Anterior Cervical Triangle 1
advertisement

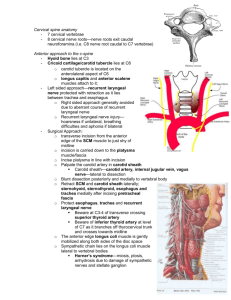
Anterior Cervical Triangle 1 To describe the anterior cervical triangle. To list the contents of this triangle. To describe the carotid sheath & its relations. Anterior cervical triangle is divided into: 1) Carotid triangle 3 2) Submandibular triangle 2 1 3) Submental triangle 4) Muscular triangle 4 Carotid triangle: Common carotid artery (CCA): Arises from the brachiocephalic trunk on the right & from aortic arch on the left side Ascends in the carotid sheath with the IJV & vagus nerve Ends at C3-4 by dividing into ECA & ICA Gives no branches CCA pulse is best felt between trachea & strap muscles Carotid sinus: -Dilatation at carotid bifurcation -Contain baroreceptors Carotid body: -A mass of chemoreceptor cells in the sinus BOTH are supplied by the sinucarotid branch of IX nerve Carotid body tumor: A pulsetile swelling on the side of the neck Carotid massage Afferent by IX nerve Medulla oblongata Efferent by X nerve to the cardiac plexus Bradycardia Hypotension Carotid reflex Internal carotid artery (ICA): •Lies posterior to the ECA •Enters the carotid canal (petrous bone) at skull base •Passes inside cavernous sinus in the middle cranial fossa •Supplies the brain & orbital structures •It gives no branch in the neck External carotid artery (ECA): •Ascends anterior to ICA •It is the artery of head & neck giving 8 branches •Ends behind the neck of the mandible by dividing into its 2 terminal branches Anterior branches: 1- Superior thyroid artery: -Descends with the external laryngeal nerve -Gives superior laryngeal artery to the larynx -Enters the apex of thyroid lobe -Supplies thyroid & parathyroid glands 2- Lingual artery: -Directed to the oral cavity after an upward loop -XII nerve lies lateral to it -Supplies the tongue & structures in the floor of the mouth 3- Facial artery: -Crosses the submandibular triangle before reaching the face -Supplies the tonsils, palate & submandibular gland -Enters the face by turning below the lower border of the mandible Posterior branches: 4- Occipital artery: -Crosses the apex of posterior triangle -Supplies the back of scalp 5- Posterior auricular artery: -Lies superficial to the mastoid process -Supplies the auricle -Gives stylomastoid branch to the middle ear Medial branch: 6- Ascending pharyngeal artery: Ascends along pharyngeal wall Terminal branches: 7- Superficial temporal artery: Ascends upward to the temporal fossa 8- Maxillary artery: Passes forward to the infratemporal fossa Internal jugular vein (IJV): Emerges from jugular foramen Lies posterior to the catotid artery at the skull base & lateral to it at the root of the neck The part of the carotid sheath surrounding it is almost deficient Ansa cervicalis & deep cervical nodes are closely related to it Ends by subclavian uniting vein brachiocephalic vein with the forming the 2 Tributaries: 1 4 1- Inferior petrosal sinus 2- Occipital veins 3 3- Thyroglossofacial veins 4- Pharyngeal veins 5- Middle thyroid vein 5 Vagus nerve: •Leaves the jugular foramen & descends in the carotid sheath •Takes the cranial part of XI which is distributed to pharyngeal & laryngeal muscles •Has two ganglia •Contains the major parasympathetic power in the body (70%) •Branches: 1 2 1- Meningeal; to the meninges 3 2- Auricular; to the external ear 4 3- Pharyngeal: to muscles of the pharynx & soft palate 5 4- Superior laryngeal; to the larynx 5- Cervical cardiac nerve; to the cardiac plexuses in the thorax 6- Recurrent laryngeal; to the larynx 6 Hypoglossal nerve (XII): Crosses lateral to the ECA in its way to the floor of the mouth Branches in the neck are of C1 origin: -Ansa superior root -Nerve to thyrohyoid -Nerve to geniohyoid Enters the floor of the mouth to supply all tongue muscles except palatoglossus Hypoglossal nerve injury causes deviation of the tongue to the .?. side Submandibular triangle: Digastric: Origin: -Anterior belly: digastric fossa -Posterior belly: digastric notch Insertion: Intermediate tendon, hyoid bone Nerve supply: -Anterior belly: myelohyoid n. (Vc) -Posterior belly: facial nerve (VII) Action: -Elevate the hyoid bone -Opens the mouth widely Stylohyoid: -From the styloid process to the hyoid bone -Overlies the posterior belly of digastric with the same innervation & action Mylohyoid: Origin: mylohyoid line Insertion: mylohyoid raphe & hyoid bone Nerve supply: nerve to mylohyoid Action: -Forms the floor of the mouth -Plays a major role in swallowing Hyoglossus: Origin: greater cornu of the hyoid Insertion: side of the tongue Nerve supply: XII nerve. Action: -Elevates the hyoid -Depresses the tongue Contents of the triangle: 1- Submandibular gland 2- Facial artery: -Crosses the triangle in S shape course 3 2 -Before reaching the face it supplies the gland, tonsils & palate 3- Common facial vein: -Anterior facial + anterior division of retromandibular veins -Passes superficial to the gland -Drains to the IJV 4- Submandibular lymph nodes 5- Cervical branch of VII 4 1 Ludwig’s angina: Cellulitis (inflammation of the soft tissues) of the submandibular triangle & floor of the mouth May cause airway obstruction Submental triangle: Boundaries: -Digastric anterior bellies -Hyoid Contents: 1- Submental branch of facial artery. 2- beginning of AJV. 3- Submental lymph nodes. 4- Nerve to myelohyoid: Submental swellings