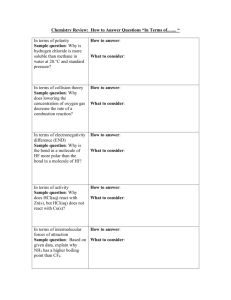
BIOL 2210 Study Guide CHEMISTRY Dr. Yoga sundram Matter
advertisement

BIOL 2210 Study Guide CHEMISTRY Matter Anything that occupies space and has mass Matter can be Solid, Liquid or Gas Energy can neither be created nor distroyed ( 1st law of thermodynamics) Energy can be Kinetic (produced by motion) or Potential (stored energy) Element is matter having unique physical and chemical properties Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Potassium, Sodium, Major elements in human body Calcium, Iron, Magnesium, Phosphorus, Chloride, Sulphur, Iodine C HOPKIN'S CaFe, Mighty Good, and add a pinch of Salt Atom Smallest particle of matter Nucleus: Protons and Neutrons Shell: Electrons Atomic Number # of Protons in an atom Atromic Weight # Protons + # Netrons in an atom Octet Rule Electrons are found in different levels of shells. Innermost has a maximum of 2 and the rest a maximum of 8. An atom will always try to stabilize itself by getting the maximum of 8 in its outermost shell (Octet Rule) Molecule More than one of same element O2 (oxygen) Compound More than one of different elements CO2 (carbon dioxide) Solution Substance dissolved homogenously in a liquid Solute: the substance that is dissolved Solvent: the liquid in which it is dissolved Bonds: To satisfy the octet rule or to stabilize themselves, bonds are formed between atoms Ionic Bond when an atom gives an electron the other atom receives it to make them stable Covalent Bond is when two atoms share electrons to make them stable Monovalent when one electron is shared: Hydrogen H H Bivalent when two electrons are shared: Oxygen O=O Trivalent when three electrons are shared: Nitrogen N N The number of bonds each atom has is called valency Hydrogen Bond is when hydrogen binds with an atom: H - O - H Water is a polar molecule because of the bonding between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms: one end being slightly negatively charged and the other end being slightly positively charged. Because of this polarity water binds with large number of atoms Dr. Yoga sundram Properties of water Universal solvent (because of its polarity) Able to hydrolyse acids and bases Has a high heat capacity Has a high heat of vaporization Hydrolysis Dissociation of an acid or base into anions and cations (charged particles) Acidity Amount of H+ ions present in a solution pH A measure of acidity 0 Maximum acidity on a scale of 0 thru 14 7 Neutral 14 Minimum Acidity Acidic Basic ( pH value decreases with increase in acidity ) Reactions A reaction is an interaction between 2 or more atoms or molecules Examples Na + Cl = NaCl NaOH + HCl = NaCl + H2O The atoms on the left of the equation are reactants and one on the right is the products Exergonic Reaction is when energy is released during the reaction Endergonic reaction is when energy is absorbed Activation Energy Energy needed to start a reaction Catalyst A substance that decrease the activation energy needed for a reaction and makes it proceed faster Enzyme A biological catalyst is called an enzyme and is produced in the body Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins and Nucleic Acids CARBOHYDRATES Monosachcharides (Single base unit) Have Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen in their molecule (C, H, O) Glucose, Fructose, Galactose, Ribose, Deoxyribose Disachcharides (Two base units) Maltose (glucose + glucose), Sucrose (Glucose + fructose), Lactose (glucose + galactose) Polysachcharides (Many base units) Cellulose, Starch, Chitin, Glycogen LIPIDS Have Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen in their molecule (C, H, O) Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Glycolipids, Lipoproteins, Steroids, Cholesterol, Vitamin D etc Tryglyceride (Fat): 1 glyceride molecule attached to 3 fatty acid molecules Saturated Fat: Animal origin, solid at room temperature Unsaturated fat: Plant origin, liquid at room temperature Phospholipid: I glyceride molecule, 2 fatty acid molecule and 1 phophate molecule Triglyceride Glycerol Fatty acid Fatty acid Fatty acid Fatty acid Phospholipid Phosphate Glycerol Fatty acid PROTEINS Have Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen and any other molecules (C, H, O, N, R) Amino acids Dipeptides Polypeptides (protein) ( Single base unit) (Two base units) (Multiple base units) Protein is a complex structure of folded amino acid chains. Extreme heat or pH levels unfolds these chains and is called denaturing NUCEIC ACIDS: Have Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen and Phosphorus (C, H, O, N, and P) Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid (DNA) Ribo Nucleic Acid (RNA) The above are the genetic material which replicate (and divide) during cell division , thus transferring genetic traits to the progeny Adenosine Monophosphate (AMP) Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP) Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) The above three are involved in storing and releasing energy. Energy is stored in bonds between phosphates when they are made and are released when they are broken Energy stored AMP Energy stored ADP Energy released ATP Energy released Energy is stored when AMP is converted to ADP or ADP is converted to ATP Energy is released when ATP is converted to ADP or ADP is converted to AMP Yoga sundram