Problem set 1
advertisement

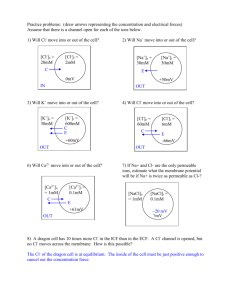
NS201A Fall 2010 Problem set 1. 1. Derive using the N ernst-Planck flux equation an expression for the voltage across a m em brane w hen net current = 0. Assum e only N a + , K+ , and Cl- are perm eant, so Itotal = IN a + IK + ICl and I = F z iJi, w here F is the Farad ay constant 2. Tw o solutions are separated by m em brane of thickness = d. The m em brane is perm eable only to K+ and Cl- and the fluxes are d escribed by the N ernst-Planck flux equation assum ing constant field . Mem brane thickness d = 5 x 10 =7 cm w ith d iffusion coefficients K+ = D K and Cl- = D Cl and partition coefficients K+ = k k+ and Cl- = k Cl-. Find: a. an expression of fluxes of K + and Cl- as a function of the voltage across the m em brane. b. an expression for current d ensity as a function of the transm em brane vo ltage w here F z iJi c. an expression for the voltage in the cond ition of zero net m em brane current. What is the num erical value of the current if: D K+ = D Cl- = 5 x 10-8 cm 2/ second KK+ = 10-3 and k Cl- = 2 x 10-4 Concentration of KCl on sid e 1 = 10 -2 M and sid e 2 = 10-1 M 3. In certain pathological cond itions, such as d ehyd ration, renal failure, cardiac glycosid e poising and seizure activity in the brain, large changes in the extracellular K concentration occur. Changes in extracellular K concentration can have large effects on m em brane electrical excitability, m ost dram atically in cells w here the resting potential d epend s on the inw ard ly rectifying K channel. The effect on the m em brane potential via K ir w ill differ in different cell types d epend ing on the P N a / P K ratio. The exam ple below gives values for N a and K ion concentrations and perm eabilities in pacem aker versus non -pacem aker cells in the heart. Card iac m uscle contains prim arily Kir. The values are given for norm al, low (hypokalem ia), and high (hyperkalem ia) serum K concentrations. Calculate: a) the equilibrium potential for N a and K using the N ernst equation; b) the resting m em brane potential E m using the Gold m an-Hod gkin-Katz equation. NS201A Fall 2010 PN a N ao N ai PK Ko Ki N on-p acem aker (N PM) norm al K 1 150 15 200 5 120 N PM: hyperkalem ia 1 150 15 400 7.5 120 N PM: hypokalemia 1 150 15 100 2.5 120 Pacem aker (PM) norm al K 1 150 15 20 5 120 PM: hyperkalem ia 1 150 15 40 7.5 120 PM: hypokalem ia 1 150 15 10 2.5 120 EN a EK Questions: a) What is the effect of hyperkalem ia on the m em brane potential E m of nonpacem aker cells? Does it d iffer from the K equilibrium potential? b) What is the effect of hypokalem ia on E m in non-pacem aker cells? c) What is the effect of hyperkalem ia on Em in pacem aker cells? Does it differ from non-pacem akers? Why? What effect w ould this have on pacem aker frequency (heart rate) d ) What is the effect of hypokalem ia on E m in pacem aker cells? Does it d iffer from non-pacem akers? Why? Does hypokalem ia increase or d ecrease heart rate? 4. Suppose a neuron contains only K + as the internal cation at a concentration of [K+ ]i and N a + as the only external cation at a concentration [N a + ]o. Design an experim ent to d etermine the perm eability ratio P N a / P K of the sod ium channel Em NS201A Fall 2010 using the constant field equation. What is the m eaning of the perm eability constant.