganglionic neurons, adrenal medulla Muscarinic Receptors • Parasympathetic target organs Adrenergic Receptors • alpha and beta receptors • alpha 1, 2, Beta 1, 2, 3. • can be either excitatory or inhibitory Pharmacological Effects • Atropine (anticholinergic) • Neostigmine (anticholinesterase) • B2 activators (dilate airways) • Beta Blockers (slow heart rate, lower BP) Interactions of the Autonomic Divisions • Dual Innervation • Antagonistic Interactions • Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Tone • Unique roles of the Sympathetic Division • • thermoregulatory response to heat, renin release, metabolic effects Localized Versus diffuse effects Control of Autonomic Function • Brain Stem and Spinal Cord controls • Hypothalamic Controls • Cortical Controls