PANEL 2–8 Details of the 10 Steps of Glycolysis
advertisement

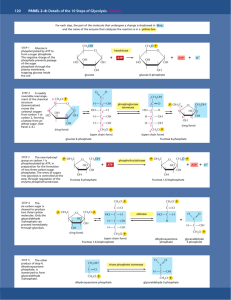
PANEL 2–8 Details of the 10 Steps of Glycolysis For each step, the part of the molecule that undergoes a change is shadowed in blue, and the name of the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction is in a yellow box. STEP 1 Glucose is phosphorylated by ATP to form a sugar phosphate. The negative charge of the phosphate prevents passage of the sugar phosphate through the plasma membrane, trapping glucose inside the cell. CH2OH CH2O P O HO O hexokinase + OH ATP OH + OH HO OH glucose 6-phosphate H O 1CH2OH C1 H C OH HO C H H C OH H H C OH H 2 3 4 5 phosphoglucose isomerase C O C H C OH C OH 2 HO CH2O P 6 (open chain form) 3 4 5 The sixSTEP 4 carbon sugar is cleaved to produce two three-carbon molecules. Only the glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate can proceed immediately through glycolysis. P OH2C phosphofructokinase + HO 4 OH 1 HO 2 3 OH (ring form) P OH2C CH2O P O ATP + HO OH ADP + H+ OH OH fructose 6-phosphate fructose 1,6-bisphosphate CH2O P C CH2O P O HO OH OH (ring form) CH2O P O HO C H H C OH H C OH aldolase HO O C H dihydroxyacetone phosphate O H CH2O P dihydroxyacetone phosphate + C C OH CH2O P triose phosphate isomerase O O H H CH2O P CH2OH C C H (open chain form) fructose 1,6-bisphosphate STEP 5 The other product of step 4, dihydroxyacetone phosphate, is isomerized to form glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. 5 OH P OH2C CH2OH O fructose 6-phosphate CH2OH O P OH2C 6 CH2O P 6 (open chain form) glucose 6-phosphate The new hydroxyl STEP 3 group on carbon 1 is phosphorylated by ATP, in preparation for the formation of two three-carbon sugar phosphates. The entry of sugars into glycolysis is controlled at this step, through regulation of the enzyme phosphofructokinase. H+ OH OH glucose A readily STEP 2 reversible rearrangement of the 6 CH2O P chemical structure 5 O (isomerization) moves the 4 1 carbonyl oxygen OH from carbon 1 to 2 HO OH 3 carbon 2, forming a ketose from an OH aldose sugar. (See Panel 2–4.) (ring form) + ADP C H C OH CH2O P glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate