Tissue Repair - Johns Hopkins Medicine
advertisement

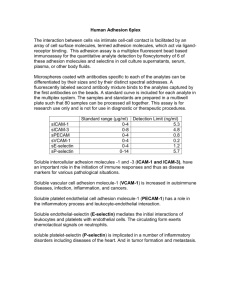
Tissue Repair “Systems Biology” 8-29-11 Robert A. Anders M.D., Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology CRB 2 Rm 346 rander54@jhmi.edu The Systems • • • • • • Tissue homeostasis Cell Cycle Soluble mediators Extracellular matrix Integration of repair mechanisms Pathology of repair Tissue Reactions • Hypertrophy – Increase in cell size • Hyperplasia – Increase in cell number • Renewal – Replacement of cells • Scar – Replacement with fibrosis Intestinal Homeostasis Epidermal Homeostasis Liver Homeostasis Tissue Stem Cells Cellular Transplant “let’s repair diseased tissue with tissue stem cells” X = tissue 1 Y = tissue 2 1 = Partial phenotype 2 = Unknown progenitor 3 = in vivo not in vitro in vitro reprogramming 4 = Low frequency events Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol 17:387403 2001 Cell Cycle Cell Cycle • Ordered series of events • Critical to maintain genome – Copy number – Integrity • • • • Division of cytoplasmic organelles Quiescent = G0 Ready to divide = G1 to R point Dividing = R point to S, G2, M Cell Cycle Go Interphase = G1+S+G2 M = mitosis = pro-,meta-,ana-,telophase Cell Cycle Cyclins + CDK Retinoblastoma Inhibitors Soluble Mediators Soluble Mediators -signaling• Growth factors – Peptides – Steroids – Small molecules • Extracellular matrix – Dynamic fluid like environment – Interstitial space • Area between cells – Basement membrane • Interwoven dense mesh of collagen glycoproteins Signaling Patterns Sept 2 2009 NEJM Signaling In Cancer Cells Growth Factors Growth Factors -classification• Function – Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor • Composition – Protein, steroid • Receptor – G-protein coupled, receptor tyrosine kinase • Structure – Ion channel, 7 pass transmembrane • Orphan / Decoy – Ligand / function unclear Growth Factors In Regeneration and Wound Healing -what is in a name?- Growth Factor Receptors Steroids adaptors P P Effectors Pharm PKC Receptor Types -different signaling pathways- TGF beta Signaling -kinases, adaptors, transcription factorsLigand GS Receptors II GS P I Gene Transcription TGF beta Superfamily TGF beta Signaling -epithelial cells- P Context Dependent Signaling Matrix Extracellular Matrix • Everything outside the cell – Interstitial – Basement membrane • Dynamic • Influences cytoplasmic events • Holds – – – – Tissues Water Minerals Growth factors • Three main constituents – Collagen and elastin – Adhesive proteins – Proteoglycans and hyaluronic acid Preview Collagen • Most abundant protein in animals • Types I, II, III, V form fibrills • Type IV forms sheets and basement membrane • Inherited disorder = Ehlers Danlos • Acquired defect = Scurvy Collagen Synthesis Vit C Elastic fibers • • • • Recoil of tissue Distensible / stretchable Elastin core protein Microfibril network of fibrillin Elastic fibers • • • • Recoil of tissue Distensible / stretchable Elastin core protein Microfibril network of fibrillin Elastin Fibrillin Mutations = Marfans’ syndrome Marfan Syndrome • • • • • Autosomal dominant Mutations in fibrillin 1 FBN1 gene Abnormal elastin fiber Normally binds and pools TGF-beta 1896 Anoine Marfan (peds) recognizes striking features in child • 1991 Ramierez at Mt. Sinai gene ident. Marfans Syndrome Eye lens dislocation Spontaneous pneumothorax Spinal cord sac other matrix proteins…. • Fibronectin – Large dimeric protein that binds collagen, proteoglycans and • Lamin – Woven into basement membrane • Proteoglycans and – Polysaccharide coated protein – Diverse composition and function! – Heparin & Chondrotin sulfate • Hyaluronic acid – Binds vast amounts of water Proteoglycans and Hyaluronic acid Proteoglycans and Growth Factor Reservoirs Adhesion Major Classes of Adhesion Molecules Same cell type Leukocyte Cell Adhesion Molecules • Anchored in the membrane • Immunoglobin superfamily – PECAM, VCAM • Integrins • Selectins • Cadherins Integrins • Superfamily of ~ 30 homologous members • Non-covently linked alpha and beta chain • Globular heads, transmembrane region and short cytoplasmic tails • Diverse functions – Beta1 (VLA) bind collagen, lamins, fibronectin – Beta 2 (CD11) bind leukocytes – Beta 3 (GPIIb) involved in clotting Integrins Stimulate Cytoplasmic Signaling Cell Adhesion Molecules • Anchored in the membrane • Immunoglobin superfamily – PECAM, VCAM • Integrins • Selectins • Cadherins Selectin • Single chain transmembrane • L-selectin – Expressed on lymphocytes – Homing to activated endothelial cells (lymph node > inflammatory site – KO mice have small lymph nodes • E-selectin – Homing as above < peripheral inflammation • P-selectin – Similar to E – E and P KO mice have poor WBC recruitment Cell Adhesion Molecules • Anchored in the membrane • Immunoglobin superfamily – PECAM, VCAM • Integrins • Selectins • Cadherins Cadherins • 90 members • Transmembrane proteins – Extracellular adhesion – Transmembrane – Intracellular connection to cytoskeleton • Identical cell to cell interactions – Desmosomes linked to intermediate filaments – Zona adherens / belt desmosome linked to actin • Roles – Differentiation, proliferation, and motility • Contact inhibition in cell culture General Cadherin Structure E-Cadherin Function Summary Angiogenesis Fresh and Mature Healing -vessel density- Trichrome Stain Angiogenesis • Paradigms – Branch extension – Stem cell mobilization from bone marrow Branch Extension Smooth muscle Pericytes Stem Cell Mobilization Angiogenesis • Paradigms – Branch extension – Stem cell mobilization from bone marrow • Multiple steps – Remodeling, migration, proliferation, maturation Angiogenesis Angiogenesis • Paradigms – Branch extension – Stem cell mobilization from bone marrow • Multiple steps – Remodeling, migration, proliferation, maturation • Growth factors – – – – VEGF (stroma) and VEGFR 2 (endo. cell) Angiopoietins stablization, periendothelial cells PDGF smooth muscle recruitment TGF beta matrix production Angiogenesis • Extracellular matrix – Integrins cell matrix interaction – Matricellular proteins destabilize cell /matrix – Proteinases remodel • Plasminogen activators • Matrix metalloproteinases cleave matrix bound growth factors Control of Matrix Metalloproteinase Tissue Repair -integration of systemsExamples: Fresh and Old scar & Partial Hepatectomy Fresh and Mature Healing -observations- Trichrome Stain Healing Phases Partial Hepatectomy -mouse liver- Partial Hepatectomy -Murine Model- Intact Liver B A X C A B C Partial Hepatectomy 1931 Wild Type Wild Type 48 hrs post PHX Decreased DNA Synthesis -48 hrs Following Partial HepatectomyWild Type TNFR I -/- Partial Hepatectomy in Humans Partial Hepatectomy in Humans Liver Regeneration -Cell Cycle- Priming G0 Progression S Hepatocyte G1 Division G2 M Modified from Nelson Fausto Liver Regeneration Growth Factors / Cytokines HGF TGF Priming TNF Antibody TNFR I IL-6 KO KO G0 Progression S Hepatocyte G1 Division G2 M Modified from Nelson Fausto Model of Liver Regeneration Integrated Model of Liver Regeneration Cytokines LPS JAK/STAT IL6 C3a Stem Cells Adhesion TNF Extracellular Matrix C5a Growth Factors TGF-α HGF Metabolic iNOS Steroids Bile acids G proteins Sympathetic neural stimulation Serotonin FAS TIMP Metaloproteinase Modified from Nelson Fausto Nature Medicine Oct 2005 Integrated Model of Liver Regeneration Cytokines LPS JAK/STAT IL6 C3a Stem Cells Adhesion TNF Extracellular Matrix C5a Growth Factors TGF-α HGF Metabolic iNOS Steroids Bile acids G proteins Sympathetic neural stimulation Serotonin FAS = Science or Nature TIMP Metaloproteinase Modified from Nelson Fausto Nature Medicine Oct 2005 Pathology of Repair Healing First Intention Myocardial Infarction Myocardial Infarction Myocardial Infarction Myocardial Infarction Myocardial Infarction Trichrome Hepatitis and Cirrhosis Pathways vs Networks • Nutrition – Vitamin C • Systemic illness – Diabetics angiopathy • Circulation – Atherosclerosis • Hormones – Glucocorticoids • Local factors – Infection, mechanical stress Summary • • • • • • Tissue homeostasis Cell Cycle Soluble mediators Extracellular matrix Integration of repair mechanisms Pathology of repair Thought Experiments Experiment One You noticed in todays lecture, TGF-beta inhibits epithelial cell growth. You are going to inhibit cancer cell growth by uncovering TGF-beta dependent cell cycle inhibitors. How? Thought Experiment Two 1) What mechanisms can you think of to disrupt angiogenesis? 2) What might some of the side effects be? Experiment Three • It is difficult to make a lot of hepatocytes from embryonic stem cells (ESC) using traditional cell culture techniques. • Now we use plastic dishes, growth factors and feeder layers • Convinced by today's lecture, you are going to investigate how the extra matrix could facilitate ESC to liver cell conversion. How?