10.2 Lesson Plan
advertisement

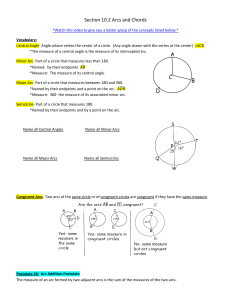
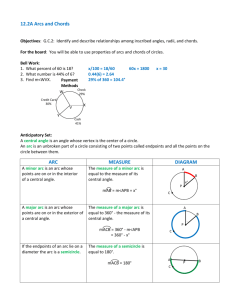
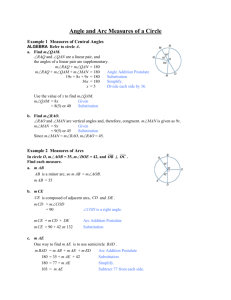
10.2 Lesson Plan Title: Angles and Arcs Course: Geometry (Mainly 9th and 10th Grade) Objectives: Students will: 1. Identify major arcs of circles, minor arcs of circles, semicircles, and central angles of circles as well as each of their measures. 2. Calculate measures of central angles. 3. Calculate measures of arcs. 4. Analyze information from a circle graph and use the percentages in the graph to calculate the measurements of central angles and to analyze the relationships between arcs on the circle graph that correspond to those central angles. 5. Solve for an arc length using proportions. Reporting Categories: Circles, Central Angles, and Arcs Related SOL: G.10 The student will investigate and solve practical problems involving circles, using properties of angles, arcs, chords, tangents, and secants. Problems will include finding arc length and the area of a sector, and may be drawn from applications of architecture, art, and construction. Vocabulary: Central Angle, Minor Arc, Major Arc, Semicircle Materials: Glencoe Mathematics Geometry textbook, paper and pencil, calculator (optional) Time Required: 90 minutes Procedures: • Warm‐Up Activities (20 minutes) o When students come in, they will work on the following warm‐up problems found on the board: A square with sides measuring 1inch is inside a circle (see picture below). Calculate the value of the diameter of the circle. o Go over the homework assigned last class. Read the solutions and have the students suggest problems they had difficulties with to go over. o (5 minutes) Begin discussion of today’s lesson: How to recognize major arcs, minor arcs, and central angles and their measures. Also how to find arc length. Have a brief discussion/review about what an arc of a circle is using Math Open Reference. (http://www.mathopenref.com/arc.html) • Lesson Activities (60 minutes) o (10 minutes) Measures of Central Angles Use Math Open Reference to show an example of a central angle and review the definition of central angle as it appears in the book. (http://www.mathopenref.com/circlecentral.html) Draw an example of a circle with a central angle on the board and explain how to find its measure by using given information and its relationship to other angles. Put up the transparency of Example 1 from page 529 in the textbook on the board and have the class solve for x then find m∠AOD and the m∠AOE . o (10 minutes) Measures of Arcs Use Math Open Reference to show examples of major and minor arcs and review the definition of major arc and minor arc as it appears in the book. Be sure to explain how € € semicircle relates to these two types of arcs. Also, be sure to explain how the measure of a central angle relates to the measure of an arc (THEY ARE EQUAL!) (http://www.mathopenref.com/arcminormajor.html) Draw a circle containing various angles and some angle measurements. Next, explain how to find measures of arcs by using the relationships between parts of the circle and given angle measurements. Put up the transparency of Example 2 from page 531 on the board and have students solve for the measure of arc BE, arc CBE, and arc ACE. o (10 minutes) Circle Graphs Tell the students “in a circle graph, the central angles divide a circle into wedges to represent data, often expressed as a percent. The size of the angle is proportional to the percent.” Ask the students for examples of information that might be portrayed by using a circle graph. Have students give you data about their favorite sports to watch (Soccer, Football, Ice Hockey, Baseball, Basketball). • • • • First, have them make a bar graph out of the information. Next, have them cut out the bars then put them together to form a circle. Finally, have them discuss what part of the circle the bars represent when the central angles are drawn in. After discussing, use Shodor Interactivate to create a circle graph based on the classes favorite colors based on the information gathered.(http://www.shodor.org/interactivate/activities/CircleGraph/?version=1. 5.0_16&browser=Mozilla&vendor=Apple_Inc.) Discuss how the percentage is calculated from the value and how this percentage relates to the central angle. Then, use the percentages to find the measurement of the central angle for each color represented. Finally, use the central angles to identify any arcs that are congruent. Which colors, if any, have arcs that are congruent? Show students how different parts of the circle graph relate (for example, are they congruent?). o (10 minutes) Arc Length Discuss the relationship between a circle’s given measurements and its arc lengths (ARC LENGTH = ANOTHER WAY TO MEASURE AN ARC). Use Math Open Reference to show students visually how the radius and measure of the central angle are used in calculating the value of the arc length. (http://www.mathopenref.com/arclength.html) Put up the transparency of Example 4 from the student text (page 532) to demonstrate how arc length can be solved using an equation and given measurements. o (20 minutes) Practice Problems Draw In‐Class Example 1 from page 530 on the board and have the class find m∠RTS and m∠QTR . € Draw In‐Class Example 2 from page 531 on the board and have the class find the measures € of arcs OK, LM, and JKO. Show the transparency of In‐Class Example 3 from page 531. Draw In‐Class Example 4 from page 532 on the board and discuss how one would find the length of arc AD by using the measurement of diameter AC = 9 and the m∠ABD = 40°. € • • Closing Activities (10 minutes) o Review the answers to the practice problems and address any lingering questions. o Assign the homework. If there is extra time, students may begin their homework during class. Evaluation: Successful completion of practice problems; Homework page 533‐534, #15‐23 odd, 27, 31, 35, 39, 43, and 44‐46 Adaptations for Students with Special Needs: • Have students work in cooperative learning groups on the warm‐up. • Fewer homework problems as needed. Citation of Web Cites: Math Open Reference. (2007). Plane Geometry: Circles and Arcs. Retrieved November 8, 2008, from http://www.mathopenref.com/ Shodor Interactivate. (2006). Circle Graph: Activity. Retrieved November 8, 2008, from http://www.shodor.org/interactivate/activities/CircleGraph/?version=1.5.0_16&browser=Mozilla&vendor=Apple_In c.#printing